INFORMATION:
Cayman Islands sea turtles back from the brink
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) Sea turtles in the Cayman Islands are recovering from the brink of local extinction, new research shows.
Monitoring from 1998-2019 shows loggerhead and green turtle nest numbers increased dramatically, though hawksbill turtle nest numbers remain low.
In the first counts in 1998-99, just 39 sea turtle nests were found in total on the three islands. By 2019, the figure was 675.
Captive breeding of green turtles and inactivity of a traditional turtle fishery due to tightening of restrictions in 2008 contributed to this - but populations remain far below historical levels and still face threats including illegal hunting.
The study was carried out by the Cayman Islands Department of Environment and the University of Exeter.
"Our findings demonstrate a remarkable recovery for sea turtle populations that were once thought to be locally extinct," said Dr Janice Blumenthal, of the Cayman Islands Department of Environment.
"A combination of factors is thought to have led to this conservation success story.
"It is likely that a captive breeding operation by the Cayman Turtle Farm (now the Cayman Turtle Centre) drove the increase in Grand Cayman's green turtle population in the early years of monitoring.
"For loggerhead turtles, the most important factor was the restrictions placed on the legal turtle fishery in 2008."
Dr Jane Hardwick, also of the Cayman Islands Department of Environment, added: "For both species, the recovery was assisted by protection efforts by the Cayman Islands Department of Environment on nesting beaches, including patrols by conservation officers to reduce illegal hunting.
"However, our study finds that illegal take is an ongoing threat, with a minimum of 24 turtles taken from 2015-19, many of which were nesting females.
"Artificial lighting on nesting beaches, which can direct hatchlings away from the sea, increased over the period of our study.
"Additionally, as highly migratory endangered species, sea turtles are influenced by threats and conservation efforts outside of the Cayman Islands, showing a need for international co-operation in sea turtle management."
Historically, the Cayman Islands had among the world's largest sea turtle nesting populations, with turtles numbering in the millions. By the early 1800s, the populations had collapsed due to human overexploitation.
The new study shows that, despite reaching critically low levels, nesting populations of green and loggerhead turtles have recovered significantly.
Hawksbill turtle nest numbers have not increased in tandem with loggerhead and green turtles - with a maximum of 13 hawksbill nests recorded in a single monitoring season.
Information on turtle nests is being used by the Cayman Islands authorities to target management efforts.
This includes "turtle-friendly lighting" initiatives, and a greater level of habitat protection for key areas has been proposed under the National Conservation Law of the Cayman Islands.
Professor Brendan Godley, of the University of Exeter, said: "I was fortunate to have been involved in establishing the turtle monitoring programme with the Department of Environment in the Cayman Islands back in 1998 and it is fantastic to see how protection and awareness has resulted in an increase in nesting turtles.
"The wonderful team and leadership of the Department of Environment have been instrumental in driving the monitoring and conservation."
Department of Environment Director Gina Ebanks-Petrie said: "We are extremely grateful to the many volunteers, interns, property owners, businesses, organisations and members of the public who have assisted with sea turtle conservation efforts over the past two decades.
"Sea turtles are a national symbol of the Cayman Islands and our community has come together to demonstrate our commitment to their protection. This research gives us essential information for strategically targeted management efforts to secure future survival of these populations."
The paper, published in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science, is entitled: "Cayman Islands sea turtle nesting population increases over 22 years of monitoring."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
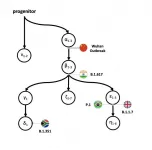
New study traces back the progenitor genomes causing COVID-19 and geospatial spread
2021-05-04
In the field of molecular epidemiology, the worldwide scientific community has been steadily sleuthing to solve the riddle of the early history of SARS-CoV-2. Despite recent efforts by the World Health Organization, no one to date has identified the first case of human transmission, or "patient zero" in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Finding the earliest possible case is needed to better understand how the virus may have jumped from its animal host first to infect humans as well as the history of how the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome has mutated over time and spread globally.
Since the first SARS-CoV-2 virus infection was detected in December 2019, well over a million genomes of SARS-CoV-2 have been sequenced worldwide, ...
New clinical practice guideline on community acquired pneumonia
2021-05-04
May 04, 2021 - In its latest clinical practice guideline on community-acquired pneumonia the American Thoracic Society's guidelines panel addresses the use of nucleic acid-based testing for non-influenza viral pathogens. The guideline was published online in the May 1 issue of the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. An explainer video may be viewed here.
Community-acquired pneumonia is caused by a wide range of respiratory pathogens, prominently including viruses. However, the only viral pathogen addressed by the 2019 clinical practice guideline was influenza. The panel determined that, given the increasing recognition of non-influenza viral causes ...
New study shows tree nuts may play a role in both weight loss and weight maintenance
2021-05-04
DAVIS, CA, May 4, 2021 - In a randomized, controlled study* published online in the journal, Nutrients, researchers found that including mixed tree nuts in a weight management program resulted in significant weight loss and improved satiety.
