Fifty shades of reading: Who reads contemporary erotic novels and why?
New study is the first to explore empirically the readership and the reading rewards underlying the current large-scale cultural phenomenon of erotic novels
2021-05-10
(Press-News.org) Soon after E.L. James's Fifty Shades of Grey appeared in 2015, the book market was inundated with a flood of erotic bestsellers. People from all corners began wondering what this type of novel's secret of success could be. Now, a research team at the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics (MPIEA) in Frankfurt/Main, Germany, has taken a closer look at the readership of erotic novels and investigated the causes of this literary predilection.
In the media as well as the academy, contemporary erotica is typically dismissed as being of low literary value. Critics and scholars tend to classify its readers as having mediocre to poor taste, without, however, examining their motivations and experiences in more detail. Against this background, the MPIEA team conducted an online study to investigate who actually reads erotic novels and why. The findings have just been published as an Open Access article in the journal Humanities & Social Sciences Communications.
The study included data sets from around 420 female participants. The majority of respondents were heterosexual women in stable relationships with an above-average level of education. They described themselves as being enthusiastic frequent readers who enjoyed sharing their reading experiences with others. Most of the study participants were between 20 and 40 years old.
The majority of respondents indicated that they read erotic novels as a diversion, and feelings of ease and relaxation were frequently named as a motivating factor. The sexual explicitness of the novels and their potential to provide orientation in readers' own lives also played a role for the participants, although this role was less significant than had been assumed in previous studies. Readers' opinions about erotic novels also came as a surprise, by contrast with more general critical ideas about contemporary erotica.
"Many of the study participants saw erotic novels - at least in part - as being emancipated, feminist, and progressive. We attribute this finding primarily to the respondents' more traditional views of male and female gender roles," explains lead author Maria Kraxenberger.
This study is the first to investigate empirically the readership and motivations for reading that underlie a major contemporary cultural phenomenon. Although readers of erotica have a significant impact on the international book market, the mainstream conversation about literature and reading is still reserved for "serious" readers of "good," if less popular, kinds of books. The study's findings underscore the need for more research that explores reading experiences outside the canon of serious literature.
INFORMATION:
Original Publication:
Kraxenberger, M., Knoop, C. A., & Menninghaus, W. (2021). Who reads contemporary erotic novels and why? Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 8, Article 96.
Published: 28 April 2021
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-10
Twenty dollars a month might not seem like a lot to pay for health insurance. But for people getting by on $15,000 a year, it's enough to make some drop their coverage - especially if they're healthy, a new study of Medicaid expansion participants in Michigan finds.
That could keep them from getting preventive or timely care, and could leave their insurance company with a sicker pool of patients than before, say the researchers from the University of Michigan and University of Illinois Chicago. They have published their findings as a working paper through the National Bureau of Economic Research, ahead of publication in the American Journal of Health Economics.
The study has implications for other states that require ...
2021-05-10
DURHAM, N.C. - A potential new vaccine developed by members of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute has proven effective in protecting monkeys and mice from a variety of coronavirus infections -- including SARS-CoV-2 as well as the original SARS-CoV-1 and related bat coronaviruses that could potentially cause the next pandemic.
The new vaccine, called a pan-coronavirus vaccine, triggers neutralizing antibodies via a nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is composed of the coronavirus part that allows it to bind to the body's cell receptors and is formulated with a chemical booster called an adjuvant. ...
2021-05-10
A Flinders University researcher has finally fathomed why large numbers of killer whales gather at a single main location off the Western Australian southern coastline every summer.
In a new paper published in Deep Sea Research, physical oceanographer Associate Professor Jochen Kampf describes the conditions which have produced this ecological natural wonder of orcas migrating to the continental slope near Bremer Bay in the western Great Australian Bight from late austral spring to early autumn (January-April).
"The aggregation is connected to the local marine food web that follows from the upwelling of benthic particulate organic matter (POM) ...
2021-05-10
A novel approach to immunotherapy design could pave the way for new treatments for people with an aggressive form of brain cancer called glioblastoma.
Using specifically designed receptors, researchers were able to completely clear brain cancer tumours in preclinical models, using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy.
