(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO, CA (May 10, 2021) -- The Gulf of Guinea islands harbor an abundance of species found nowhere else on Earth. But for over 100 years, scientists have wondered whether or not a population of limbless, burrowing amphibians--known as caecilians--found on one of the islands is a single or multiple species. Now, a team of researchers from the California Academy of Sciences and the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History has contributed the strongest evidence to date that there is not one, but two different species of caecilians on São Tomé island. Their findings, published today in Molecular Ecology, also suggest that volcanic activity may have led to the divergence of the species.
"To judge whether one species is in fact composed of multiple lineages, scientists have to build a case," says senior author and Academy Curator of Herpetology Rayna Bell. "By conducting a population level genomic study of these amphibians across the entire island, we are adding a crucial line of evidence that the São Tomé caecilian is actually two unique species."
Initially described by Portuguese scientists during colonial times, the São Tomé caecilians were later split into two distinct species based on their variation in color and location on the island--solid lemon yellow in the north and yellow with brown splotches to the south. Since then, subsequent research has bounced back and forth, grouping the species together then separating them out again, based on the best available evidence.
Then, in 2014, a study by former Academy Curator of Herpetology Robert Drewes and graduate student Ricka Stoelting using mitochondrial DNA indicated that not only were there likely two unique species, but they might be interbreeding. Bell and her colleagues build upon those previous findings by sampling 85 caecilians from 21 locations across the island for genome-wide genetic markers that more accurately confirm the presence--and interbreeding--of the two species.
"That earlier study was the first clue towards unraveling the mystery of the São Tomé caecilians," Bell says. "Our study provides further proof of the presence of two separate, interbreeding species and quantifies how much overlap--or hybridization--is occurring between them."
Once the research team confirmed the existence of two different but interbreeding species, they started to work backward through time to try to determine how the species diverged.
"It's pretty remarkable that there are two unique species on such a small island," says Academy collections manager and study co-author Lauren Scheinberg. "It really makes you wonder how natural selection is acting to drive speciation."
Through their analysis, the researchers found that the two species diverged around 300,000 years ago, a time period that coincides with a burst of volcanic activity on the island. The researchers suggest that lava flows during this period may have led to the speciation of the caecilians by dividing the island into a patchwork of smaller habitats with unique environmental pressures. As the lava flows eroded, resulting in suitable habitat for caecilians, the two species came back into contact and started to hybridize, obscuring the evidence of their separation.
"These findings are an important reminder that islands are not static," Bell says. "Even though they can be small and isolated, they are dynamic systems that are actively accumulating new species. It's also an important consideration for the conservation of São Tomé caecilians to know that we have two, genetically and morphologically unique species."
Though the picture of their past is becoming clearer, there is still much to learn about these enigmatic amphibians. For example, while most caecilians spend a majority of their time underground, the São Tomé caecilians can be readily found on the forest floor, raising questions about how the bright yellow amphibians avoid predation.
While one century-long mystery is nearing a resolution, it seems more are taking its place. But Bell is looking forward to the challenge. "These are perhaps the most well-studied caecilians on Earth because of their accessibility and how long ago they were described to science. Yet there is still so much to learn about them, from their mating behavior to how they deter predators," Bell says. "For a biologist, what could be more exciting than that?"
INFORMATION:
About Research at the California Academy of Sciences
The Institute for Biodiversity Science and Sustainability at the California Academy of Sciences is at the forefront of efforts to understand two of the most important topics of our time: the nature and sustainability of life on Earth. Based in San Francisco, the Institute is home to more than 100 world-class scientists, state-of-the-art facilities, and nearly 46 million scientific specimens from around the world. The Institute also leverages the expertise and efforts of more than 100 international Associates and 450 distinguished Fellows. Through expeditions around the globe, investigations in the lab, and analysis of vast biological datasets, the Institute's scientists work to understand the evolution and interconnectedness of organisms and ecosystems, the threats they face around the world, and the most effective strategies for sustaining them into the future. Through innovative partnerships and public engagement initiatives, they also guide critical sustainability and conservation decisions worldwide, inspire and mentor the next generation of scientists, and foster responsible stewardship of our planet.
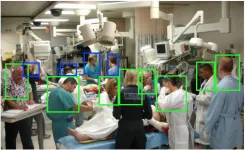
Computer scientists at the University of California San Diego have developed a more accurate navigation system that will allow robots to better negotiate busy clinical environments in general and emergency departments more specifically. The researchers have also developed a dataset of open source videos to help train robotic navigation systems in the future.
The team, led by Professor Laurel Riek and Ph.D. student Angelique Taylor, detail their findings in a paper for the International Conference on Robotics and Automation taking place May 30 to June 5 in Xi'an, China.
The project stemmed from conversations with clinicians over several years. The consensus was that robots would best help physicians, nurses and staff ...