Researchers at UCLA compared 95 overweight/obese men and women (BMI 27.0-35.0 kg/m2) ages 30-68 years who consumed either 1.5 ounces of mixed tree nuts or a pretzel snack. Both snacks provided the same number of calories, as part of a hypocaloric weight loss diet (500 calories less than resting metabolic rate) over 12 weeks. This was followed by an isocaloric weight maintenance program for an additional ...
Intestinal polyps in close relatives can increase risk of colorectal cancer
2021-05-04
Cancer of the colon and rectum is one of the deadliest forms of cancer, and has in recent years affected growing numbers of young people. In the largest registry study to date, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and Harvard University in the USA demonstrate a possible connection between colorectal polyps in close relatives and the risk of developing colorectal cancer. The study, which is published in the British Medical Journal, is of potential consequence for different countries' screening procedures.
Colorectal cancer is the second deadliest form of cancer in the world, according to the World Health ...
Pandemic worsened older adults' mental health & sleep; others show long-term resilience
2021-05-04
Nearly one in five older adults say their mental health has gotten worse since the pandemic began in March 2020, and an equal percentage say their sleep has suffered in that time too. More than one in four say they're more anxious or worried than before the COVID-19 era, according to a new poll of people age 50 to 80.
Women, people in their 50s and early 60s, and older adults who have a college degree or higher were more likely than others to report worse mental health than before the pandemic, according to the END ...
Air pollution linked to high blood pressure in children; other studies address air quality and the heart
2021-05-04
DALLAS, May 4, 2021 -- A meta-analysis of 14 air pollution studies from around the world found that exposure to high levels of air pollutants during childhood increases the likelihood of high blood pressure in children and adolescents, and their risk for high blood pressure as adults. The study is published in a special issue on air pollution in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
Other studies look at: the effects of diesel exhaust on the muscle sympathetic nerve; the impact of pollutants on high blood pressure; rates of hospital readmission for heart failure among those exposed ...
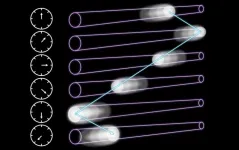
Laser light makes a comeback (literally)
2021-05-04
Osaka, Japan --Straight-line constant-speed propagation in free space is a basic characteristic of light. In a recent study published in Communications Physics, researchers from Osaka University discovered the phenomenon of reciprocating propagation of laser pulse intensity in free space.
Spatiotemporal couplings have been recently used to produce light with tunable group-velocity, direction, and trajectory in free space. For example, the flying focus (a moving laser pulse intensity in the extended Rayleigh length), where longitudinal chromatism and temporal chirp are combined to control the spectrum-dependent focus-separation ...
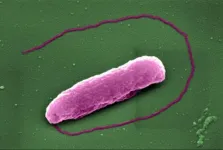
'Last resort' antibiotic pops bacteria like balloons
2021-05-04
Scientists have revealed how an antibiotic of 'last resort' kills bacteria.
The findings, from Imperial College London and the University of Texas, may also reveal a potential way to make the antibiotic more powerful.
The antibiotic colistin has become a last resort treatment for infections caused by some of the world's nastiest superbugs. However, despite being discovered over 70 years ago, the process by which this antibiotic kills bacteria has, until now, been something of a mystery.
Now, researchers have revealed that colistin punches holes in bacteria, causing them to pop like balloons. The work, funded by the Medical Research Council and Wellcome Trust, and published in the journal eLife, also identified a way of making the antibiotic more effective at killing bacteria.
Colistin ...
One cup of leafy green vegetables a day lowers risk of heart disease
2021-05-04
New Edith Cowan University (ECU) research has found that by eating just one cup of nitrate-rich vegetables each day people can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease.
The study investigated whether people who regularly ate higher quantities of nitrate-rich vegetables, such as leafy greens and beetroot, had lower blood pressure, and it also examined whether these same people were less likely to be diagnosed with heart disease many years later.
Cardiovascular diseases are the number one cause of death globally, taking around 17.9 million lives each year.
Researchers examined data from over 50,000 people residing in Denmark taking part in the Danish Diet, ...
Microplastics found in Europe's largest ice cap
2021-05-04
In a recent article in Sustainability, scientists from Reykjavik University (RU), the University of Gothenburg, and the Icelandic Meteorological Office describe their finding of microplastic in a remote and pristine area of Vatnajokull glacier in Iceland, Europe's largest ice cap. Microplastics may affect the melting and rheological behaviour of glaciers, thus influencing the future meltwater contribution to the oceans and rising sea levels.
This is the first time that the finding of microplastic in the Vatnajökull glacier is described. The group visualised and identified microplastic particles of various sizes and materials by optical microscopy and μ-Raman spectroscopy.
The discussion about microplastics has mainly been focused on the contamination ...