New class of drug gives hope to some ovarian cancer patients
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) A study published today in Nature Communications shows that the drug rucaparib has been effective in treating certain types of ovarian cancers if used early in treatment, after a diagnosis, and before the cancer cells build up a resistance to chemotherapy.
Rucaparib is in a relatively new class of drugs - Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase or PARP inhibitors - which have been approved for therapy in ovarian cancers. This study provides insights into both how the cancers resist treatments, and which patients may respond favorably to the drug, said lead author Dr. Elizabeth Swisher, a UW Medicine gynecologic oncologist and a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington School of Medicine. She also co-directs the Breast and Ovarian Cancer Research Program at the Seattle Cancer Care Alliance.
The paper represents collaborative work of researchers in 75 universities and focuses on treatments of 493 patients between April 2013 and October 2016.
"PARP inhibitors are a drug class that has become an important therapeutic for ovarian and some other cancers. This study looked at pretreatment biopsies to define predictors of response to treatment and mechanisms of resistance (within the cancer cells), which is critical to understanding best use of these therapies," Swisher said.
The best responders included those patients with ovarian cancer associated with inherited or somatic (not inherited) mutations in the ovarian cancer susceptibility genes BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51C and RAD51D, all genes involved in DNA repair, Swisher noted.
"PARP inhibitors target the Achilles heel of cancers which have certain types of defects in DNA repair," she said.
The study found that cancers exposed to previous platinum chemotherapy have built up resistance by improving their DNA repair capabilities, which then creates cross-resistance to rucaparib. This explains why PARP inhibitors work better earlier in the course of treatment, Swisher said.
The researchers correlated many molecular alterations to response to treatment including inherited and somatic mutations, methylation alterations (epigenetic changes) and genomic scars (mutational patterns created by defective DNA repair).
The authors defined which mutation and methylation events correlated with response to rucaparib.
But in patients who had received previous chemotherapy, cancers had developed a resistance to rucaparib.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
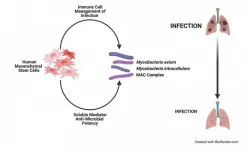
Durham, NC - A study released today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine offers hope for those suffering from a chronic, difficult to treat condition called non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) lung infection. The study describes how researchers at Case Western University developed a new model of NTM lung infection and then used it to show how effective human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) are in treating this condition - and even which donor cells might be best for doing so.
"The potential to use human mesenchymal stem cells to treat difficult lung infections is promising," said Anthony Atala, M.D., Editor-in-Chief of STEM ...
2021-05-04
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Professor Arda Gozen looks to a future someday in which doctors can hit a button to print out a scaffold on their 3-D printers and create custom-made replacement skin, cartilage, or other tissue for their patients.
Gozen, George and Joan Berry associate professor in the Washington State University School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, and a team of researchers have developed a unique scaffolding material for engineered tissues that can be fine-tuned for the tricky business of growing natural tissue. They report on their research in the journal, Bioprinting. The team also includes researchers from WSU's ...
2021-05-04
Dating violence - physical, sexual, psychological or emotional within a relationship, including stalking - is pervasive on college campuses with far-reaching health implications. One in five women experience a sexual assault in college and students living in sorority houses are three times more likely to experience rape. College students are vulnerable to dating violence because of the influence of their social and living environments.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's College of Education in collaboration with Sacred Heart University conducted a study to understand the dating violence experience and perpetration of college-age women, ...
2021-05-04
Astronomers have identified more than 4,000, and counting, confirmed exoplanets -- planets orbiting stars other than the sun -- but only a fraction have the potential to sustain life.
Now, new research from UBC's Okanagan campus is using the geology of early planet formation to help identify those that may be capable of supporting life.
"The discovery of any planet is pretty exciting, but almost everyone wants to know if there are smaller Earth-like planets with iron cores," says Dr. Brendan Dyck, assistant professor of geology in the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Science and lead author on the study.
"We typically hope to find these planets in the so-called 'goldilocks' or habitable ...
2021-05-04
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Duke University improved HIV care by gamifying it with a mobile gaming application.
Gaming features - like those used to drive airline loyalty and track daily steps --- helped young men living with HIV achieve viral suppression and doubled their chances for reaching near perfect adherence to medication plans, according to a study in AIDS and Behavior.
Gamification can inspire changes in behavior when a doctor's advice or a patient's good intentions are not enough. In this case, motivating those living with HIV to stick to ...
2021-05-04
Research funding agencies around the world are testing creative approaches to address urgent needs while laying the foundation for discoveries that will meet the unpredictable demands of the future. According to a new expert panel report from the Council of Canadian Academies (CCA), Canada can bolster its research capacity by reducing administrative burdens, experimenting with funding approaches, and cultivating a robust, resilient, and diverse scientific workforce.
"In the past year we have seen the power and promise of transformative research and the ability of researchers and funding organizations to pivot in times of crisis," said Shirley M. Tilghman, PhD, O.C., FRS, Chair of the Expert Panel. "But the pandemic has also exacerbated existing inequalities ...
2021-05-04
Almost half of the parents who have children together with a parent with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, are themselves burdened by psychological issues. This can affect family life and the children. This is shown in the research result from the major Danish psychiatry project iPSYCH.
We typically choose a partner who resembles us in relation to social status, education and, to some extent, also income. Research has previously established this. A new study now shows that almost half of the parents who have children with a partner who suffers from schizophrenia or bipolar disorder themselves meet the criteria for a mental disorder. By comparison, this is 18 percent for parents in the control group.
The results stem from The Danish High-Risk and Resilience ...
2021-05-04
Aging is the biggest risk factor for perturbation of the nervous system, even in the absence of distinct disease or trauma. For yet unknown reasons, the impulse conducting, myelinated projections and synaptic connections between nerve cells are especially vulnerable to aging-related degeneration. These pathological alterations often manifest as cognitive, sensory, and motor decline in older adults and represent a serious socio-economic challenge.
Malactivation leads to damage
Scientists have long assumed that inflammation plays an important role in this process. Mal- or overactivation of distinct cells belonging to the innate immune system - the microglia - appears to promote damage of nerve fibers and synapses ...
2021-05-04
As the digital revolution has now become mainstream, quantum computing and quantum communication are rising in the consciousness of the field. The enhanced measurement technologies enabled by quantum phenomena, and the possibility of scientific progress using new methods, are of particular interest to researchers around the world.
Recently two researchers at Tampere University, Assistant Professor Robert Fickler and Doctoral Researcher Markus Hiekkamäki, demonstrated that two-photon interference can be controlled in a near-perfect way using ...
2021-05-04
For the first time, international experts in psychology have built a framework to diagnose Compulsive Buying-Shopping Disorder - promising help for people struggling to manage their spending behaviour and mental wellbeing.
The new guidelines, published in the Journal of Behavioral Addictions, confirms that excessive buying and shopping can be so serious as to constitute a disorder, giving researchers and clinicians new powers to develop more targeted interventions for this debilitating condition.
The international collaboration, led by Professor Mike Kyrios from Flinders University's Órama Institute for Mental ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New class of drug gives hope to some ovarian cancer patients