Current trend reversed
Physicists at ETH Zurich demonstrate that a tiny cloud of atoms can be turned from a heat engine into a cooler by cranking up the interactions between the particles
2021-05-13
(Press-News.org) When a piece of conducting material is heated up at one of its ends, a voltage difference can build up across the sample, which in turn can be converted into a current. This is the so-called Seebeck effect, the cornerstone of thermoelectric effects. In particular, the effect provides a route to creating work out of a temperature difference. Such thermoelectric engines do not have any movable part and are therefore convenient power sources in various applications, including propelling NASA's Mars rover Perseverance. The Seebeck effect is interesting for fundamental physics, too, as the magnitude and sign of the induced thermoelectric current is characteristic of the material and indicates how entropy and charge currents are coupled. Writing in Physical Review X, the group of Prof. Tilman Esslinger at the Department of Physics of ETH Zurich now reports on the controlled reversal of such a current by changing the interaction strength among the constituents of a quantum simulator made of extremely cold atoms trapped in shaped laser fields. The capability to induce such a reversal means that the system can be turned from a thermoelectric engine into a cooler.
Which way please?
The experiment, conducted by doctoral researcher Samuel Häusler and co-workers in the Esslinger group, starts with a cloud of fermionic Lithium atoms that are cooled to temperatures low enough that quantum effects determine the behaviour of the ensemble. The cloud is then separated into two independent halves of equal atom number. One of them is heated, before the two reservoirs are connected by a two-dimensional channel. The equilibrium state that thus develops is as expected: after a sufficiently long time, the two halves contain equal atom numbers at equal temperatures. More interesting is the transient behaviour. During the equilibration process, the atom number in each reservoir changes, with the atoms ebbing and flowing between them. In which direction and with what amplitude this happens depends on the thermoelectric properties of the system.
Thanks to the exquisite control over the system, the researchers were able to measure the transient behaviours for different interaction strengths and atomic densities inside the channel and compared them to a simple model. In contrast to solid-state systems, where most thermoelectric properties can be measured in simple, well-defined experiments, in these small clouds of atoms the parameters are inferred from fundamental quantities such as the atom density. Finding a procedure that properly extracts the thermoelectric quantities over a wide range of parameters was a key point of the work.
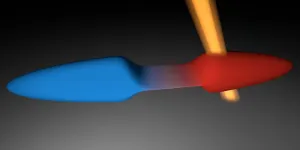
The team found that the current direction results from a competition between two effects (see the figure). On the one hand (left), the thermodynamic properties of the reservoirs favour the increase of atom number in the hot reservoir, to equilibrate the chemical potentials of the two halves. On the other hand (right), the properties of the channel typically make the transport of hot, energetic particles easier -- because they have a large number of possible pathways (or, modes) available to them -- leading to an increase of the atom number in the cold reservoir.
A superfluid traffic regulator
With a non-interacting gas, it is possible to compute the dominating trend between the two competing effects once the precise shape of the atom cloud is known and taken into account. In the system of Häusler et al. this can be done very accurately. Both in the computation and in the measurements, the initial atom current flows from the hot to the cold reservoir and is stronger for low atomic densities in the channel. When the interactions are tuned up to the so-called unitary regime, the behaviour of the system becomes considerably more difficult to predict. The computation becomes intractable without wide-ranging approximations, due to the strong correlations that build up in the gas.
In this regime, the quantum simulation device of the ETH researchers showed that for high-enough mean temperature and low atom density in the channel, the current also flows from the hot to the cold reservoir. However, it can be reversed when the channel density is increased using an attractive gate potential. Above a certain density threshold, the atoms in the channel undergo a phase transition where they form pairs showing superfluid behaviour. This superfluid region in the channel limits the transport of unpaired, energetic particles, favouring the transport from the cold to the hot reservoir and hence the reversal of the thermoelectric current.
Towards better thermoelectric materials thanks to interactions
Understanding the properties of matter through thermoelectric measurement improves the fundamental understanding of interacting quantum systems. Equally important is to identify new ways to design well-performing thermoelectric materials that could efficiently transform small heat differences into work or, if used in reverse mode, act as a cooling device (known as a Peltier cooler).
The efficiency of a thermoelectric material is characterized by the thermoelectric figure of merit. Häusler et al. have measured a strong enhancement of the value of this figure when cranking up the interactions. While this enhancement cannot be directly translated into material science, this excellent cooling capability could already be used to reach lower temperatures for atomic gases, which in turn might enable a broad range of novel fundamental experiments in quantum science.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-13
A small drug molecule that appears to protect normal tissue from the damaging effects of radiation, may simultaneously be able to boost the cancer-killing effect of radiation therapy, according to a new study led by scientists at University of Iowa, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, and Galera Therapeutics, Inc.
The study, published online May 12 in Science Translational Medicine, suggests that the drug's dual effect is based on a fundamental difference between the ability of cancer cells and healthy cells to withstand the damaging effects of a highly reactive molecule called hydrogen peroxide, which is produced during the dismutation of superoxide.
The drug, known as Avasopasem manganese, is made by Galera Therapeutics. ...
2021-05-13
The stock market is a staple of business news, but it is unclear how meaningful stock prices are to the larger economy. Do changes in stock prices directly affect shorter-term consumption, or are they just leading indicators for subsequent economic activity? The U.S. Federal Reserve, for its part, usually seems to act as if stock-based wealth does help drive spending and employment. But is this correct?
