University of Miami researchers report COVID-19 found in penile tissue could contribute to ED
First to demonstrate COVID-19 present in penis tissue long after COVID-19 recovery
2021-05-11
(Press-News.org) University of Miami Miller School of Medicine researchers are the first to demonstrate that COVID-19 can be present in the penis tissue long after men recover from the virus.
The widespread blood vessel dysfunction, or endothelial dysfunction, that results from the COVID-19 infection could then contribute to erectile dysfunction, or ED, according to the study recently published in the World Journal of Men's Health. Endothelial dysfunction is a condition in which the lining of the small blood vessels fails to perform all of its functions normally. As a result, the tissues supplied by those vessels could undergo damage.
"Our research shows that COVID-19 can cause widespread endothelial dysfunction in organ systems beyond the lungs and kidneys. The underlying endothelial dysfunction that happens because of COVID-19 can enter the endothelial cells and affect many organs, including the penis," said study author Ranjith Ramasamy, M.D., associate professor and director of the Miller School's Reproductive Urology Program. "In our pilot study, we found that men who previously did not complain of erectile dysfunction developed pretty severe erectile dysfunction after the onset of COVID-19 infection."
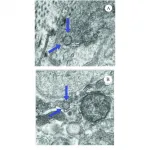
Dr. Ramasamy and colleagues collected penile tissue from two men with a history of COVID-19 infection who underwent penile prosthesis surgery for ED. One of the men was hospitalized for COVID-19, while the other patient only had mild symptoms when he contracted the virus.
The researchers also collected tissue from two additional men with no history of COVID-19 infection undergoing the same surgery for ED. The investigators analyzed all the tissue samples for not only evidence of the virus but also endothelial dysfunction.
They found COVID-19 was present in the penile tissue of both men who had been infected, but not in the men with no history of the virus. The men had been infected six and eight months prior, respectively. These men had evidence of endothelial dysfunction, while the men who had been free of the virus did not.
"This suggests that men who develop COVID-19 infection should be aware that erectile dysfunction could be an adverse effect of the virus, and they should go to a physician if they develop ED symptoms," Dr. Ramasamy said.
The authors hypothesize that similar to other COVID-19 related complications, widespread infection and subsequent endothelial dysfunction could result in ED, and that worsening of ED could be due to the virus's presence in the penile tissue, itself.
In a previously published study, Dr. Ramasamy and Miller School colleagues found that COVID-19 can also invade testis tissue in some men who are infected with the virus, which might be the first step in understanding the virus's potential impact on male fertility and whether COVID-19 can be sexually transmitted.
"These latest findings are yet another reason that we should all do our best to avoid COVID-19," said first author Eliyahu Kresch, a medical student working with Dr. Ramasamy.
"We recommend vaccination and to try to stay safe in general," Kresch said.
INFORMATION:
Miller School coauthors are medical student Justin K. Achua, M.S.; clinical research coordinator Russell Saltzman; clinical research associate Kajal Khodamoradi, Ph.D.; Research Assistant Professor of Urology Himanshu Arora, Ph.D.; Assistant Professor of Urology and Neurological Surgery Emad Ibrahim, M.D., HCLD; Associate Professor of Pathology Oleksandr N. Kryvenko, M.D.; Transmission Electron Microscopy Core Vania Wolff Almeida; Fakiha Firdaus; and Founding Director of the Interdisciplinary Stem Cell Institute Joshua M. Hare, M.D.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-11
Researchers have mapped out the changes in metabolism that occur after a heart attack, publishing their findings today in the open-access eLife journal.
Their study in mice reveals certain genes and metabolic processes that could aid or hinder recovery, and might be good targets for treatments to prevent damage after a heart attack.
"Although some studies have looked at how changes in individual body tissues underlie mechanisms of disease, the crosstalk between different tissues and their dysregulation has not been examined in heart attacks or other cardiovascular-related complications," explains first author Muhammad Arif, a PhD student at KTH Royal ...
2021-05-11
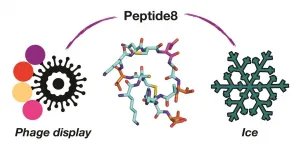
Controlling, and mitigating the effects of ice growth is crucial to protect infrastructure, help preserve frozen cells and to enhance texture of frozen foods. An international collaboration of Warwick Scientists working with researchers from Switzerland have used a phage display platform to discover new, small, peptides which function like larger antifreeze proteins. This presents a route to new, easier to synthesise, cryoprotectants.Caption: Using viruses (phage display) to identify the one molecule in a billion (peptide8) that controls the formation of ice. Credit: University of Warwick
Ice binding proteins, which includes antifreeze proteins, are produced by a large range of species from fish, ...
