Emissions from human activity modify biogenic secondary organic aerosol formation
2021-05-07
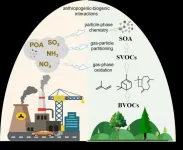
(Press-News.org) Despite their extremely small size, submicron atmospheric aerosols are critical pollutants with climate change, air quality, and human health implications. Of these particles, secondary organic aerosols (SOA) form when volatile organic compounds (VOCs) oxidize to lower volatility products that bond with and increase aerosol particle size, or in some cases, they may simply exist by themselves. SOA constitutes a significant fraction of the global aerosol mass. Scientists are attempting to improve future aerosol modeling, but several discrepancies still exist between model-simulated and field-observed SOA budgets.
''Large uncertainties in model assessments of SOA budgets and correspondingly, its climate effects, motivated extensive research to find out why these exist.'' said Prof. Lin Du from the Environmental Research Institute, Shandong University. ''Biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs) produced by terrestrial vegetation are globally major SOA precursors, and their SOA formation potential can be modified by anthropogenic emissions."
Prof. Du's research group systematically summarized the field evidence and chemical processes behind SOA formation through anthropogenic-biogenic interactions. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences published their review work titled ''Anthropogenic Effects on Biogenic Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation.''
The predominant anthropogenic pollutants, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), aerosol particles, sulfur dioxide (SO2), ammonia (NH3), and other amines mediate SOA formation through both gas- and particle-phase reactions. The extent of these interactions is highly related to the BVOC precursors, pollutant levels, oxidants, and other atmospheric conditions.
''The nonlinear interactions between human and natural systems are far more complex than their current representation in atmospheric models.'' said Prof. Du. "Meanwhile, the complexity and variability of the atmospheric environment itself makes the exploration of these interactions more challenging.''
Researchers have observed strong correlations between biogenic SOA formation and anthropogenic pollutants in many regions influenced by both anthropogenic and biogenic sources. Though BVOCs emitted from natural sources cannot be controlled directly, humans can mitigate a fraction of biogenic SOA by limiting anthropogenic pollutants. Shedding light on anthropogenic-biogenic interactions is necessary to improve estimates of how and to what extent anthropogenic emissions could modify global aerosol concentrations. These studies should help shape more effective pollution control measures as well as reduce uncertainties in the SOA budget and its associated climate effects.
''Based on comprehensive review of fundamental insights, future efforts, such as laboratory studies under more relevant atmospheric conditions, development of more authentic standards, field observations of the temporal and spatial distribution of both BVOCs, and anthropogenic pollutants, are recommended.'' said Prof. Du. "With increasing studies on the qualitative and quantitative analysis of anthropogenic-biogenic interactions through laboratory explorations and field observations, better reproduction of SOA concentrations by atmospheric models would be expected.''
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-07
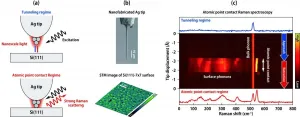
Nanofabrication of electronic devices has reached a single nanometer scale (10-9 m). The rapid advancement of nanoscience and nanotechnology now requires atomic-scale optical spectroscopy in order to characterize atomistic structures that will affect the properties and functions of the electronic devices.
The international team headed by Takashi Kumagai at Institute for Molecular Science discovered a huge enhancement of Raman scattering mediated by a formation of an atomic point contact between a plasmonic silver tip and a Si(111)-7×7 reconstructed surface. This was achieved by means of state-of-the-art low-temperature tip-enhanced ...
2021-05-07
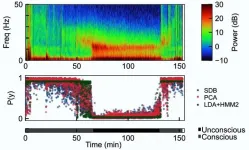
Anesthestic drugs act on the brain but most anesthesiologists rely on heart rate, respiratory rate, and movement to infer whether surgery patients remain unconscious to the desired degree. In a new study, a research team based at MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital shows that a straightforward artificial intelligence approach, attuned to the kind of anesthetic being used, can yield algorithms that assess unconsciousness in patients based on brain activity with high accuracy and reliability.
"One of the things that is foremost in the minds of anesthesiologists is 'Do I have somebody who is lying in front of me who may be conscious and I don't realize it?' Being ...
2021-05-07
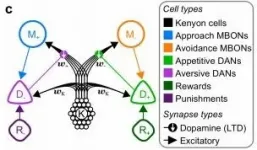
Even the humble fruit fly craves a dose of the happy hormone, according to a new study from the University of Sussex which shows how they may use dopamine to learn in a similar manner to humans.