A new study co-authored by an MIT economist brings data to the discussion and finds that increased stock market wealth has moderate but clear economic effects. After looking at the U.S. on a county-by-county basis, the study finds that after large market ...
2021-05-13
Sydney, Australia; New York City, USA (May 13, 2021)--In a collaborative report published today in Cell, scientists from Sydney and New York describe the critical worldwide need to improve the diversity of cells used in medical research. Currently, 95% of all human cell lines used in research are of European descent. The authors provide actionable steps that researchers and the biomedical community can take to promote more inclusivity in preclinical and basic science research.
The commentary, "Ancestry Matters: Building inclusivity into preclinical study design," is co-authored by Sophie Zaaijer, PhD, who co-founded FIND Genomics (findgen.bio), a company that aims to improve reproducible ...
2021-05-13
The once-abundant California condor briefly went extinct in the wild, with only 22 individuals living in captivity by 1982. Today, 300 condors live freely in the wild and another 200 are in captivity. But, despite the condor's struggles, a new study of the California condor genome reported in the journal Current Biology on May 13 has found a surprising amount of genetic diversity.
The study is the first to begin quantifying diversity across the entire California condor genome, which offers researchers needed baseline information to inform future research and conservation of this iconic species, ...
2021-05-13
New York, NY (May 13, 2021)-- Artificial food colorants can cause disease when the immune system has become dysregulated, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai researchers report. The study, published in Cell Metabolism in May, was the first to show this phenomenon.
The study, conducted in mice, found that the mice developed colitis when they consumed food with the artificial food colorants FD&C Red 40 and Yellow 6 when a specific component of their immune system, known as cytokine IL-23, was dysregulated. While it remains unclear whether food colorants have similar effects in humans, researchers plan to investigate exactly how cytokine IL-23 promotes the development of colitis after food colorant exposure.
Colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and cytokine ...
2021-05-13
Fossilised footprint tracks, recently discovered within the Hanna Formation in Wyoming, USA, which have been dated to 58 million years ago, may represent the earliest evidence of mammals gathering by the sea, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The findings suggest that mammals may have first used marine habitats at least 9.4 million years earlier than previously thought, in the late Paleocene (66-56 million years ago), rather than the Eocene (56-33.9 million years ago).
Drs. Anton Wroblewski and Bonnie Gulas-Wroblewski examined and photographed over 1,000 metres of fossilised footprints in an area dated back to 58 million years ago by plant and pollen fossils. The authors identified various different tracks. One set showed relatively large, five-toed ...
2021-05-13
Climate change may be accelerating the degradation of ancient rock paintings in Indonesia, including the oldest known hand stencil in the world which dates back to 39,900 years ago, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Rock paintings made using red and mulberry-coloured pigments in the limestone caves and rock shelters of Maros-Pangkep, Indonesia have been dated to between 20,000 and 45,000 years old. Anecdotal evidence suggests that the paintings have been deteriorating at an accelerated rate in recent decades, but the reasons for this have been unclear.
Jillian Huntley and colleagues investigated the potential causes of accelerated rock art degradation at 11 cave art sites in Maros-Pangkep, by analysing ...
2021-05-13
Radical changes to the food system are needed to safeguard our food supply and combat malnutrition in the face of climate change, environmental degradation and epidemics, says new report.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge say our future global food supply cannot be safeguarded by traditional approaches to improving food production. They suggest state-of-the-art, controlled-environment systems, producing novel foods, should be integrated into the food system to reduce vulnerability to environmental changes, pests and diseases. Their report is published today in the journal Nature Food.
The researchers say that global malnutrition could be eradicated by farming foods including spirulina, chlorella, larvae of insects such as the house fly, mycoprotein (protein derived ...
2021-05-13
A new study with zebrafish shows that a deadly form of skin cancer -- melanoma -- alters the metabolism of healthy tissues elsewhere in the body. The research from Washington University in St. Louis suggests that these other tissues could potentially be targeted to help treat cancer.
"Tumors rely on a constant supply of nutrients to grow. Instead of competing with tumors for nutrients, other tissues can reprogram their metabolism to be complementary. In some instances, this may even allow healthy tissues to feed the tumor," said Gary Patti, the Michael and Tana Powell Professor of Chemistry in Arts & Sciences at Washington University and a professor of chemistry and medicine at the School of Medicine.
Patti is the corresponding author of the study published May 13 in Cell Metabolism.
Cancer ...
2021-05-13
Scientists exploring the drivers of Antarctic climate change have discovered a new and more efficient pathway for the creation of natural aerosols and clouds which contribute significantly to temperature increases.
The Antarctic Peninsula has shown some of the largest global increases in near-surface air temperature over the last 50 years, but experts have struggled to predict temperatures because little was known about how natural aerosols and clouds affect the amount of sunlight absorbed by the Earth and energy radiated back into space.
Studying data from seas around the Peninsula, experts have discovered that most new particles are formed in air masses arriving from the partially ice-covered Weddell Sea - a significant source ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Current trend reversed
Physicists at ETH Zurich demonstrate that a tiny cloud of atoms can be turned from a heat engine into a cooler by cranking up the interactions between the particles



