New look at a bright stellar nursery
VLA observations reveal changes over time
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) This overlay shows radio (orange) and infrared images of a giant molecular cloud called W49A, where new stars are being formed. A team of astronomers led by Chris DePree of Agnes Scott College used the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to make new, high-resolution radio images of this cluster of still-forming, massive stars. W49A, 36,000 light-years from Earth, has been studied for many decades, and the new radio images revealed some tantalizing changes that have occurred since an earlier set of VLA observations in 1994 and 1995.
The VLA radio images show the shape and movement of giant clouds of ionized hydrogen gas formed by the intense ultraviolet radiation from young stars. Comparing old and new VLA images of these ionized regions has shown changes indicating new activity in some of the regions. This new activity includes a narrow, fast-moving jet in one region, supersonic gas motions in three others, and an unexpected reduction in the radio brightness in another.
The astronomers, who reported their findings in the Astronomical Journal, plan to continue observing this region regularly to track changes that will reveal new details about the complex processes of star formation and interactions of the outflows from young stars.
INFORMATION:
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
CREDIT: DePree, et al.; Sophia Dagnello, NRAO/AUI/NSF; Spitzer/NASA.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
Scientists have developed a new "key-hole surgery" technique to extract metals from the earth - which could revolutionise the future of metal mining
A team of international researchers, including Dr Rich Crane from the Camborne School of Mines, University of Exeter, have developed a new method to extract metals, such as copper, from their parent ore body.
The research team have provided a proof of concept for the application of an electric field to control the movement of an acid within a low permeability copper-bearing ore deposit to selectively dissolve and recover the metal in situ.
This is in contrast to the conventional approach for the mining of such deposits ...
2021-05-04
Swansea University scientists have uncovered potentially dangerous chemical pollutants that are released from disposable face masks when submerged in water.
The research reveals high levels of pollutants, including lead, antimony, and copper, within the silicon-based and plastic fibres of common disposable face masks.
The work is supported by the Institute for Innovative Materials, Processing and Numerical Technologies (IMPACT) and the SPECIFIC Innovation & Knowledge Centre
Project lead Dr Sarper Sarp of Swansea University College of Engineering said:
"All of us need to keep wearing masks as they are essential in ending the pandemic. But we also urgently need more research and regulation on mask production, so we can reduce any risks to the environment and ...
2021-05-04
Pyrosomes, named after the Greek words for 'fire bodies' due their bright bioluminescence, are pelagic tunicates that spend their entire lives swimming in the open ocean. They are made up of many smaller animals, known as zooids, that sit together in a tubular matrix, known as tunic (hence the name pelagic tunicates). Because they live in the open ocean, they generally go unnoticed. In spite of this, increasing research points to their importance in marine environments, as they can form dense blooms that impact food web dynamics and contribute to the movement and transformation of organic carbon.
The study conducted with GEOMAR research vessel POSEIDON in 2018 and 2019 in the vicinity of the Cabo Verde Islands, of which the results have now been published ...
2021-05-04
Scientists at the Walter Reed Army Institute for Research demonstrated that biomarkers associated with traumatic brain injury were elevated among law enforcement and military personnel, particularly in active duty participants with longer duration of service. Most notably, these elevated biomarker levels were observed in individuals without a diagnosed brain injury or concussion.
Some law enforcement and military personnel are regularly exposed to low levels of blast, particularly during training, due to the use of explosive charges and high caliber weapons. Understanding effects from these occupational exposures is a military health care priority to improve ...
2021-05-04
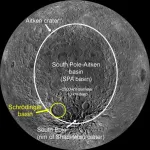
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - A new map including rover paths of the Schrodinger basin, a geologically important area of the moon, could guide future exploration missions.The map was created by a team of interns at the Lunar and Planetary Institute, including Ellen Czaplinski, a University of Arkansas graduate student researcher at the Arkansas Center for Planetary Sciences and first author of a paper published in The Planetary Science Journal.
The researchers identified significant geologic features of the Schrödinger basin, located near the lunar south ...
2021-05-04
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) developed a breakthrough in energy-efficient phototransistors. Such devices could eventually help computers process visual information more like the human brain and be used as sensors in things like self-driving vehicles.
The structures rely on a new type of semiconductor--metal-halide perovskites--which have proven to be highly efficient at converting sunlight into electrical energy and shown tremendous promise in a range of other technologies.
"In general, these perovskite semiconductors are a really unique ...
2021-05-04
Hypertension is a common medical condition and a primary cause of cardiovascular diseases and stroke worldwide. Unfortunately, as Professor Wei-Li Zhang of the Chinese National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases notes, "the unaffordability of drugs is a major barrier to medication adherence among patients living in low- and middle-income areas."
One of the countries where hypertension is becoming a major problem is China where, researchers estimate, between 244 million and 300 million adults are living with hypertension. But true to Prof. Zhang's words, most cases of hypertension in China are not adequately ...
2021-05-04
With the explosion in digital entertainment options over the past several decades and the more recent restrictions on outdoor and in-person social activities, parents may worry that excessive engagement with digital technology could have long-term effects on their children's mental health.
A new study published in the journal Clinical Psychological Science, however, found little evidence for an increased association between adolescents' technology engagement and mental health problems over the past 30 years. The data did not consistently support the suggestion that the technologies we worry about most (e.g., smartphones) are becoming more ...
2021-05-04
DURHAM, N.C. - When patients complain of coughing, runny nose, sneezing and fever, doctors are often stumped because they have no fundamental tool to identify the source of the respiratory symptoms and guide appropriate treatments.
That tool might finally be on its way. In a study proving feasibility, researchers at Duke Health showed that their testing technology can accurately distinguish between a viral and a bacterial infection for respiratory illness - a critical difference that determines whether antibiotics are warranted. And, importantly, the test provided results in under an hour.
"This is exciting progress," said study lead Ephraim Tsalik, associate professor in the departments of Medicine ...
2021-05-04
A new study published in Medical Care Research and Review found that the Affordable Care Act, which expanded Medicaid programs to cover people previously uninsured, provided a financial boost to hospitals.
The study conducted by faculty at the Colorado School of Public Health on the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is the first to investigate the effects of Medicaid expansion by comparing estimates using data from both the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS).
"The IRS and CMS data sources serve as primary resources for assessing the impact of Medicaid expansion on hospitals' financial status. The comparison of the two is timely and can inform ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New look at a bright stellar nursery
VLA observations reveal changes over time