Informatics experts at the University of Sussex have developed a new computational model that demonstrates a long sought after link between insect and mammalian learning, as detailed in a new paper published today in Nature Communications.
Incorporating anatomical and functional data from recent experiments, Dr James Bennett and colleagues modelled how the anatomy and physiology of the fruit fly's brain can support learning according to the reward prediction error (RPE) hypothesis.
The computational model indicates how dopamine neurons in an area of ...
2021-05-07
PITTSBURGH, May 7, 2021 - In a paper published today in Nature Communications, an international group of collaborators led by researchers at UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh have identified a genetic cause of a rare neurological disorder marked by developmental delay and loss of coordination, or ataxia.
The disorder, scientists found, is caused by mutations in a protein called GEMIN5--one of the key building blocks of a protein complex that controls RNA metabolism in neurons. No mutations in GEMIN5 were previously linked to any genetic disease. ...
2021-05-07
Luxembourg, 7 May 2021 - In a new position statement, Alzheimer Europe has issued a call for prioritisation of people with dementia and their carers in national COVID-19 vaccination strategies, urging governments to recognise the disproportionate effect of the pandemic on these groups.
Alzheimer Europe has today issued a call for people with dementia and their carers to be given priority in the ongoing COVID-19 vaccination campaigns across Europe.
In its position statement, Alzheimer Europe notes that people with dementia have almost twice the risk for developing COVID-19 compared to their ...
2021-05-07
Systemic inequalities mean that low-income households in London are more likely to be exposed to higher levels of indoor air pollution, according to a report by UCL researchers.
The biggest factors are the quality of housing and the characteristics of the surrounding environment, taking location and levels of outdoor air pollution into account - factors beyond occupants' control.
Air pollution exposure is the greatest environmental health threat in the UK, with long-term exposures estimated to cause 28,000-36,000 premature deaths a year.
In the paper, published in Buildings and Cities, researchers used available data and models, assembling evidence to examine five factors explaining why lower socio-economic groups may be exposed to higher levels of indoor air pollution ...
2021-05-07
LUGANO, 7 May, 2021- Findings presented at today's EADV 2021 Spring Symposium suggest that an imbalance in gut microbiota (dysbiosis), could play a significant role in the progression of inflammatory skin disease, Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS). HS is a painful, long-term skin condition, with a chronic and relapsing nature that significantly impacts patients' quality of life.
Researchers at Hacettepe University collected faecal samples from 15 patients with HS and 15 age and sex matched healthy individuals and analysed regions of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene to investigate ...
2021-05-07
LUGANO, 6 May, 2021- The dermatological impact of COVID-19 is a burning topic at EADV's 2021 Spring Symposium. New research presented today highlights the effect that stringent hand hygiene during the pandemic has had on hand skin health.1
Researchers at Father Muller Medical College, India, analysed transepidermal water loss (TEWL - an essential parameter for measuring skin barrier function) from 582 people (291 healthcare professionals (HCPs) and 291 healthy individuals from the general population). Results indicated that hand dermatitis was now present among 92.6% of HCPs and 68.7% of the general population, despite only ~3% of HCPs and 2.4% of the general public in the study having reported a prior history of hand dermatitis (obtained through medical history ...
2021-05-07
Are penalty shots a soccer player's dream or nightmare? What should be an easy shot can become a mammoth task when the hopes and fears of an entire nation rest on a player's shoulders, leading them to choke under pressure. Understanding the brain activity behind choking is the driving force behind a new study in open-access journal Frontiers in Computer Science. The study is the first to measure brain activity during penalty shots in a soccer pitch environment. It finds that people who choked activated areas of the brain involved in long-term thinking, suggesting that they were overthinking the consequences of missing the shot. ...
2021-05-07
Researchers from University of Southern California, Bocconi University, and Vrije Universitei Amsterdam published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that explains the six types of judgements consumers make when determining a product's authenticity and how marketers can use this insight to deliver more authentic offerings.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "The Concept of Authenticity: What it Means to Consumers" and is authored by Joseph Nunes, Andrea Ordanini, and Gaia Giambastiani.
Consumers crave authenticity. Yet marketing itself is typically considered inherently inauthentic. Hence, firms must learn to understand, manage, and excel at rendering authenticity. The critical question is: how? Marketers who wish to deliver authentic consumption experiences ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Emissions from human activity modify biogenic secondary organic aerosol formation