Oregon State researchers discover new class of cancer fighting compounds
2021-05-11
(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. - A team of Oregon State University scientists has discovered a new class of anti-cancer compounds that effectively kill liver and breast cancer cells.
The findings, recently published in the journal Apoptosis, describe the discovery and characterization of compounds, designated as Select Modulators of AhR-regulated Transcription (SMAhRTs).
Edmond Francis O'Donnell III and a team of OSU researchers conducted the research in the laboratory of Siva Kolluri, a professor of cancer research at Oregon State. They also identified the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) as a new molecular target for development of cancer therapeutics.
"Our research identified a therapeutic lead that acts through a new molecular target for treatment of certain cancers," Kolluri said.
O'Donnell added: "This is an exciting development which lays a foundation for a new class of anti-cancer therapeutics acting through the AhR."
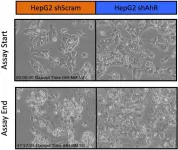
The researchers employed two molecular screening techniques to discover potential SMAhRTs and identified a molecule - known as CGS-15943 - that activates AhR signaling and kills liver and breast cancer cells.
Specifically, they studied cells from human hepatocellular carcinoma, a common type of liver cancer, and cells from triple negative breast cancer, which account for about 15% of breast cancers with the worst prognosis.
"We focused on these two types of cancers because they are difficult to treat and have limited treatment options," said Kolluri, a professor in the Department of Environmental and Molecular Toxicology in the College of Agricultural Sciences. "We were encouraged by the results because they are unrelated cancers and targeting the AhR was effective in inducing death of both of these distinct cancers."
The researchers also identified the AhR-mediated pathways that contribute to the anti-cancer actions of CGS-15943. Developing cancer treatments requires a detailed understanding of how they act to induce anti-cancer effects. The researchers determined that CGS-15943 increases the expression of a protein called Fas Ligand through the AhR and causes cancer cell death.
These results provide exciting new leads for drug development, but human therapies based on these results would not be available to patients for years, the researchers said.
INFORMATION:
An editorial commemorating the 25th anniversary issue of the journal Apoptosis highlighted this discovery and the detailed investigation of cancer cell death promoted by CGS-15943.
In addition to Kolluri and O'Donnell, who recently completed medical school and is an orthopaedic surgery resident at UC Davis Medical Center, other authors of the paper are: Hyo Sang Jang and Nancy Kerkvliet, both from Oregon State; and Daniel Liefwalker, who formerly worked in Kolluri's lab and is now at Oregon Health and Science University. Kolluri is also part of Oregon State's Linus Pauling Institute and The Pacific Northwest Center for Translational Environmental Health Research.
Funding for the research came from the American Cancer Society, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, the U.S. Army Medical Research and Material Command, the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program, Oregon State University and the National Cancer Institute.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-11
Researchers looking to help people suffering from addiction, depression, and pain are studying how certain brain neurons operate to see if they can be controlled.
In a paper published May 11 in Neuron, researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine and Washington University in St. Louis, along with several other universities, successfully used a protein called parapinopsin to turn off brain circuits. This protein is found in lamprey - an ancient lineage of jawless fish similar to eel. Reserachers said the ability to inhibit neurons could eventually lead to turning ...
2021-05-11
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Americans are in chronic pain, and a comprehensive new study exploring trends in this major public health concern reveals that what has been a long-standing and under-acknowledged problem is getting substantially worse.
The findings, published in the latest issue of the journal Demography, suggest blanket increases across multiple measures, with pain rising in every adult age group, in every demographic group, and at every site of pain for which data exists. People today are experiencing more pain than individuals of the same age in earlier decades. In fact, each subsequent birth group is in greater pain than the one that came before it.
"We ...
2021-05-11
BOSTON - It's a real-life plot worthy of a classic spy novel: Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and other Boston-area research centers are turning the tables on glioblastomas, the most devastating and aggressive form of brain cancer, by transforming a type of cell that normally protects tumors and inhibits effective drug therapy into a stone-cold glioblastoma killer.
