Ion-selective smart porous membranes
2021-05-13
(Press-News.org) A research group has developed an ion-selective smart porous membrane that can respond to outer stimuli, potentially paving the way for new applications in molecular separation and sensing applications.
Porous thin films have attracted the attention of scientists because of their potential use in sensors, energy harvesting, and ion/molecular separation.
Nanostructure properties, such as pore size, thickness, and film density, affect molecular selectivity and molecular permeability. Surface properties also have a significant impact on molecular selectivity.
Thus it is important to be able to control both the 3D nanostructures and surface properties of ultrathin porous films.
Previous research shed light on smart porous membranes, which are covered with molecules that can respond to external stimuli such as light, temperature, and pH. Yet their application to porous thin-films with an extremely thin film thickness of below 10 nm has proved immensely challenging for scientists.
"In our study, we succeeded in developing responsive porous SiO2 thin films with an extremely thin film thickness of 8 nm with a uniformly covered surface in a pH-responsive silane coupling agent," said Yuya Ishizaki from the Graduate School of Engineering at Tohoku University and co-author of the study. "The responsive porous thin film can adjust the surface charge depending on the pH change in the solution, resulting in selective ion permeation."
To prepare the porous films with a controlled structure to nm-scale accuracy, the research group focused on polymer thin films containing silsesquioxanes, which have unique cage structures.
The polymer films were fabricated using the Langmuir-Blodgett technique, chosen because it provides molecular-scale controllability in the film thickness. Langmuir-Blodgett polymer nanosheets also make it possible to fabricate porous SiO2 thin films with controlled nanostructures by simple UV-right irradiation under ambient conditions.
"We plan to develop highly efficient separation membranes and sensing materials that take advantage of the extremely thin film thickness and controlled surface properties in the future," added Ishizaki.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-13
Eating a diet rich in fruit and vegetables is associated with less stress, according to new research from Edith Cowan University (ECU).
The study examined the link between fruit and vegetable intake and stress levels of more than 8,600 Australians aged between 25 and 91 participating in the Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle (AusDiab) Study from Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute.
The findings revealed people who ate at least 470 grams of fruit and vegetables daily had 10 per cent lower stress levels than those who consumed less than 230 grams. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends ...
2021-05-13
Arizona! The sunsets. The saguaros. The snakes.
All of them are part of life in the sunny Southwest, but keeping cool when the latter is holed up in a golf bag, air compressor or swimming pool pump house is a big ask for a lot of people.
Not as big as you'd think, however.
The first study to analyze snake removals in a social-ecological context was recently published by an Arizona State University conservation biologist working with a local rattlesnake removal company.
"I think one of the surprises was that people don't hate snakes," said researcher Heather Bateman of the College of Integrative Sciences and Arts. "A lot of them responded that the snakes are important to the desert ecosystem and the snake belongs ...
2021-05-13
Optical imaging systems have been playing an essential role in scientific discovery and societal progress for several centuries. For more than 150 years scientists and engineers have used aberration theory to describe and quantify the deviation of light rays from ideal focusing in an imaging system. Until recently most of these imaging systems included spherical and aspherical refractive lenses or reflective mirrors or a combination of both. With the introduction of new ultra-precision manufacturing methods, it has become possible to fabricate lenses and mirrors that lack the common translational or ...
2021-05-13
The relevance for radiology applications is probably the most known advantage of X-ray beams (keV energies) with respect to visible radiation (eV energies) and can be traced back to their superior penetration depth. On a more fundamental ground, however, the relevance of this photon energy range relies on the capability of probing inner shell electrons (as they have comparable binding energies) and mapping molecular structures on the atomic-scale (as typical interatomic spacings are comparable to X-ray wavelengths). Building on such capabilities, large efforts have been devoted by the scientific community to develop X-ray sub-picosecond sources able to access matter properties with a time resolution sufficient to access elemental molecular motions. Free electron lasers (FEL), nowadays available ...
2021-05-13
UNSW medical researchers have found a way to starve pancreatic cancer cells and 'disable' the cells that block treatment from working effectively. Their findings in mice and human lab models - which have been 10 years in the making and are about to be put to the test in a human clinical trial - are published today in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Pancreatic cancer has seen minimal improvement in survival for the last four decades - and without immediate action, it is predicted to be the world's second biggest ...
2021-05-13
The Indian public blamed foreigners, minority groups and doctors for the rapid spread of COVID-19 across the country during the first wave, due to misinformation, rumour and long-held discriminatory beliefs, according to an international study led by Monash University.
This resulted in people refusing to get tested for fear of humiliation or public reprisals, which included attacks on Muslims and health care workers.
However, when presented with accurate and reliable information about the virus spread, the Indian public back-pedalled on those negative sentiments and were more likely to get tested and seek medical help, highlighting the importance of health advice from credible sources.
A ...
2021-05-13
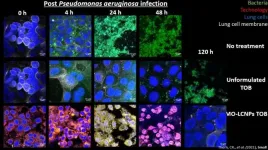
World-first nanotechnology developed by the University of South Australia could change the lives of thousands of people living with cystic fibrosis (CF) as groundbreaking research shows it can improve the effectiveness of the CF antibiotic Tobramycin, increasing its efficacy by up to 100,000-fold.
The new technology uses a biomimetic nanostructured material to augment Tobramycin - the antibiotic prescribed to treat chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections in severe cases of CF - eradicating the infection in as little as two doses.
In Australia, cystic fibrosis (CF) affects one in 2500 babies - or one baby born every four days - causing severe impairments to a person's ...
2021-05-13
Cancer death rates have fallen dramatically in the United States, but factor in obesity, as researchers did at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, and the picture changes.
In a study published May 10 in JAMA Network Open, researchers showed that obesity-related cancer deaths are improving, but at a slowing pace.
Based on mortality data for 50 million people, deaths from cancers not associated with obesity -- that's lung cancer and skin cancer, among others - are declining at a rate almost three times faster than cancers linked to obesity, such as stomach, colorectal, uterine, thyroid and postmenopausal breast cancer.
"These are cancers where we could see even larger mortality improvements with creative and practical tools to combat ...
2021-05-13
Compared with the superresolution microscopy that bases on squeezing the point spread function in the spatial domain, the superresolution microscopy that broadens the detection range in the spatial frequency domain through the spatial-frequency-shift (SFS) effect shows intriguing advantages including large field of view, high speed, and good modularity, owing to its wide-field picture acquisition process and universal implementation without using special fluorophores labeling.
To enable spatial-frequency-shift microscopy with a superresolution at the subwavelength scale, it is essential to use the near-field evanescent wave with a larger wave vector than the far-field propagation wave for illumination, which can be built on the integrated photonics, paving the way for compact ...
2021-05-13
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), collaborating with scientists from the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) and RIKEN, develop a novel technique for live-cell fluorescent imaging which leads them to discover a new actin structure in starfish early embryos.
Tokyo, Japan - Monitoring alignments of the building blocks of cells is important to understand how the cells are built. By collaborating with imaging scientists at the MBL, researchers from Japan have developed a new probe which they call POLArIS, allowing real-time imaging of molecular orientations in live cells.
A fluorophore emits polarized light as it glows. The orientation of polarized fluorescence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ion-selective smart porous membranes