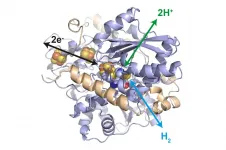
(Press-News.org) An enzyme could make a dream come true for the energy industry: It can efficiently produce hydrogen using electricity and can also generate electricity from hydrogen. The enzyme is protected by embedding it in a polymer. An international research team with significant participation of scientists from Technical University of Munich (TUM) has presented the system in the renowned science journal Nature Catalysis.
Fuel cells turn hydrogen into electricity, while electrolysers use electricity to split water to produce hydrogen. Both need the rare and thus expensive precious metal platinum as a catalyst. Nature has created a different solution: Enzymes, referred to as hydrogenases. They catalyze the conversion of hydrogen very quickly and almost without energy loss.
However, in the past these biocatalysts were not considered suitable for industrial use because of their high sensitivity to oxygen. Now a research team from the Technical University of Munich (TUM), Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB), the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) in Marseille and the Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Energy Conversion has succeeded in embedding the sensitive enzymes in a protective polymer in a way that makes them viable for use in technical hydrogen conversion.
Durability vs. activity
"When the sensitive hydrogenases are embedded in suitable polymers they continue to work for several weeks, even in the presence of oxygen," says Nicolas Plumeré, Professor for Electrobiotechnology at the TUM Campus Straubing for Biotechnology and Sustainability. "Without this protection they lose their activity within a matter of minutes."
Embedding the hydrogenases in polymers whose side chains can transfer electrons, referred to as redox polymers, had nevertheless two decisive disadvantages: a high level of resistance countervailed the flow of electrons through the redox polymer. This required the investment of energy which was then lost in the form of heat. And the embedded hydrogenases completely lost their ability to generate hydrogen.
Fine tuning potential
With a clever selection of the right polymer side chains, the research team has now succeeded in setting the redox potential of the polymer in such a way that only a small overvoltage is necessary to overcome the resistance.
More detailed investigations then revealed that the potential of the side chains had shifted slightly to positive values due to the embedding in the polymer matrix. In a further attempt they used a side chain with a corresponding negative potential. This trick was the breakthrough: The hydrogenase was now capable of catalyzing the reaction in both directions without energy loss.
Biocatalyst for hydrogen conversion
Utilizing this system the research team then built a fuel cell, in which oxygen is reduced by the enzyme bilirubin oxidase from the bacterium Myrothecium verrucaria, while the hydrogenase embedded in the polymer film oxidizes the hydrogen from the bacterium desulfovibrio desulfuricans, generating electricity in the process.
The cell achieved a value, with an open circuit voltage of 1.16 V, the highest ever measured for a system of this type and close to the thermodynamic maximum. With three milliamperes per square centimeter the cell achieved a very high power density for biological cells at the same time.
The system can also be used for the reverse reaction, producing hydrogen by consuming electrons: The energy conversion efficiency is close to 100 percent, even with power densities of over four milliamperes per square centimeter.
Blueprint for new biocatalysts
"The reduction in energy loss has two decisive advantages," says Nicolas Plumeré. "First, it makes the system significantly more efficient; second, the heat generated in a fuel cell stack at high performance levels would pose a problem for biological systems."
In order to make their system competitive with systems that use platinum-based catalysts, the team's ongoing research is now focused on improving the stability of the hydrogenases at higher power densities.
Furthermore, the findings can also be transferred to other highly-active but sensitive catalysts for energy conversion and electrosynthesis. Direct objectives here are primarily carbon dioxide-reducing enzymes that can use electricity to produce liquid fuels or intermediate products from carbon dioxide.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by a Starting Grant from the European Research Council (ERC), by the French Center National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) and the Aix Marseille Université, the German Research Foundation (DFG) joint funding with the Agence Nationale de la Recherche, the DFG priority program "Iron - Sulfur for Life" (SPP 1927), the Max Planck Society and in the case of the RESOLV cluster of excellence by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under the Excellence Strategy of the Federal Government and the German Federal States.
Publication:
Reversible H2 oxidation and evolution by hydrogenase embedded in a redox polymer film
Steffen Hardt, Stefanie Stapf, Dawit T. Filmon, James A. Birrell, Olaf Rüdiger, Vincent Fourmond, Christophe Léger & Nicolas Plumeré
Nature Catalysis Vol. 4, 251-258 (2021) - DOI: 10.1038/s41929-021-00586-1
Experts in virtual reality locomotion have developed a new resource that analyses all the different possibilities of locomotion currently available.
Moving around in a virtual reality world can be very different to walking or employing a vehicle in the real world and new approaches and techniques are continually being developed to meet the challenges of different applications.
Called Locomotion Vault, the project was developed by researchers at the Universities of Birmingham, Copenhagen, and Microsoft Research. It aims to provide a central, freely-available ...