Glioblastoma, a type of brain tumor, is rapidly fatal: Most patients die within two years of diagnosis despite aggressive therapies such as brain surgery, whole-brain radiation and chemotherapy.
Despite hopes that a class of drugs known as immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs) - drugs that have revolutionized the treatment ...
2021-05-11
DURHAM, N.C. -- With mosquito season upon us, people are stocking up on repellents to prevent itchy bites. Bug repellents are important because they don't just protect against the buzzing, blood-sucking little pests -- they also safeguard against the diseases they carry, which kill some 700,000 people worldwide each year.
Surprisingly, despite widespread use, no one understood exactly how most mosquito repellents keep the insects away. Now researchers are starting to uncover the first pieces of the puzzle.
A new study has identified a scent receptor in mosquitoes that helps them sniff out and avoid trace amounts of pyrethrum, a plant extract used for centuries to repel biting insects.
One ...
2021-05-11
INFORMS Journal Manufacturing & Service Operations Management Study Key Takeaways:
The study looked at archival data on 240 U.S. federal government technology programs across 24 federal agencies.
Researchers found that the practice of moving baseline targets is a key driver in continually increasing budgets for federal government technology programs.
The componentization of a program into smaller work units and increasing the level of competency in program management can dampen this increase, resulting in significant cost savings.
CATONSVILLE, MD, May 11, 2021 ...
2021-05-11
HERSHEY, Pa. -- Over the past year, studies have revealed that certain pre-existing conditions, such as cancer, diabetes and high blood pressure, can increase a person's risk of dying from COVID-19. New research shows that individuals living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) -- an estimated 38 million worldwide, according to the World Health Organization -- have an increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and fatal outcomes from COVID-19.
In a new study, published in Scientific Reports, Penn State College of Medicine researchers found that people living ...
2021-05-11
A newly described horned dinosaur that lived in New Mexico 82 million years ago is one of the earliest known ceratopsid species, a group known as horned or frilled dinosaurs. Researchers reported their find in a publication in the journal PalZ (Paläontologische Zeitschrift).
Menefeeceratops sealeyi adds important information to scientists' understanding of the evolution of ceratopsid dinosaurs, which are characterized by horns and frills, along with beaked faces. In particular, the discovery sheds light on the centrosaurine subfamily of horned dinosaurs, of which Menefeeceratops is believed to be the oldest member. Its remains offer a clearer picture of the group's evolutionary path ...
2021-05-11
Researchers have developed a global earthquake monitoring system that uses the Global Navigational Satellite System (GNSS) to measure crustal deformation.
The monitoring system within seconds can rapidly assess earthquake magnitude and fault slip distribution for earthquakes of magnitude 7.0 and larger, making it a potentially valuable tool in earthquake and tsunami early warning for these damaging events, Central Washington University geophysicist Timothy Melbourne and colleagues report in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America.
GNSS can potentially characterize a large earthquake much more rapidly than the global seismic network, ...
2021-05-11
Covid-19 patients who receive oxygen therapy or experience fever show reduced gray matter volume in the frontal-temporal network of the brain, according to a new study led by researchers at Georgia State University and the Georgia Institute of Technology.
The study found lower gray matter volume in this brain region was associated with a higher level of disability among Covid-19 patients, even six months after hospital discharge.
Gray matter is vital for processing information in the brain and gray matter abnormality may affect how well neurons function and communicate. The study, published in the May 2021 issue of Neurobiology ...
2021-05-11
A new approach to road safety that relies on design and engineering principles--the "Safe System" approach--could lead to dramatic reductions in vehicle-related deaths and injuries if implemented in the U.S., according to a report from a consortium of experts convened by researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Institute of Transportation Engineers.
The Safe System approach engineers road systems so that they are safe when used intuitively, the way people tend to use them. A Safe System minimizes the chances for mistakes by drivers, pedestrians, and bicyclists, and reduces the intensity ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Oregon State researchers discover new class of cancer fighting compounds