(Press-News.org) Brain implants are used to treat neurological dysfunction, and their use for enhancing cognitive abilities is a promising field of research. Implants can be used to monitor brain activity or stimulate parts of the brain using electrical pulses. In epilepsy, for example, brain implants can determine where in the brain seizures are happening.
Over time, implants trigger a foreign body response, creating inflammation and scar tissue around the implant that reduces their effectiveness.
The problem is that traditional implants are much more rigid than brain tissue, which has a softness comparable to pudding. Stress between the implant and the tissue caused by constant movement of the brain with respect to the implant signals the body to treat the implant as a foreign object. This interaction between the implant and the brain is similar to a knife cutting into a piece of pudding. An implant as soft as brain tissue would be ideal, but such soft implants would be difficult to manufacture and implant on the microscale.
A team of researchers from The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) and McGill's Department of Biomedical Engineering found a solution using silicone and sugar.
By using silicone polymers, widely known for their medical applications, the scientists were able to make the softest brain implant to date with the thickness of a thin sewing thread (~0.2 mm), and the consistency of soft pudding - as soft as the brain itself. They were then able to implant it into the brain using a trick from the cookbook.
They adopted classical cooking techniques of sugar melting, caramelizing and molding both for making the implant, as well as for encapsulating it into a needle made of hardened sugar.
When surgically inserted into the brain of an anesthetized rat, the sugar needle carried the implant to the right location, and dissolved within seconds, leaving the delicate implant in place. Sugar is non-toxic and is naturally metabolized by the brain. Examining brain tissue three and nine weeks after implantation, the team found higher neuronal density and lower foreign body response compared to traditional implants.
While more research is needed to develop electrically active, soft implants, and to prove the safety and effectiveness of the technique in humans, one day it could be used to unlock the potential of brain implants in treating neurological disease and dysfunction.
"The implants we created are so soft that the body doesn't see it as a big threat, allowing them to interact with the brain with less interference," says Edward Zhang, the study's first author. "I am excited about the future of brain implant technology and believe our work helps pave the path for a new generation of soft implants that could make brain implants a more viable medical treatment."
"By reducing the brains inflammatory response, our new, very soft implants are a good thing for the brain and a good thing for the long-term function of an implant," says Tim Kennedy, a researcher at The Neuro and the study's co-senior author. "The miniature sugar needle devised by Zhang is a sweet solution to placing the super-soft implant into equally soft brain tissue."
"Biomedical engineering research is about making the impossible, possible," says David Juncker, a professor of biomedical engineering at McGill and the study's co-senior author. "Here we set out to make an implant as soft as the brain and implant it into the brain, which was a major challenge. We are excited about the results, and the possibility it opens up for long lasting, well-tolerated brain implants"
INFORMATION:
This study was published in the March issue of the journal Advanced Materials Technologies. It was funded by the The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, The Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Healthy Brains, Healthy Lives.
The Neuro
The Neuro - The Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital - is a world-leading destination for brain research and advanced patient care. Since its founding in 1934 by renowned neurosurgeon Dr. Wilder Penfield, The Neuro has grown to be the largest specialized neuroscience research and clinical center in Canada, and one of the largest in the world. The seamless integration of research, pa tient care, and training of the world's top minds make The Neuro uniquely positioned to have a significant impact on the understanding and treatment of nervous system disorders. In 2016, The Neuro became the first institute in the world to fully embrace the Open Science philosophy, creating the Tanenbaum Open Science Institute. The Montreal Neurological Institute is a McGill University research and teaching institute. The Montreal Neurological Hospital is part of the Neuroscience Mission of the McGill University Health Centre. For more information, please visit http://www.theneuro.ca
A new auroral phenomenon discovered by Finnish researchers a year ago is probably caused by areas of increased oxygen atom density occurring in an atmospheric wave channel. The speculative explanation offered by the researchers gained support from a new study.
Observations made by University of Helsinki researchers increased the validity of a speculative mechanism according to which a type of aurora borealis named 'dunes' is born. In the new study, photographs of the phenomenon taken by an international group of hobbyists in Finland, Norway and Scotland were compared to concurrent satellite data.
The rare type of aurora borealis was seen in the sky on 20 January 2016 and recorded in photos taken by ...
