Locomotion Vault will help guide innovations in virtual reality locomotion
2021-05-12
(Press-News.org) Experts in virtual reality locomotion have developed a new resource that analyses all the different possibilities of locomotion currently available.
Moving around in a virtual reality world can be very different to walking or employing a vehicle in the real world and new approaches and techniques are continually being developed to meet the challenges of different applications.
Called Locomotion Vault, the project was developed by researchers at the Universities of Birmingham, Copenhagen, and Microsoft Research. It aims to provide a central, freely-available resource to analyse the numerous locomotion techniques currently available.
The aim is to make it easier for developers to make informed decisions about the appropriate technique for their application and researchers to study which methods are best. By cataloguing available techniques in the Locomotion Vault, the project will also give creators and designers a head-start on identifying gaps where future investigation might be necessary. The database is an interactive resource, so it can be expanded through contributions from researchers and practitioners.
Researcher Massimiliano Di Luca, of the University of Birmingham, said: "Locomotion is an essential part of virtual reality environments, but there are many challenges. A fundamental question, for example, is whether there should be a unique 'best' approach, or instead whether the tactics and methods used should be selected according to the application being designed or the idiosyncrasies of the available hardware. Locomotion Vault will help developers with these decisions."
The database also aims to address vital questions of accessibility and inclusivity. Both of these attributes were assessed in relation to each technique included in the Vault.
Co-researcher, Mar Gonzalez-Franco, of Microsoft Research, said: "As new and existing technologies progress and become a more regular part of our lives, new challenges and opportunities around accessibility and inclusivity will present themselves. Virtual reality is a great example. We need to consider how VR can be designed to accommodate the variety of capabilities represented by those who want to use it."
The research team are presenting Locomotion Vault this week at the online Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2021).
"This is an area of constant and rapid innovation," says co-author Hasti Seifi, of the University of Copenhagen. "Locomotion Vault is designed to help researchers tackle the challenges they face right now, but also to help support future discoveries in this exciting field."
INFORMATION:
To use the database or suggest a new locomotion method, visit the Locomotion Vault GitHub repo
Notes to editor:
The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world's top 100 institutions. Its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers, teachers and more than 6,500 international students from over 150 countries.
Di Luca et al. (2021). 'Locomotion Vault: the Extra Mile in Analyzing VR Locomotion Techniques'. CHI.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-12
A study published in the journal Scientific Reports reveals the genetic structure of the land snail Xerocrassa montserratensis and it provides new scientific tools for the improvement of the conservation of this endemic and threatened species in Catalonia. This land mollusc, identified in the late 19th century in the Montserrat mountain, has a reduced geographical distribution limited to the province of Barcelona, and it is a protected species in the area of the natural parks of Montserrat and Sant Llorenç del Munt i l'Obac.
The study is led by the lecturer Marta Pascual, from the Faculty of Biology and the Biodiversity Research Institute of the University of Barcelona ...
2021-05-12
Skeletal muscles make a tremendous variety of actions stabilizing the body in different positions. Despite their endurance during daily activities, they can undergo several mild injuries caused by sport, accidental overstretching, or sudden overtwisting. Luckily mild injuries can be quickly healed; however, when a large part of muscles is damaged or resected surgically, the full recovery can be impossible. Muscle regeneration is challenging, but the development of innovative biocompatible materials tackles that problem. Recently, a multinational team of scientists led by dr. Marco Costantini from ...
2021-05-12
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B Volume 11, Issue 4 Publishes
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/vol/11/issue/4
Special Issue: The Biological Fate of Drug Nanocarriers
This special issue includes seven review and nine research articles from some leading scientists in the field that further the discussion on subtopics of in vivo fate of drug nanocarriers.
Guest Editors: Wei Wu, Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai, China; Tonglei Li, Professor, Department of Industrial & Physical Pharmacy, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA; Ying Zheng, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Institute of Chinese Medical Sciences, University of Macau, Macau, China.
The Journal ...