An international team led by researchers from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography (XIEG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of Geneva has found that flash floods may triple across the Earth's "Third Pole" in response to ongoing climate change.
Their findings were published in Nature Climate Change on May 6.
The Hindu Kush-Himalaya, Tibetan Plateau and surrounding mountain ranges are widely known as the "Third Pole" of the Earth. It contains the largest number of glaciers outside the polar regions.
Due to global warming, the widespread and accelerated melting of glaciers over ...
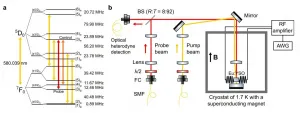
Remote quantum distribution on the ground is limited because of the loss of photon in optical fibers. One solution for remote quantum communication lies in quantum memories: photons are stored in the long-lived quantum memory (quantum flash drive) and then quantum information is transmitted by the transportation of the quantum memory. Given the speed of aircrafts and high-speed trains, it is critical to increase the storage time of the quantum memories to the order of hours.
In a new study published in Nature Communications, a research team led by Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. ZHOU Zongquan from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) extended the storage time of the optical memories to over one hour. It broke the record of one minute achieved by German researchers in 2013, ...
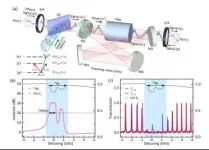
Chinese researchers achieved 51.5dB nonreciprocal isolation in the atomic ensemble, which is the highest isolation ratio in the non-magnetic nonreciprocal field. They discussed the quantum noise problem in nonreciprocal devices for the first time.
The result was published on Nature Communications on April 22, 2021.
Nonreciprocity is an important basic concept in the optical field. The isolators and circulators derived from it are all indispensable components in the optical path. Faraday isolator based on circular birefringence of magneto-optical effect is widely used because of its easy construction, high isolation and low loss.
However, in the integrated optical path, the traditional faraday isolator is subject to various limitations. ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Watching meaningful films - those that we find moving and poignant - can make us feel more prepared to deal with life's challenges and want to be a better person, a new study found.
The findings point to one reason why people may choose to see movies that make them sad as well as happy and that may explore difficult subjects that aren't always uplifting.
Researchers found that when people recalled watching meaningful films like The Shawshank Redemption and Up, they reported a variety of positive reactions, such as being better able to accept the human condition and make sense of problems in life.
Those positive experiences were less likely to be reported when people thought about watching Hollywood fare like The Big Lebowski or Catch Me ...
TAMPA, Fla. (May 10, 2021) -- Blocking the fat-busting enzyme lipoxygenase with a synthetic inhibitor throws the immune system's innate inflammatory response out of whack, compromising cardiac repair during acute heart failure, USF Health researchers found.
Their new preclinical study was published April 13 in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
Acute heart failure - triggered by a heart attack, severely irregular heartbeats, or other causes -- occurs suddenly when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's demands.
Following a heart attack or any cardiac injury, signals to immune cells called leukocytes ...
WASHINGTON - A neurologic pathway by which non-damaging but high frequency brain impact blunts normal brain function and causes long-term problems with learning and memory has been identified. The finding suggests that tailored drug therapy can be designed and developed to reactivate and normalize cognitive function, say neuroscientists at Georgetown University Medical Center.
The investigators, working with collaborators at the National Institutes of Health, had previously found that infrequent mild head impacts did not have an effect on learning and memory, but in their new study, reported May 10 in Nature Communications (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22744-6), the investigators found that when the frequency of these ...
How is it possible to move in the desired direction without a brain or nervous system? Single-celled organisms apparently manage this feat without any problems: for example, they can swim towards food with the help of small flagellar tails.
How these extremely simply built creatures manage to do this was not entirely clear until now. However, a research team at TU Wien (Vienna) has now been able to simulate this process on the computer: They calculated the physical interaction between a very simple model organism and its environment. This environment is a liquid with a non-uniform ...
The morphological compatibility between flowers and insects was given in the famous textbook example of Darwin's orchids and hawkmoths. As in this example, many studies have shown that geographical variations in flower size match the size of insects in each region. In other words, studies have shown "flower-sized regional adaptation" in which large flowers evolve in areas pollinated by large insects and small flowers evolve in areas pollinated by small insects.
However, when examining the genetic similarity between populations, are plants in each region more similar, or are plants with large ...
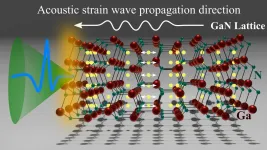
A team of researchers at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University, in collaboration with Bielefeld University and Technical University Braunschweig in Germany, came closer to unraveling the complicated optical response of wide-bandgap semiconductor multiple quantum wells and how atomic-scale lattice vibration can generate free space terahertz emission. Their work provides a significant push towards the application of laser terahertz emission microscopes to nano-seismology of wide-bandgap quantum devices.
Terahertz (THz) waves can be generated by ultrafast processes occurring in a material. By looking at THz emission, researchers have ...