(Press-News.org) Obesity increases the risk of developing 10 of the most common cancers, regardless of how it is measured, according to a study of more than 400,000 adults in the UK, being presented at The European Congress on Obesity (ECO) held online this year, with central fatness (larger waist and hips) and general obesity (body mass index [BMI] and body fat percentage) associated with similar estimates of cancer risk.
The results suggest that BMI is an adequate measure of cancer risk from excess weight, and there is no advantage in using more complicated or expensive measures such as waist circumference or body fat percentage.
It is well known that being overweight or obese is linked to an elevated risk of some cancers and premature death. However, most of the evidence is based on BMI, and little is known about the association between cancer and other markers of adiposity (eg, central obesity and body fat).
Using data from the UK Biobank prospective cohort study, researchers from the University of Glasgow identified 437,393 adults (54% women; average age 56 years) who were cancer-free, to investigate the risk of developing and dying from 24 cancers according to six markers of obesity: BMI, body fat percentage, waist-to-hip ratio, waist-to-height ratio, and waist and hip circumferences.
The results were adjusted for age, sex, ethnicity, deprivation, education, smoking, alcohol consumption, intakes of fruit and vegetables, red and processed meat, oily fish, physical activity, and sedentary behaviours [1]. After an average of 9 years follow-up, there were 47,882 cases of cancer, and 11,265 cancer deaths.
The researchers found that all six obesity measures were positively and similarly associated with higher risk for 10 cancers. For example, each 4.2 kg/m2 (men) and 5.1 kg/m2 (women) increase in BMI above 25 kg/m2 (defined as being overweight) was linked with higher risk of cancers of the stomach (35% increase), gallbladder (33%), liver (27%), kidney (26%), pancreas (12%), bladder (9%), colorectal (10%), endometrial (73%), uterine (68%), postmenopausal breast (8%), and overall (3%) cancer.
Based on the results, the researchers estimate that if these associations were causal, being overweight or obese could be responsible for around 40% of endometrial and uterine cancers and 29% of gallbladder cancers; and could account for 64%, 46%, and 40% of deaths from these cancers respectively (see figure 8 in link below).
"We observed a linear association - the more severe obesity is, the higher the risk of developing and dying from these cancers, except for postmenopausal breast cancer", says Dr Carlos Celis-Morales from the University of Glasgow, UK, who led the research. "But there was a lot of variation in the effects of obesity on different cancers. This tells us that obesity must affect cancer risk through a different number of processes, depending on the cancer type."
This is an observational study, so can't establish cause, and the researchers say they cannot rule out the possibility that other unmeasured factors (residual confounding) may have influenced the results. They also note that the study is not a representative sample of the UK adult population, so the results might not be generalisable to the general population.
INFORMATION:
A study of more than 173,000 women in Denmark, presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) held online this year, suggests that girls with a higher body mass index (BMI) during childhood are less likely than their peers with a lower BMI to develop breast cancer as adults, both before and after the menopause.
The findings contrast with those for adult BMI, which indicate that women who gain weight after menopause have an increased risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. While the authors are unsure why children with a higher BMI appear to be protected ...
New research presented at this year's European Congress on Obesity (held online, 10-13 May) finds evidence that structures called inflammasomes (a part of the innate immune system that helps to regulate inflammation) could play an important role in the development of obesity-associated colon cancer. The study is by Dr Victoria Catalán and Professor Gema Frühbeck, University Hospital Navarra and CIBEROBN, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Pamplona, Spain, and colleagues.
Inflammasomes* form part of the innate immune system which provides the first line of defence against pathogens using a wide range of physical, chemical, ...
Researchers have successfully developed a new Strep A human challenge model, paving the way to test vaccines against the common deadly bacteria that causes sore throats, scarlet fever and skin sores.
The collaborative research effort, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published in The Lancet Microbe, found the model, which deliberately infected healthy adult volunteers with the bacteria in a controlled environment, was safe and would now be used to trial Strep A candidate vaccines.
