Having a ball: New English Premier League soccer ball more stable, drags more
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba compare a new English Premier League soccer ball with previous versions in wind-tunnel experiments, and find increased drag and stability, which may lead to a better understanding of aerodynamics in sports
2021-05-07
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan - Scientists from the Faculty of Health and Sports Sciences at the University of Tsukuba used aerodynamics experiments to empirically test the flight properties of a new four-panel soccer ball adopted by the English Premier League this year. Based on projectile and wind-tunnel data, they computed the drag and side forces and found that the new ball was marginally more stable than previous versions but may not fly as far. This work may help improve the design of future sports equipment.
Sports players know that millions of dollars in salary and potential endorsement deals can be at stake during each match. Soccer players often complain about the aerodynamic properties of the ball because a random flutter in flight can turn a harmless shot into a goal. Old-school soccer balls have 32 panels, with a mix of hexagons and pentagons. More recently, top soccer leagues have experimented with 6-panel versions with strips similar to a volleyball. For the new season, the English Premier League has introduced the Flight 2020 Soccer Ball by Nike, which is advertised as having molded grooves that provide consistent flight.
Now, researchers at Tsukuba University have tested these claims with wind tunnel experiments. They measured the drag coefficient for the ball, along with two previous models, as a function of the Reynolds number. The Reynolds number, an important parameter in fluid dynamics, controls the transition from smooth to turbulent flow. According to author Professor Takeshi Asai, "at low Reynolds numbers, smooth flow occurs, because viscosity can damp out turbulence. At high Reynolds numbers, chaotic air vortices can lead to unstable and unpredictable flight patterns."
The team found increased drag at high Reynolds numbers for the new ball. This led to reduced flight range but may have also reduced lateral forces that can destabilize the trajectory. This was especially true in the "asymmetric" orientation of the ball, when one of the grooves was facing forward. "The smaller fluctuations in the side and lift forces of the Flight 2020 indicates that it is less likely to experience irregular changes in trajectory, thereby possibly leading to greater stability during flight," says Professor Asai.
The team partially attributed this tradeoff in stability at the expense of range to increased surface roughness. This finding may be useful for designing other sports equipment to increase the importance of skill and reduce the impact of luck.
INFORMATION:
The work is published in Scientific Reports as "Aerodynamics of the newly approved football for the English Premier League 2020-21 season" (DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89162-y).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-07
Researchers have traced the remaining last steps of the biological pathway that gives oats resistance to the deadly crop disease take-all.
The discovery creates opportunities for new ways of defending wheat and other cereals against the soil-borne root disease.
The research team have already taken the first step in this aim by successfully reconstituting the self-defence system in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana.
Further experiments to establish the avenacin biosynthetic pathway in wheat's more complex genome, to test if it will provide the same resistance ...
2021-05-07
They may be tiny weapons, but Brigham Young University's holography research group has figured out how to create lightsabers -- green for Yoda and red for Darth Vader, naturally -- with actual luminous beams rising from them.
Inspired by the displays of science fiction, the researchers have also engineered battles between equally small versions of the Starship Enterprise and a Klingon Battle Cruiser that incorporate photon torpedoes launching and striking the enemy vessel that you can see with the naked eye.
"What you're seeing in the scenes we create is real; there is nothing computer generated about them," said lead researcher Dan Smalley, a professor of electrical engineering at BYU. "This is not like the movies, where the lightsabers ...
2021-05-07
May 7, 2021 - Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare systems scrambled to modify patient care processes - particularly when it came to strategies aimed at reducing the risk of hospital-related complications. A look at how one hospital applied its learning health system (LHS) framework to respond to a COVID-19-related increase in hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs) is presented in the May/June Journal for Healthcare Quality (JHQ), the peer-reviewed journal of the National Association for Healthcare Quality (NAHQ). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Given the significant challenges ...
2021-05-07
Today, deliveries via cesarean sections, or c-sections, have become quite common globally. Sometimes, c-sections are a medical necessity when normal deliveries become risky either for the mother or the baby. At other times, it can be a choice. C-sections today have become a considerably safer procedure than it was a few decades ago, but there is need to refine it further.