This overlay shows radio (orange) and infrared images of a giant molecular cloud called W49A, where new stars are being formed. A team of astronomers led by Chris DePree of Agnes Scott College used the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to make new, high-resolution radio images of this cluster of still-forming, massive stars. W49A, 36,000 light-years from Earth, has been studied for many decades, and the new radio images revealed some tantalizing changes that have occurred since an earlier set of VLA observations in 1994 and 1995.
The ...
Scientists have developed a new "key-hole surgery" technique to extract metals from the earth - which could revolutionise the future of metal mining
A team of international researchers, including Dr Rich Crane from the Camborne School of Mines, University of Exeter, have developed a new method to extract metals, such as copper, from their parent ore body.
The research team have provided a proof of concept for the application of an electric field to control the movement of an acid within a low permeability copper-bearing ore deposit to selectively dissolve and recover the metal in situ.
This is in contrast to the conventional approach for the mining of such deposits ...
Swansea University scientists have uncovered potentially dangerous chemical pollutants that are released from disposable face masks when submerged in water.
The research reveals high levels of pollutants, including lead, antimony, and copper, within the silicon-based and plastic fibres of common disposable face masks.
The work is supported by the Institute for Innovative Materials, Processing and Numerical Technologies (IMPACT) and the SPECIFIC Innovation & Knowledge Centre
Project lead Dr Sarper Sarp of Swansea University College of Engineering said:
"All of us need to keep wearing masks as they are essential in ending the pandemic. But we also urgently need more research and regulation on mask production, so we can reduce any risks to the environment and ...
Pyrosomes, named after the Greek words for 'fire bodies' due their bright bioluminescence, are pelagic tunicates that spend their entire lives swimming in the open ocean. They are made up of many smaller animals, known as zooids, that sit together in a tubular matrix, known as tunic (hence the name pelagic tunicates). Because they live in the open ocean, they generally go unnoticed. In spite of this, increasing research points to their importance in marine environments, as they can form dense blooms that impact food web dynamics and contribute to the movement and transformation of organic carbon.
The study conducted with GEOMAR research vessel POSEIDON in 2018 and 2019 in the vicinity of the Cabo Verde Islands, of which the results have now been published ...
Scientists at the Walter Reed Army Institute for Research demonstrated that biomarkers associated with traumatic brain injury were elevated among law enforcement and military personnel, particularly in active duty participants with longer duration of service. Most notably, these elevated biomarker levels were observed in individuals without a diagnosed brain injury or concussion.
Some law enforcement and military personnel are regularly exposed to low levels of blast, particularly during training, due to the use of explosive charges and high caliber weapons. Understanding effects from these occupational exposures is a military health care priority to improve ...
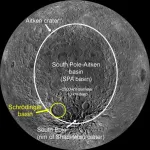
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - A new map including rover paths of the Schrodinger basin, a geologically important area of the moon, could guide future exploration missions.The map was created by a team of interns at the Lunar and Planetary Institute, including Ellen Czaplinski, a University of Arkansas graduate student researcher at the Arkansas Center for Planetary Sciences and first author of a paper published in The Planetary Science Journal.
The researchers identified significant geologic features of the Schrödinger basin, located near the lunar south ...
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) developed a breakthrough in energy-efficient phototransistors. Such devices could eventually help computers process visual information more like the human brain and be used as sensors in things like self-driving vehicles.
The structures rely on a new type of semiconductor--metal-halide perovskites--which have proven to be highly efficient at converting sunlight into electrical energy and shown tremendous promise in a range of other technologies.
"In general, these perovskite semiconductors are a really unique ...
Hypertension is a common medical condition and a primary cause of cardiovascular diseases and stroke worldwide. Unfortunately, as Professor Wei-Li Zhang of the Chinese National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases notes, "the unaffordability of drugs is a major barrier to medication adherence among patients living in low- and middle-income areas."
One of the countries where hypertension is becoming a major problem is China where, researchers estimate, between 244 million and 300 million adults are living with hypertension. But true to Prof. Zhang's words, most cases of hypertension in China are not adequately ...
With the explosion in digital entertainment options over the past several decades and the more recent restrictions on outdoor and in-person social activities, parents may worry that excessive engagement with digital technology could have long-term effects on their children's mental health.
A new study published in the journal Clinical Psychological Science, however, found little evidence for an increased association between adolescents' technology engagement and mental health problems over the past 30 years. The data did not consistently support the suggestion that the technologies we worry about most (e.g., smartphones) are becoming more ...