(Press-News.org) Meat that is certified organic by the U.S. Department of Agriculture is less likely to be contaminated with bacteria that can sicken people, including dangerous, multidrug-resistant organisms, compared to conventionally produced meat, according to a study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The findings highlight the risk for consumers to contract foodborne illness--contaminated animal products and produce sicken tens of millions of people in the U.S. each year--and the prevalence of multidrug-resistant organisms that, when they lead to illness, can complicate treatment.
The researchers found that, compared to conventionally processed meats, organic-certified meats were 56 percent less likely to be contaminated with multidrug-resistant bacteria. The study was based on nationwide testing of meats from 2012 to 2017 as part of the U.S. National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS).
In order for meat to be certified organic by the USDA, animals can never have been administered antibiotics or hormones, and animal feed and forage such as grass and hay must be 100 percent organic. A longstanding concern about antibiotic use in livestock and livestock feed is the increased prevalence of antibiotic-resistant pathogens. To monitor this trend, in 1996 the federal government developed NARMS to track antibiotic resistance in bacteria isolated from retail meats, farmed animals, and patients with foodborne illness in the U.S.
For their study, the Bloomberg School research team analyzed U.S. Food and Drug Administration-NARMS data from randomly sampled chicken breast, ground beef, ground turkey, and pork for any contamination and for contamination by multidrug-resistant organisms. The analysis covers four types of bacteria: Salmonella, Campylobacter, Enterococcus, and Escherichia coli.
The study covered a total of 39,348 meat samples, of which 1,422 were found to be contaminated with at least one multidrug-resistant organism. The rate of contamination was 4 percent in the conventionally produced meat samples and just under 1 percent in those that were produced organically.
The study was published May 12 in Environmental Health Perspectives.
"The presence of pathogenic bacteria is worrisome in and of itself, considering the possible increased risk of contracting foodborne illness," says senior author Meghan Davis, DVM, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Environmental Health and Engineering at the Bloomberg School. "If infections turn out to be multidrug resistant, they can be more deadly and more costly to treat."
The analysis also suggested that the type of processing facility may influence the likelihood of meat contamination. Meat processors fall into three categories: exclusively organic, exclusively conventional, or those that handle both organic and conventional meats--so-called "split" processors. The study found that among conventional meats, those processed at facilities that exclusively handled conventional meats were contaminated with bacteria one-third of the time, while those handled at facilities that processed both conventional and organic meats were contaminated one-quarter of the time. The prevalence of multidrug-resistant bacteria was roughly the same in these two meat processor categories.
"The required disinfection of equipment between processing batches of organic and conventional meats may explain our findings of reduced bacterial contamination on products from facilities that process both types of meats," says Davis.
The authors believe their findings have relevance for regulatory agencies and consumers. "How we raise animals matters," says Davis. "As a veterinarian, I recognize that we sometimes need to use antibiotics to treat sick animals, but taking advantage of opportunities to reduce antibiotics use could benefit everyone. Consumer choice and regulatory oversight are two strategies to do this."
INFORMATION:
First author Gabriel Innes, VMD, PhD, led the study while completing his PhD at the Bloomberg School, where he was a Center for a Livable Future-Lerner Fellow.
"Contamination of Retail Meat Samples with Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Relation to Organic and Conventional Production and Processing: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Data from the United States National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System, 2012-2017" was co-authored by Gabriel Innes, Keeve Nachman, Alison Abraham, Joan Casey, Andrew Patton, Lance Price, Sara Tartof and Meghan Davis.
Support for the research was provided by the National Institutes of Health (1R01AI130066-01A1, K01OD019918), the Johns Hopkins Center for a Livable Future, and the Johns Hopkins Berman Institute for Bioethics.
Loss of smell, or anosmia, is one of the earliest and most commonly reported symptoms of COVID-19. But the mechanisms involved had yet to be clarified. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur, the CNRS, Inserm, Université de Paris and the Paris Public Hospital Network (AP-HP) determined the mechanisms involved in the loss of smell in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 at different stages of the disease. They discovered that SARS-CoV-2 infects sensory neurons and causes persistent epithelial and olfactory nervous system inflammation. Furthermore, ...
Many people live with chronic pain, and in some cases, cannabis can provide relief. But the drug also can significantly impact memory and other cognitive functions. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Medicinal Chemistry have developed a peptide that, in mice, allowed Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main component of Cannabis sativa, to fight pain without the side effects.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 20% of adults in the U.S. experienced chronic pain in 2019. Opioids, the mainstay for ...
