Complex shapes of photons to boost future quantum technologies
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) As the digital revolution has now become mainstream, quantum computing and quantum communication are rising in the consciousness of the field. The enhanced measurement technologies enabled by quantum phenomena, and the possibility of scientific progress using new methods, are of particular interest to researchers around the world.
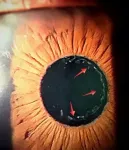
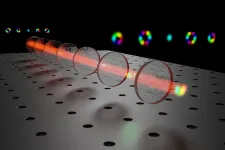
Recently two researchers at Tampere University, Assistant Professor Robert Fickler and Doctoral Researcher Markus Hiekkamäki, demonstrated that two-photon interference can be controlled in a near-perfect way using the spatial shape of the photon. Their findings were recently published in the prestigious journal Physical Review Letters.
"Our report shows how a complex light-shaping method can be used to make two quanta of light interfere with each other in a novel and easily tuneable way", explains Markus Hiekkamäki.
Single photons (units of light) can have highly complex shapes that are known to be beneficial for quantum technologies such as quantum cryptography, super-sensitive measurements, or quantum-enhanced computational tasks. To make use of these so-called structured photons, it is crucial to make them interfere with other photons.
"One crucial task in essentially all quantum technological applications is improving the ability to manipulate quantum states in a more complex and reliable way. In photonic quantum technologies, this task involves changing the properties of a single photon as well as interfering multiple photons with each other;" says Robert Fickler, who leads the Experimental Quantum Optics group at the university.
Linear optics bring promising solutions to quantum communications
The demonstrated development is especially interesting from the point of view of high-dimensional quantum information science, where more than a single bit of quantum information is used per carrier. These more complex quantum states not only allow the encoding of more information onto a single photon but are also known to be more noise-resistant in various settings.
The method presented by the research duo holds promise for building new types of linear optical networks. This paves the way for novel schemes of photonic quantum-enhanced computing.
"Our experimental demonstration of bunching two photons into multiple complex spatial shapes is a crucial next step for applying structured photons to various quantum metrological and informational tasks", continues Markus Hiekkamäki.
The researchers now aim at utilizing the method for developing new quantum-enhanced sensing techniques, while exploring more complex spatial structures of photons and developing new approaches for computational systems using quantum states.
"We hope that these results inspire more research into the fundamental limits of photon shaping. Our findings might also trigger the development of new quantum technologies, e.g. improved noise-tolerant quantum communication or innovative quantum computation schemes, that benefit from such high-dimensional photonic quantum states", adds Robert Fickler.
INFORMATION:
Read more about research High-Dimensional Two-Photon Interference Effects in Spatial Modes. https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.123601
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
For the first time, international experts in psychology have built a framework to diagnose Compulsive Buying-Shopping Disorder - promising help for people struggling to manage their spending behaviour and mental wellbeing.
The new guidelines, published in the Journal of Behavioral Addictions, confirms that excessive buying and shopping can be so serious as to constitute a disorder, giving researchers and clinicians new powers to develop more targeted interventions for this debilitating condition.
The international collaboration, led by Professor Mike Kyrios from Flinders University's Órama Institute for Mental ...
2021-05-04
SINGAPORE - A team of researchers from the Agency for Science, Technology and Research's (A*STAR) Genome Institute of Singapore (GIS) and Bioprocessing Technology Institute (BTI), as well as Singapore Eye Research Institute (SERI), have identified a genetic mutation (functionally defective CYP39A1 gene) associated with exfoliation syndrome, the most common cause of glaucoma. The findings could pave the way for future research on the cause of exfoliation syndrome and potential cures. Their research was published in Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) on 24 February 2021.
Exfoliation syndrome is a systemic ...
2021-05-04
Artificial intelligence that enhances remote monitoring of water bodies - highlighting quality shifts due to climate change or pollution - has been developed by researchers at the University of Stirling.
A new algorithm - known as the 'meta-learning' method - analyses data directly from satellite sensors, making it easier for coastal zone, environmental and industry managers to monitor issues such as harmful algal blooms (HABs) and possible toxicity in shellfish and finfish.
