(Press-News.org) Mangroves and seagrasses grow in many places along the coasts of the world, and these 'blue forests' constitute an important environment for a large number of animals. Here, juvenile fish can hide until they are big enough to take care of themselves; crabs and mussels live on the bottom; and birds come to feed on the plants.
However, the plant-covered coastal zones do not only attract animals but also microplastics, a new study shows.
- The denser the vegetation, the more plastic is captured, says Professor and expert in coastal ecology, Marianne Holmer, from the University of Southern Denmark.
She is concerned about how the accumulated microplastics affect animal and plant life.
- We know from other studies that animals can ingest microplastics and that this may affect their organism.
Animals ingest microplastics with the food they seek in the blue forests. They may suffocate, die of starvation, or the small plastic particles can get stuck different places in the body and do damage.
Another problem with microplastics is that they may be covered with microorganisms, environmental toxins or other health hazardous/disease-promoting substances that are transferred to the animal or plant that absorbs the microplastics.
- When microplastics are concentrated in an ecosystem, the animals are exposed to very high concentrations, Marianne Holmer explains.
She points out that microplastics concentrated in, for example, a seagrass bed are impossible to remove again.
The study is based on examinations of three coastal areas in China, where mangroves, Japanese eelgrass (Z. japonica) and the paddle weed Halophila ovalis grow. All samples taken in blue forests had more microplastics than samples from control sites without vegetation.
The concentrations were up to 17.6 times higher, and they were highest in the mangrove forest. The concentrations were up to 4.1 times higher in the seagrass beds.
Mangrove trees probably capture more microplastics, as the capture of particles is greater in mangrove forests than in seagrass beds.
Researchers also believe that microplastics bind in these ecosystems in the same way as carbon; the particles are captured between leaves and roots, and the microplastics are buried in the seabed.
- Carbon capture binds carbon dioxide in the seabed, and the blue forests are really good at that, but it's worrying if the same thing happens to microplastics, says Marianne Holmer.
Although the study was conducted along Chinese coasts, it may be relevant to similar ecosystems in the rest of the world, including Denmark, where eelgrass beds are widespread.
- It's my expectation that we will also find higher concentrations of microplastics in Danish and global seagrasses, she says.
The study was conducted in collaboration with colleagues from the Zhejiang University in China, among others, and is published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology.
The blue forests:
Lots of plants grow in or below sea level; mangroves, seaweed, seagrass and marsh plants. Especially mangroves and seagrasses absorb and store carbon like plants on land and are thus extremely important for the planet's carbon footprint.
INFORMATION:
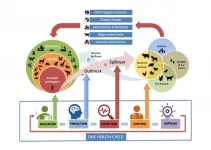
The EU-funded BIO-CRIME project - with support from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) - conducted a scientific investigation on the topic of illegal small animal trade and the associated risk of pathogen transmission.
The study focused on the key areas of "illegal small animal trade" and the level of knowledge and proper behaviours of young people and adolescents with "zoonotic diseases" and the "One Health concept". One Health is an approach that recognises that human health is closely linked to the health of animals and our shared ...
In 2019 the climate movement experienced an unprecedented growth in its mobilization capacity and its political and media impact. The success of the movement is closely linked to the figure of Greta Thunberg and the global impact of her discourse and the "Fridays for Future" movement in hundreds of cities around the world.
A study by Silvia Díaz-Pérez, Roger Soler-i-Martí and Mariona Ferrer-Fons, members of the UPF JOVIS research group of the Department of Communication, analyses the activist's speeches and messages on social networks and their legitimization through her personal story, and it also looks into the "Fridays for Future" movement in Barcelona, based on Twitter and Instagram posts. The research was based on a project that has received funding from ...
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are becoming increasingly popular. At first glance, they have many advantages: Transactions are usually anonymous, fast and inexpensive. But sometimes there are problems with them. In certain situations, fraud is possible, users can discover information about other users that should be kept secret, and sometimes delays occur.