A study published in the journal Scientific Reports reveals the genetic structure of the land snail Xerocrassa montserratensis and it provides new scientific tools for the improvement of the conservation of this endemic and threatened species in Catalonia. This land mollusc, identified in the late 19th century in the Montserrat mountain, has a reduced geographical distribution limited to the province of Barcelona, and it is a protected species in the area of the natural parks of Montserrat and Sant Llorenç del Munt i l'Obac.
The study is led by the lecturer Marta Pascual, from the Faculty of Biology and the Biodiversity Research Institute of the University of Barcelona ...
Skeletal muscles make a tremendous variety of actions stabilizing the body in different positions. Despite their endurance during daily activities, they can undergo several mild injuries caused by sport, accidental overstretching, or sudden overtwisting. Luckily mild injuries can be quickly healed; however, when a large part of muscles is damaged or resected surgically, the full recovery can be impossible. Muscle regeneration is challenging, but the development of innovative biocompatible materials tackles that problem. Recently, a multinational team of scientists led by dr. Marco Costantini from ...
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B Volume 11, Issue 4 Publishes
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/vol/11/issue/4
Special Issue: The Biological Fate of Drug Nanocarriers
This special issue includes seven review and nine research articles from some leading scientists in the field that further the discussion on subtopics of in vivo fate of drug nanocarriers.
Guest Editors: Wei Wu, Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai, China; Tonglei Li, Professor, Department of Industrial & Physical Pharmacy, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA; Ying Zheng, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Institute of Chinese Medical Sciences, University of Macau, Macau, China.
The Journal ...
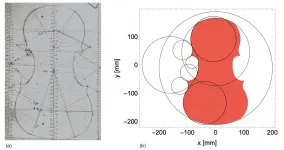
How to predict the sound produced by a tonewood block once carved into the shape of a violin plate? What is the best shape for the best sound? Artificial Intelligence offer answers to these questions.
These are the conclusions that researchers of the Musical Acoustics Lab of Politecnico di Milano presented in a study that was recently published in Scientific Reports.
In the article "A Data-Driven Approach to Violinmaking" the Chilean physicist and luthier Sebastian Gonzalez (post-doc researcher) and the professional mandolin player Davide Salvi (PhD student) show how a simple and effective neural network is able to predict the vibrational be-havior of violin plates. This prediction is obtained from a limited set of geometric and mechanical ...
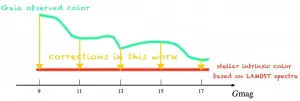
The Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) has helped Gaia achieve millimagnitude (mmag) precision in photometry, according to a study led by researchers from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) and Beijing Normal University (BNU).
Their study was published in The Astrophysical Journal.
If you look at the sky on a clear, starry night, you may notice that Aldebran is relatively red and Rigel is blue. Why? The answer stems from their intrinsic physical properties. Precisely measuring magnitudes ...
The polar vortex is a large area of upper-atmosphere cyclonic air circulation surrounding both poles. It is bounded by the polar jet stream and its associated cold air is usually confined to the polar regions. Within the Antarctic circle, and southern polar vortex, ozone quantities are the lowest, globally. A research published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, led by Dr. LUO Yuhan, corresponding author and Associate Professor at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), suggests that the polar vortex plays a key role in Antarctic stratospheric ozone depletion.
"The atmosphere over Antarctica is controlled by a strong ...
May 1, 2021 - Rheumatologists in Hong Kong joined hands to develop a set of consensus statements on COVID-19 vaccination for local adult patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. These timely statements would serve to be a guide for rheumatologists, other specialists, family physicians, specialty nurses, and the public regarding COVID-19 vaccination for patients with rheumatic diseases.
Vaccination against SAR-CoV-2 is a new campaign and a high immunization rate is believed to be the key to end the pandemic. Currently, there are two COVID-19 vaccines available in Hong Kong--the inactivated virus vaccine CoronaVac® ...
Parks played an important role for people seeking respite from the toll of social isolation during the pandemic, and according to new research from Drexel University, they did so without increasing the spread of COVID-19. The study looked at how people used 22 parks in Philadelphia and New York during the height of the pandemic and it found no strong correlation between park use and the number of confirmed cases in surrounding neighborhoods.
Published in the Journal of Extreme Events, Drexel's study "Urban Park Usage During the COVID-19 Pandemic" surveyed park visitors over a three-month period from May to July 2020 at small and mid-size parks in New York and Philadelphia. And it compared park usage numbers ...
An essential preliminary to building and construction or resource extraction is studying the geological structure of the site. One of steps of this process is geophysical investigation. This provides a continuous overview of the geological horizons rather than just data on points: boreholes. The standard methods of geophysics help successfully solve this problem in comparatively simple conditions. Yet the classical direct current methods may lead to serious inaccuracy if we have to investigate geologically complex structures with thin layers of sandy and clayey soils.
Among the most popular methods ...