Laser light makes a comeback (literally)
Researchers from Osaka University discover phenomenon of reciprocating propagation of laser pulse intensity in free space
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan --Straight-line constant-speed propagation in free space is a basic characteristic of light. In a recent study published in Communications Physics, researchers from Osaka University discovered the phenomenon of reciprocating propagation of laser pulse intensity in free space.
Spatiotemporal couplings have been recently used to produce light with tunable group-velocity, direction, and trajectory in free space. For example, the flying focus (a moving laser pulse intensity in the extended Rayleigh length), where longitudinal chromatism and temporal chirp are combined to control the spectrum-dependent focus-separation in space and spectrum-dependent pulse-location in time, respectively, has arbitrarily tunable propagating group-velocity and direction in space and time.
However, in the previous result, the flying focus can only propagate along a certain direction either forward or backward, although the propagating group-velocity can be freely controlled.
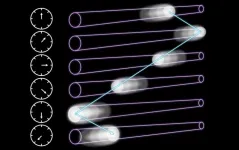
In this study, by dramatically increasing the Rayleigh length in space and the temporal chirp in time, the newly created flying focus propagates along a reciprocating straight-line trajectory in free space. A clear reciprocating flying focus with a high spatial resolution is also possible by further increasing the temporal chirp.
"The newly created flying focus propagates along the longitudinal axis first forward, then backward, and lastly forward again, showing a reciprocating straight-line trajectory in space and time. The forward-propagating velocity is the light speed in the vacuum, while the backward-propagating velocity is subluminal," explains corresponding author Zhaoyang Li.
This intriguing phenomenon changes the traditional understanding of light propagation and may be applied in both fundamental and applied physics.
"For example, in our radiation pressure simulation, it can produce an on-axis reciprocating trapping or pushing force for a small or big sphere, respectively, in the Rayleigh scattering regime," says Zhaoyang Li.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Reciprocating propagation of laser pulse intensity in free space," was published in Communications Physics at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-021-00590-8
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
Scientists have revealed how an antibiotic of 'last resort' kills bacteria.
The findings, from Imperial College London and the University of Texas, may also reveal a potential way to make the antibiotic more powerful.
The antibiotic colistin has become a last resort treatment for infections caused by some of the world's nastiest superbugs. However, despite being discovered over 70 years ago, the process by which this antibiotic kills bacteria has, until now, been something of a mystery.
Now, researchers have revealed that colistin punches holes in bacteria, causing them to pop like balloons. The work, funded by the Medical Research Council and Wellcome Trust, and published in the journal eLife, also identified a way of making the antibiotic more effective at killing bacteria.
Colistin ...
2021-05-04
New Edith Cowan University (ECU) research has found that by eating just one cup of nitrate-rich vegetables each day people can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease.
The study investigated whether people who regularly ate higher quantities of nitrate-rich vegetables, such as leafy greens and beetroot, had lower blood pressure, and it also examined whether these same people were less likely to be diagnosed with heart disease many years later.
Cardiovascular diseases are the number one cause of death globally, taking around 17.9 million lives each year.
Researchers examined data from over 50,000 people residing in Denmark taking part in the Danish Diet, ...
2021-05-04
In a recent article in Sustainability, scientists from Reykjavik University (RU), the University of Gothenburg, and the Icelandic Meteorological Office describe their finding of microplastic in a remote and pristine area of Vatnajokull glacier in Iceland, Europe's largest ice cap. Microplastics may affect the melting and rheological behaviour of glaciers, thus influencing the future meltwater contribution to the oceans and rising sea levels.
This is the first time that the finding of microplastic in the Vatnajökull glacier is described. The group visualised and identified microplastic particles of various sizes and materials by optical microscopy and μ-Raman spectroscopy.
The discussion about microplastics has mainly been focused on the contamination ...
2021-05-04
Over the coming decades, our economy and society will need to dramatically reduce greenhouse gas emissions as called for in the Paris Agreement. But even a future low-carbon economy will emit some greenhouse gases, such as in the manufacture of cement, steel, in livestock and crop farming, and in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. To meet climate targets, these emissions need to be offset. Doing so requires "negative emissions" technologies, by means of which CO2 is removed from the atmosphere and permanently stored in underground repositories.
Researchers at ETH Zurich have now calculated the potential of one of these technologies for Europe: the combination of energy extraction from biomass with the capture and ...
2021-05-04
Small changes in the structure of DNA have been implicated in breast cancer and other diseases, but they've been extremely difficult to detect -- until now.
Using what they describe as a "chemical nose," UC Riverside chemists are able to "smell" when bits of DNA are folded in unusual ways. Their work designing and demonstrating this system has been published in the journal Nature Chemistry.
"If a DNA sequence is folded, it could prevent the transcription of a gene linked to that particular piece of DNA," said study author and UCR chemistry professor Wenwan Zhong. "In other words, this could have a positive effect by silencing a gene with the potential to cause cancer or promote tumors."
Conversely, DNA folding ...
2021-05-04
Talking about your bad day at work could lead to great solutions. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Associate Professor Saket Navlakha and his wife, Dr. Sejal Morjaria, an infectious disease physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), found a way to predict COVID-19 severity in cancer patients. The computational tool they developed prevents unnecessary expensive testing and improves patient care.
Morjaria says, "Generally, I have good intuition for how patients will progress." However, that intuition failed her when confronted with COVID-19. She says:
"When the pandemic ...
2021-05-04
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Increased use of minimally invasive non-endoscopic tests for Barrett's esophagus screening could impact detection and prevention of esophageal cancer
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-7164
URL ...
2021-05-04
Throughout the history of the West, human actions have often rushed the desert -- and their actions backfired. In the 1920s, the Colorado River Compact notoriously overallocated water still used today by several western states because water measurements were taken during a wet period.
More currently, operators of the massive Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System in the Mojave Desert are spending around $45 million on desert tortoise mitigation after initial numbers of the endangered animals were undercounted before its construction.
A study published in the journal Ecological Applications from the University of California, Davis, and UC Santa Cruz warns against another potential desert timing mismatch amid the race against climate change and toward rapid renewable ...
2021-05-04
The importance of pollinators to ensure successful harvests and thus global food security is widely acknowledged. However, the specific pollinators for even major crops - such as cocoa - haven't yet been identified and there remain many questions about sustainability, conservation and plantation management to enhance their populations and, thereby, pollination services. Now an international research team based in Central Sulawesi, Indonesia and led by the University of Göttingen has found that in fact ants and flies - but not ceratopogonid midges as was previously thought - appear to have a crucial role to play. In addition, they found ...
2021-05-04
Today, the Sumatran rhinoceros (Dicerorhinus sumatrensis) is critically endangered, with fewer than 100 individuals surviving in Indonesia on the islands of Sumatra and Borneo. To ensure survival of the threatened species, accurate censusing is necessary to determine the genetic diversity of remaining populations for conservation and management plans.
A new study reported in BMC Research Notes characterized 29 novel polymorphic microsatellite markers -- repetitive DNA sequences -- that serve as a reliable censusing method for wild Sumatran rhinos. The study was a collaborative effort involving the University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Laser light makes a comeback (literally)
Researchers from Osaka University discover phenomenon of reciprocating propagation of laser pulse intensity in free space