Published today in Clinical & Translational Immunology and led by Associate Professor Misty Jenkins, the research is a crucial step towards developing new immunotherapy treatments for this devastating illness.
More than 1800 Australians are diagnosed with brain cancer every year. ...
2021-05-10
A new micro-light-emitting diode (micro-LED) developed at KAUST can efficiently emit pure red light and may help in the quest to develop full-color displays based on just a single semiconductor.
Micro-LEDs are a promising technology for the next generation of displays. They have the advantage of being energy efficient and very small. But each LED can only emit light over a narrow range of colors. A clever solution is to create devices that combine many different LEDs, each emitting a different color. Full-color micro-displays can be created by combining red, green and blue (RGB) micro-LEDs. Now, a KAUST team of Zhe Zhuang, Daisuke Iida and Kazuhiro Ohkawa have worked to develop ...
2021-05-10
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (May 10, 2021) -- The Gulf of Guinea islands harbor an abundance of species found nowhere else on Earth. But for over 100 years, scientists have wondered whether or not a population of limbless, burrowing amphibians--known as caecilians--found on one of the islands is a single or multiple species. Now, a team of researchers from the California Academy of Sciences and the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History has contributed the strongest evidence to date that there is not one, but two different species of caecilians on São Tomé ...
2021-05-10
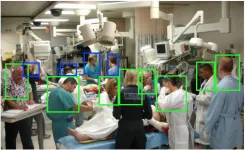
Computer scientists at the University of California San Diego have developed a more accurate navigation system that will allow robots to better negotiate busy clinical environments in general and emergency departments more specifically. The researchers have also developed a dataset of open source videos to help train robotic navigation systems in the future.
The team, led by Professor Laurel Riek and Ph.D. student Angelique Taylor, detail their findings in a paper for the International Conference on Robotics and Automation taking place May 30 to June 5 in Xi'an, China.
The project stemmed from conversations with clinicians over several years. The consensus was that robots would best help physicians, nurses and staff ...
2021-05-10
An international team led by researchers from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography (XIEG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of Geneva has found that flash floods may triple across the Earth's "Third Pole" in response to ongoing climate change.
Their findings were published in Nature Climate Change on May 6.
The Hindu Kush-Himalaya, Tibetan Plateau and surrounding mountain ranges are widely known as the "Third Pole" of the Earth. It contains the largest number of glaciers outside the polar regions.
Due to global warming, the widespread and accelerated melting of glaciers over ...
2021-05-10
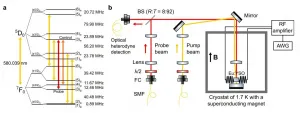
Remote quantum distribution on the ground is limited because of the loss of photon in optical fibers. One solution for remote quantum communication lies in quantum memories: photons are stored in the long-lived quantum memory (quantum flash drive) and then quantum information is transmitted by the transportation of the quantum memory. Given the speed of aircrafts and high-speed trains, it is critical to increase the storage time of the quantum memories to the order of hours.
In a new study published in Nature Communications, a research team led by Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. ZHOU Zongquan from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) extended the storage time of the optical memories to over one hour. It broke the record of one minute achieved by German researchers in 2013, ...
2021-05-10
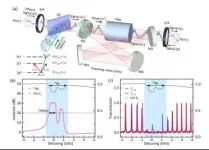
Chinese researchers achieved 51.5dB nonreciprocal isolation in the atomic ensemble, which is the highest isolation ratio in the non-magnetic nonreciprocal field. They discussed the quantum noise problem in nonreciprocal devices for the first time.
The result was published on Nature Communications on April 22, 2021.
Nonreciprocity is an important basic concept in the optical field. The isolators and circulators derived from it are all indispensable components in the optical path. Faraday isolator based on circular birefringence of magneto-optical effect is widely used because of its easy construction, high isolation and low loss.
However, in the integrated optical path, the traditional faraday isolator is subject to various limitations. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fifty shades of reading: Who reads contemporary erotic novels and why?
New study is the first to explore empirically the readership and the reading rewards underlying the current large-scale cultural phenomenon of erotic novels