In a END ...
2021-05-07
Children ages two to five who have the most common form of cystic fibrosis (CF), caused by two copies of the F508 gene mutation, have not had any modulator treatments available to them until recently. A new study authored by researchers at Children's Hospital Colorado and published May 6, 2021, in Lancet Respiratory Medicine shows that the CFTR modulator - lumacaftor/ivacaftor - can be safe and well-tolerated for this age range for up to 120 weeks, allowing younger children to begin proactive treatment of CF earlier in their lives.
CF affects more than 70,000 people worldwide and is a chronic, progressive, life-shortening genetic disease caused by an absent or defective protein called the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein, resulting from mutations in both copies ...
2021-05-07
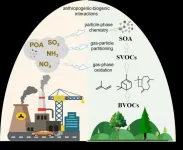
Despite their extremely small size, submicron atmospheric aerosols are critical pollutants with climate change, air quality, and human health implications. Of these particles, secondary organic aerosols (SOA) form when volatile organic compounds (VOCs) oxidize to lower volatility products that bond with and increase aerosol particle size, or in some cases, they may simply exist by themselves. SOA constitutes a significant fraction of the global aerosol mass. Scientists are attempting to improve future aerosol modeling, but several discrepancies still exist between model-simulated and field-observed SOA budgets.
''Large uncertainties in model assessments of SOA budgets and correspondingly, its climate effects, ...
2021-05-07
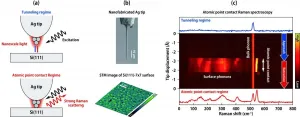
Nanofabrication of electronic devices has reached a single nanometer scale (10-9 m). The rapid advancement of nanoscience and nanotechnology now requires atomic-scale optical spectroscopy in order to characterize atomistic structures that will affect the properties and functions of the electronic devices.
The international team headed by Takashi Kumagai at Institute for Molecular Science discovered a huge enhancement of Raman scattering mediated by a formation of an atomic point contact between a plasmonic silver tip and a Si(111)-7×7 reconstructed surface. This was achieved by means of state-of-the-art low-temperature tip-enhanced ...
2021-05-07
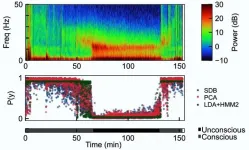
Anesthestic drugs act on the brain but most anesthesiologists rely on heart rate, respiratory rate, and movement to infer whether surgery patients remain unconscious to the desired degree. In a new study, a research team based at MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital shows that a straightforward artificial intelligence approach, attuned to the kind of anesthetic being used, can yield algorithms that assess unconsciousness in patients based on brain activity with high accuracy and reliability.
"One of the things that is foremost in the minds of anesthesiologists is 'Do I have somebody who is lying in front of me who may be conscious and I don't realize it?' Being ...
2021-05-07
Even the humble fruit fly craves a dose of the happy hormone, according to a new study from the University of Sussex which shows how they may use dopamine to learn in a similar manner to humans.
Informatics experts at the University of Sussex have developed a new computational model that demonstrates a long sought after link between insect and mammalian learning, as detailed in a new paper published today in Nature Communications.
Incorporating anatomical and functional data from recent experiments, Dr James Bennett and colleagues modelled how the anatomy and physiology of the fruit fly's brain can support learning according to the reward prediction error (RPE) hypothesis.
The computational model indicates how dopamine neurons in an area of ...
2021-05-07
PITTSBURGH, May 7, 2021 - In a paper published today in Nature Communications, an international group of collaborators led by researchers at UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh have identified a genetic cause of a rare neurological disorder marked by developmental delay and loss of coordination, or ataxia.
The disorder, scientists found, is caused by mutations in a protein called GEMIN5--one of the key building blocks of a protein complex that controls RNA metabolism in neurons. No mutations in GEMIN5 were previously linked to any genetic disease. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Having a ball: New English Premier League soccer ball more stable, drags more
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba compare a new English Premier League soccer ball with previous versions in wind-tunnel experiments, and find increased drag and stability, which may lead to a better understanding of aerodynamics in sports