Environmental protection agencies and industry bodies currently monitor the 'trophic state' of water - its biological productivity - as an indicator of ecosystem health. Large clusters of microscopic algae, or phytoplankton, is called eutrophication and can ...
2021-05-04
Mangroves and seagrasses grow in many places along the coasts of the world, and these 'blue forests' constitute an important environment for a large number of animals. Here, juvenile fish can hide until they are big enough to take care of themselves; crabs and mussels live on the bottom; and birds come to feed on the plants.
However, the plant-covered coastal zones do not only attract animals but also microplastics, a new study shows.
- The denser the vegetation, the more plastic is captured, says Professor and expert in coastal ecology, Marianne Holmer, from the University of Southern Denmark.
She is concerned about how the accumulated microplastics affect animal and plant life.
- We know from other ...
2021-05-04
The EU-funded BIO-CRIME project - with support from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) - conducted a scientific investigation on the topic of illegal small animal trade and the associated risk of pathogen transmission.
The study focused on the key areas of "illegal small animal trade" and the level of knowledge and proper behaviours of young people and adolescents with "zoonotic diseases" and the "One Health concept". One Health is an approach that recognises that human health is closely linked to the health of animals and our shared ...
2021-05-04
In 2019 the climate movement experienced an unprecedented growth in its mobilization capacity and its political and media impact. The success of the movement is closely linked to the figure of Greta Thunberg and the global impact of her discourse and the "Fridays for Future" movement in hundreds of cities around the world.
A study by Silvia Díaz-Pérez, Roger Soler-i-Martí and Mariona Ferrer-Fons, members of the UPF JOVIS research group of the Department of Communication, analyses the activist's speeches and messages on social networks and their legitimization through her personal story, and it also looks into the "Fridays for Future" movement in Barcelona, based on Twitter and Instagram posts. The research was based on a project that has received funding from ...
2021-05-04
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are becoming increasingly popular. At first glance, they have many advantages: Transactions are usually anonymous, fast and inexpensive. But sometimes there are problems with them. In certain situations, fraud is possible, users can discover information about other users that should be kept secret, and sometimes delays occur.
The research unit "Security and Privacy" at TU Wien (Lukas Aumayr and his supervisor Prof. Matteo Maffei) in collaboration with the IMDEA Software Institute (Prof. Pedro Moreno-Sanchez, previously postdoc at TU Wien) and the Purdue University (Prof. Aniket Kate) analyzed these problems and developed an improved protocol. It has now been published and will be presented this year at ...
2021-05-04
Sea turtles in the Cayman Islands are recovering from the brink of local extinction, new research shows.
Monitoring from 1998-2019 shows loggerhead and green turtle nest numbers increased dramatically, though hawksbill turtle nest numbers remain low.
In the first counts in 1998-99, just 39 sea turtle nests were found in total on the three islands. By 2019, the figure was 675.
Captive breeding of green turtles and inactivity of a traditional turtle fishery due to tightening of restrictions in 2008 contributed to this - but populations remain far below historical levels and still face threats including ...
2021-05-04
In the field of molecular epidemiology, the worldwide scientific community has been steadily sleuthing to solve the riddle of the early history of SARS-CoV-2. Despite recent efforts by the World Health Organization, no one to date has identified the first case of human transmission, or "patient zero" in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Finding the earliest possible case is needed to better understand how the virus may have jumped from its animal host first to infect humans as well as the history of how the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome has mutated over time and spread globally.
Since the first SARS-CoV-2 virus infection was detected in December 2019, well over a million genomes of SARS-CoV-2 have been sequenced worldwide, ...
2021-05-04
May 04, 2021 - In its latest clinical practice guideline on community-acquired pneumonia the American Thoracic Society's guidelines panel addresses the use of nucleic acid-based testing for non-influenza viral pathogens. The guideline was published online in the May 1 issue of the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. An explainer video may be viewed here.
Community-acquired pneumonia is caused by a wide range of respiratory pathogens, prominently including viruses. However, the only viral pathogen addressed by the 2019 clinical practice guideline was influenza. The panel determined that, given the increasing recognition of non-influenza viral causes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Complex shapes of photons to boost future quantum technologies