Alexandria, Va., USA -- COVID-19 was declared a global pandemic in March 2020 and given an incomplete understanding of the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 at that time, the American Dental Association recommended that dental offices refrain from providing non-emergency services. As a result, 198,000 dentists in the United States closed their doors to patients. The study "Sources of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Microorganisms in Dental Aerosols," published in the Journal of Dental Research (JDR), sought to inform infection-control science by identifying the source of bacteria and viruses in aerosol generating dental procedures.
Researchers at The Ohio State University College of Dentistry, Division of Periodontology, Columbus, USA, tracked the origins of microbiota in aerosols generated during treatment ...
Are you empathic, generous and altruistic? In short, do you possess that specific personality trait defined as agreeableness in the language of psychologists? New research from SISSA recently published in the journal NeuroImage sheds light on brain mechanisms underlying this trait.
The study showed that detached and individualistic subjects seem to process information associated with social and non-social contexts in similar ways, as demonstrated by similar activation patterns in the prefrontal cortex, whereas in more agreeable subjects the activation patterns ...
Peri-implantitis, a condition where tissue and bone around dental implants becomes infected, besets roughly one-quarter of dental implant patients, and currently there's no reliable way to assess how patients will respond to treatment of this condition.
To that end, a team led by the University of Michigan School of Dentistry developed a machine learning algorithm, a form of artificial intelligence, to assess an individual patient's risk of regenerative outcomes after surgical treatments of peri-implantitis.
The algorithm is called FARDEEP, which stands for Fast and Robust Deconvolution of Expression ...
When Museums closed their doors in March 2020 for the first COVID-19 lockdown in the UK a majority moved their activities online to keep their audiences interested. Researchers from WMG, University of Warwick have worked with OUMNH, to analyse the success of the exhibitions, and say the way Museums operate will change forever.Caption: Compton Verney's homepage for the Cranach exhibition which opened in March 2020 Credit: Compton Verney
The cultural impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has been analysed by researchers from WMG, University of Warwick in collaboration with OUMNH (Oxford University Museum of Natural History) who in the paper, 'Digital Responses ...
An international research team led by the University of Cologne has succeeded for the first time in connecting several atomically precise nanoribbons made of graphene, a modification of carbon, to form complex structures. The scientists have synthesized and spectroscopically characterized nanoribbon heterojunctions. They then were able to integrate the heterojunctions into an electronic component. In this way, they have created a novel sensor that is highly sensitive to atoms and molecules. The results of their research have been published under the title 'Tunneling current modulation in atomically precise graphene nanoribbon heterojunctions' in Nature Communications. The work was carried out in close cooperation between the Institute for ...
BOSTON - (May 12, 2021) - Scientists are rapidly gathering evidence that variants of gut microbiomes, the collections of bacteria and other microbes in our digestive systems, may play harmful roles in diabetes and other diseases. Now Joslin Diabetes Center scientists have found dramatic differences between gut microbiomes from ancient North American peoples and modern microbiomes, offering new evidence on how these microbes may evolve with different diets.
The scientists analyzed microbial DNA found in indigenous human paleofeces (desiccated excrement) from unusually dry caves in Utah and northern Mexico with extremely ...
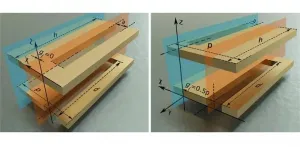
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are highly localized surface waves on the interface between metal and dielectric in the optical frequency band. SSPs do not naturally exist in the microwave and terahertz frequencies, so "spoof" surface plasmon polaritons (SSPPs) are necessary for operations in those lower frequency bands.
Like optical SPPs, microwave SSPPs exhibit highly localized electromagnetic fields, subwavelength resolution, and extraordinary field confinement. Therefore, SSPP transmission lines (TLs) have been proposed as novel types of microwaveguides that offer new solutions for miniaturization, ...
BOSTON - During the development and progression of Alzheimer's disease, a protein called tau accumulates and spreads in the brain. Understanding the mechanisms behind tau spread--and its consequences--may point to new prevention and treatment strategies for Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia. New insights now come from research that was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and involves an anesthetic known to affect cognitive function. The findings are published in Communications Biology.
The scientists note that inflammation plays an important role in Alzheimer's disease, and microglia--immune cells that reside in the brain--are thought to be involved in this process by producing an ...