The research unit "Security and Privacy" at TU Wien (Lukas Aumayr and his supervisor Prof. Matteo Maffei) in collaboration with the IMDEA Software Institute (Prof. Pedro Moreno-Sanchez, previously postdoc at TU Wien) and the Purdue University (Prof. Aniket Kate) analyzed these problems and developed an improved protocol. It has now been published and will be presented this year at ...
Sea turtles in the Cayman Islands are recovering from the brink of local extinction, new research shows.
Monitoring from 1998-2019 shows loggerhead and green turtle nest numbers increased dramatically, though hawksbill turtle nest numbers remain low.
In the first counts in 1998-99, just 39 sea turtle nests were found in total on the three islands. By 2019, the figure was 675.
Captive breeding of green turtles and inactivity of a traditional turtle fishery due to tightening of restrictions in 2008 contributed to this - but populations remain far below historical levels and still face threats including ...
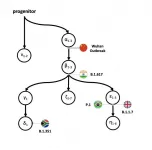
In the field of molecular epidemiology, the worldwide scientific community has been steadily sleuthing to solve the riddle of the early history of SARS-CoV-2. Despite recent efforts by the World Health Organization, no one to date has identified the first case of human transmission, or "patient zero" in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Finding the earliest possible case is needed to better understand how the virus may have jumped from its animal host first to infect humans as well as the history of how the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome has mutated over time and spread globally.
Since the first SARS-CoV-2 virus infection was detected in December 2019, well over a million genomes of SARS-CoV-2 have been sequenced worldwide, ...
May 04, 2021 - In its latest clinical practice guideline on community-acquired pneumonia the American Thoracic Society's guidelines panel addresses the use of nucleic acid-based testing for non-influenza viral pathogens. The guideline was published online in the May 1 issue of the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. An explainer video may be viewed here.
Community-acquired pneumonia is caused by a wide range of respiratory pathogens, prominently including viruses. However, the only viral pathogen addressed by the 2019 clinical practice guideline was influenza. The panel determined that, given the increasing recognition of non-influenza viral causes ...
DAVIS, CA, May 4, 2021 - In a randomized, controlled study* published online in the journal, Nutrients, researchers found that including mixed tree nuts in a weight management program resulted in significant weight loss and improved satiety.
Researchers at UCLA compared 95 overweight/obese men and women (BMI 27.0-35.0 kg/m2) ages 30-68 years who consumed either 1.5 ounces of mixed tree nuts or a pretzel snack. Both snacks provided the same number of calories, as part of a hypocaloric weight loss diet (500 calories less than resting metabolic rate) over 12 weeks. This was followed by an isocaloric weight maintenance program for an additional ...
Cancer of the colon and rectum is one of the deadliest forms of cancer, and has in recent years affected growing numbers of young people. In the largest registry study to date, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and Harvard University in the USA demonstrate a possible connection between colorectal polyps in close relatives and the risk of developing colorectal cancer. The study, which is published in the British Medical Journal, is of potential consequence for different countries' screening procedures.
Colorectal cancer is the second deadliest form of cancer in the world, according to the World Health ...
Nearly one in five older adults say their mental health has gotten worse since the pandemic began in March 2020, and an equal percentage say their sleep has suffered in that time too. More than one in four say they're more anxious or worried than before the COVID-19 era, according to a new poll of people age 50 to 80.
Women, people in their 50s and early 60s, and older adults who have a college degree or higher were more likely than others to report worse mental health than before the pandemic, according to the END ...
DALLAS, May 4, 2021 -- A meta-analysis of 14 air pollution studies from around the world found that exposure to high levels of air pollutants during childhood increases the likelihood of high blood pressure in children and adolescents, and their risk for high blood pressure as adults. The study is published in a special issue on air pollution in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
Other studies look at: the effects of diesel exhaust on the muscle sympathetic nerve; the impact of pollutants on high blood pressure; rates of hospital readmission for heart failure among those exposed ...