2021-05-11
An investigational gene therapy can safely restore the immune systems of infants and children who have a rare, life-threatening inherited immunodeficiency disorder, according to research supported in part by the National Institutes of Health. The researchers found that 48 of 50 children who received the gene therapy retained their replenished immune system function two to three years later and did not require additional treatments for their condition, known as severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency, or ADA-SCID. The findings were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
ADA-SCID, ...
2021-05-11
Low doses of a four-drug combination helps prevent the spread of cancer in mice without triggering drug resistance or recurrence, shows a study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest a new approach to preventing cancer metastasis in patients by simultaneously targeting multiple pathways within a metastasis-promoting network. They may also help identify people who would most likely benefit from such treatment.
Metastasis, the spread of cancerous cells through the body, is a common cause of cancer-related deaths. Current approaches to treating metastatic cancer have focused on high doses of individual drugs or drug combinations to hinder pathways that promote the spread of cancer cells. But these approaches can be toxic to the patient, and may inadvertently activate other pathways ...
2021-05-11
A new study from the University of Chicago has found that the photosynthetic bacterium Synechococcus elongatus uses a circadian clock to precisely time DNA replication, and that interrupting this circadian rhythm prevents replication from completing and leaves chromosomes unfinished overnight. The results, published online on May 10 in Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences, have implications for understanding how interrupted circadian rhythms can impact human health.
Circadian rhythms are the internal 24-hour clock possessed by most organisms on earth, regulating ...
2021-05-11
Argonne scientists across several disciplines have combined forces to create a new process for testing and predicting the effects of high temperatures on refractory oxides.
Cast iron melts at around 1,200 degrees Celsius. Stainless steel melts at around 1,520 degrees Celsius. If you want to shape these materials into everyday objects, like the skillet in your kitchen or the surgical tools used by doctors, it stands to reason that you would need to create furnaces and molds out of something that can withstand even these extreme temperatures.
That's where refractory oxides come in. These ceramic materials can stand up to blistering heat and retain their shape, which makes them useful for all kinds of things, from kilns ...
2021-05-11
May 11, 2021 - Like other medical specialties at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, orthopaedic surgery rapidly pivoted from in-person visits to remote appointments via telemedicine. Analysis of that initial experience finds that some groups of patients faced persistent or worsening disparities as the shift to telemedicine occurred, reports Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research® (CORR®), a publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons®. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"We found concerning disparities in access ...
2021-05-11
TAMPA, Fla. - A hallmark of cancer is its ability to evade the immune system. It is why researchers are focused on finding new strategies and targets to jumpstart the immune system so it can mount a response against tumors. One such target is the inhibitory receptor T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM-3), a protein that is overexpressed in many different types of cancer and is associated with poor patient outcomes. It is known to block the activity of immune cells, such as dendritic cells, but how remains unclear. In a new article published in the journal Immunity, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers show that TIM-3 inhibits the STING signaling pathway in dendritic cells, thereby blocking their ability to elicit an immune response.
Dysregulation ...
2021-05-11
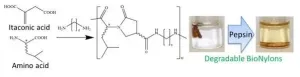
Point:
Novel chiral diacid monomers were synthesized.
Chirally interactive BioNylons were prepared.
BioNylon showed thermal/mechanical performances than conventional Nylons.
BioNylons disintegrated and degraded with pepsin.
Summary:
Marine plastic waste problems have been more serious year by year. One of the worst issues is that creatures in ocean are going extinct by mistakenly swallowing them.. Conventional biodegradable plastics are degradable in digestive enzymes, but their performances are too low to use in society. In this study, researchers from JAIST have used bio-derived resources such as itaconic acid and amino acid for the syntheses of high-performance BioNylons having the pepsin degradation function.
Ishikawa, ...
2021-05-11
Quantum mechanics can be used to create more stable and more easily produced organic solar cells. These are the findings of new research from the University of Gothenburg.
Organic solar cells have many advantages compared with traditional silicon-based solar cells. They can be manufactured cheaply at a large scale using printing presses, and they are light, malleable and flexible. The problem is that today's organic solar cells are not as stable and effective as silicon-based solar cells. In a new study, a research group has taken on this problem and found a way that can lead to more cost-effective solar cell technology.
"There are excellent opportunities for utilising quantum efficiencies to change different chemical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] University of Miami researchers report COVID-19 found in penile tissue could contribute to ED
First to demonstrate COVID-19 present in penis tissue long after COVID-19 recovery