2021-05-12
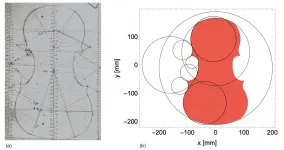
How to predict the sound produced by a tonewood block once carved into the shape of a violin plate? What is the best shape for the best sound? Artificial Intelligence offer answers to these questions.
These are the conclusions that researchers of the Musical Acoustics Lab of Politecnico di Milano presented in a study that was recently published in Scientific Reports.
In the article "A Data-Driven Approach to Violinmaking" the Chilean physicist and luthier Sebastian Gonzalez (post-doc researcher) and the professional mandolin player Davide Salvi (PhD student) show how a simple and effective neural network is able to predict the vibrational be-havior of violin plates. This prediction is obtained from a limited set of geometric and mechanical ...
2021-05-12
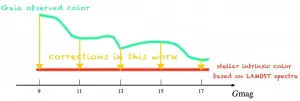
The Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) has helped Gaia achieve millimagnitude (mmag) precision in photometry, according to a study led by researchers from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) and Beijing Normal University (BNU).
Their study was published in The Astrophysical Journal.
If you look at the sky on a clear, starry night, you may notice that Aldebran is relatively red and Rigel is blue. Why? The answer stems from their intrinsic physical properties. Precisely measuring magnitudes ...
2021-05-12
The polar vortex is a large area of upper-atmosphere cyclonic air circulation surrounding both poles. It is bounded by the polar jet stream and its associated cold air is usually confined to the polar regions. Within the Antarctic circle, and southern polar vortex, ozone quantities are the lowest, globally. A research published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, led by Dr. LUO Yuhan, corresponding author and Associate Professor at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), suggests that the polar vortex plays a key role in Antarctic stratospheric ozone depletion.
"The atmosphere over Antarctica is controlled by a strong ...
2021-05-12
May 1, 2021 - Rheumatologists in Hong Kong joined hands to develop a set of consensus statements on COVID-19 vaccination for local adult patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. These timely statements would serve to be a guide for rheumatologists, other specialists, family physicians, specialty nurses, and the public regarding COVID-19 vaccination for patients with rheumatic diseases.
Vaccination against SAR-CoV-2 is a new campaign and a high immunization rate is believed to be the key to end the pandemic. Currently, there are two COVID-19 vaccines available in Hong Kong--the inactivated virus vaccine CoronaVac® ...
2021-05-12
Parks played an important role for people seeking respite from the toll of social isolation during the pandemic, and according to new research from Drexel University, they did so without increasing the spread of COVID-19. The study looked at how people used 22 parks in Philadelphia and New York during the height of the pandemic and it found no strong correlation between park use and the number of confirmed cases in surrounding neighborhoods.
Published in the Journal of Extreme Events, Drexel's study "Urban Park Usage During the COVID-19 Pandemic" surveyed park visitors over a three-month period from May to July 2020 at small and mid-size parks in New York and Philadelphia. And it compared park usage numbers ...
2021-05-12
An essential preliminary to building and construction or resource extraction is studying the geological structure of the site. One of steps of this process is geophysical investigation. This provides a continuous overview of the geological horizons rather than just data on points: boreholes. The standard methods of geophysics help successfully solve this problem in comparatively simple conditions. Yet the classical direct current methods may lead to serious inaccuracy if we have to investigate geologically complex structures with thin layers of sandy and clayey soils.
Among the most popular methods ...
2021-05-12
Leipzig/Jena/Ilmenau. Mobile apps like Flora Incognita that allow automated identification of wild plants cannot only identify plant species, but also uncover large scale ecological patterns. These patterns are surprisingly similar to the ones derived from long-term inventory data of the German flora, even though they have been acquired over much shorter time periods and are influenced by user behaviour. This opens up new perspectives for rapid detection of biodiversity changes. These are the key results of a study led by a team of researchers from Central Germany, which has recently been published in Ecography.
With the help of Artificial Intelligence, plant species ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Locomotion Vault will help guide innovations in virtual reality locomotion