Strep A infections affect about 750 million people and kill more than 500,000 globally every year - more than influenza, ...
A complicated interaction between different proteins is needed for information to pass from one nerve cell to the next. Researchers at the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have now managed to study this process in the synaptic vesicles, which play an important role in this process. The study appeared in the journal Nature Communications.
Several billion nerve cells communicate with each other in the body so that humans and other living beings can perceive and react to their environment. A host of complex chemical and electrical processes occur within a few milliseconds. "Special messenger substances - known as neurotransmitters - are released at the synapses of the nerve cells. They transmit information between the individual nerve cells," explains Dr Carla Schmidt, ...
A study presented at this year's European Congress on Obesity (held online, 10-13 May) supports recommendations to avoid pregnancy for 12 months after bariatric (obesity) surgery due to an association with adverse outcomes in pregnancy including an elevated risk of preterm birth. The study is by Dr Laura Heusschen, Vitalys Obesity Clinic, part of Rijnstate Hospital, Arnhem, The Netherlands, and colleagues.
More than half of all female patients who undergo bariatric surgery are of reproductive age, and the resulting weight loss improves fertility, as well as reducing the risk of gestational diabetes and hypertensive disorders during pregnancy. It also ...
The first global review of complementary medicines (herbal and dietary supplements) for weight loss in 16 years--combining 121 randomised placebo-controlled trials including nearly 10,000 adults--suggests that their use cannot be justified based on the current evidence.
The findings of two studies, being presented at The European Congress on Obesity (ECO) held online this year, suggest that although some herbal and dietary supplements show statistically greater weight loss than placebo, it is not enough to benefit health, and the authors call for more research into their long-term safety.
"Over-the-counter ...
Vegetarians appear to have a healthier biomarker profile than meat-eaters, and this applies to adults of any age and weight, and is also unaffected by smoking and alcohol consumption, according to a new study in over 166,000 UK adults, being presented at this week's European Congress on Obesity (ECO), held online this year.
Biomarkers can have bad and good health effects, promoting or preventing cancer, cardiovascular and age-related diseases, and other chronic conditions, and have been widely used to assess the effect of diets on health. However, evidence of the metabolic benefits associated with being vegetarian is unclear.
To understand ...
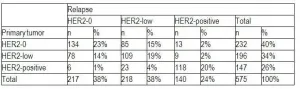
Lugano, Switzerland, 8 May 2021 - The finding that breast tumours can evolve to express low HER2 potentially widens the number of patients who can benefit from new investigational agents, typically novel antibody-drug conjugate therapies, that are currently in clinical trials for HER2-low tumours.
The first study of its kind exploring how breast cancers change from the primary to the recurrent tumour has revealed that nearly 30% of breast cancer patients convert from, or to, human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)2-low status. Specifically, the study found that 14% of triple-negative breast cancers with HER2-negative expression (also referred to as HER2-0) in the primary tumour converted to HER2-low expression in the recurrent tumour ...
Mild Covid-19 infection is very unlikely to cause lasting damage to the structure or function of the heart, according to a study led by UCL (University College London) researchers and funded by the British Heart Foundation (BHF) and Barts Charity.
The researchers say the results, published in JACC Cardiovascular Imaging, should reassure the public, as they relate to the vast majority of people who had Covid-19 infections with mild or no symptoms.
This study of 149 healthcare workers recruited from Barts Health and Royal Free London NHS Trusts is the largest and most detailed study to date into ...
The air in the United States and Western Europe is much cleaner than even a decade ago. Low-sulfur gasoline standards and regulations on power plants have successfully cut sulfate concentrations in the air, reducing the fine particulate matter that harms human health and cleaning up the environmental hazard of acid rain.
Despite these successes, sulfate levels in the atmosphere have declined more slowly than sulfur dioxide emissions, especially in wintertime. This unexpected phenomenon suggests sulfur dioxide emission reductions are less efficient than expected for cutting sulfate aerosols. A new study led by Tokyo ...