(Press-News.org) Input one, output one; input two, output two; input three; output purple --what kind of system is this? Computer algorithms can exist as non-deterministic systems, in which there are multiple possible outcomes for each input. Even if one output is more likely than another, it doesn't necessarily eliminate the possibility of putting in three and getting purple instead of three. Now, a research team from Iowa State University has developed a way to control such systems with more predictability. The results were published in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica.
"The supervisory control problem for discrete event systems under control involves identifying the supervisor, if one exists," said paper author Ratnesh Kumar, Harpole Professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Iowa State University, USA. "If there is a supervisor, if it's synchronously composed with the system, it results in a system that conforms to the control specification."
A discrete event system behaves based on its current state. If the state changes, the value changes. In the example system above, something about the system's state changed to make it take four and produce purple. Kumar's approach examines the system as it currently exists and finding the least fixed-point operator, or the piece that is most easily changed. The act of identifying such a component can result in a new model that acts as the supervisor of the system.
The researchers used quotienting to determine the possible outcomes and build parameters to identify possible controllers. In simple terms, a quotient is the known number of possibilities: Divide 10 by three. The quotient is three, with fractional possibilities. In Kumar's system, each event is referred to as a "plant" and the entire system is understood as a "warehouse." The quotient is the plant divided by a specification determined by the warehouse, resulting in multiple possible answers, depending on what the system looks like in the moment.
"Given a plant and the specification of the controlled plant, the quotienting operation generates a new specification describing the obligation on the supervisor such that the plant, when controlled by a supervisor, satisfies the specification," Kumar said.
Say the plant is the input of three, and the controller is purple. The calculus involved in describing the operation produces a new parameter of purple. The controller, or supervisor, is obligated to take the input of three and output purple. If the supervisor does not exist, the quotienting process still results in a supervisory control operation.
"The central tenant of our technique is to develop a quotienting-based technique to decide the existence of supervisor and generate the same if one exists," Kumar said.
The researchers conducted simulations to verify their approach and next plan to investigate their method in systems where only some of the actions are observable.
INFORMATION:
Reference
S. Basu and R. Kumar, "Control of non-deterministic systems with μ-calculus specifications using quotienting," IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 953-970, May 2021.
http://www.ieee-jas.net/en/article/doi/10.1109/JAS.2021.1003964
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9395538
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica aims to publish high-quality, high-interest, far-reaching research achievements globally, and provide an international forum for the presentation of original ideas and recent results related to all aspects of automation.
The first Impact Factor of IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica is 5.129, ranking among Top 17% (11/63, SCI Q1) in the category of Automation & Control Systems, according to the latest Journal Citation Reports released by Clarivate Analytics in 2020. In addition, its latest CiteScore is 8.3, and has entered Q1 in all three categories it belongs to (Information System, Control and Systems Engineering, Artificial Intelligence) since 2018.
Why publish with us: Fast and high quality peer review; Simple and effective online submission system; Widest possible global dissemination of your research; Indexed in SCIE, EI, IEEE, Scopus, Inspec. JAS papers can be found at http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/mostRecentIssue.jsp?punumber=6570654 or http://www.ieee-jas.net
The ability to visualize transparent objects such as biological cells is of fundamental importance in biology and medical diagnostics. Conventional approaches to achieve this include phase-contrast microscopy and techniques that rely on chemical staining of biological cells. These techniques, however, rely on expensive and bulky optical components or require changing, and in some cases damaging, the cell by introducing chemical contrast agents. Significant recent advances in nanofabrication technology permit structuring materials on the nanoscale with unprecedented ...
Australian researchers have documented the diversity of cells in the human breast, explaining the relationship between healthy breast cells and breast cancer cells.
The research, which relied on expertise spanning from breast cancer biology through to bioinformatics, measured gene expression in single cells taken from healthy women and cancerous breast tissue, including tissue carrying a faulty BRCA1 gene. This enabled the researchers to create an 'RNA atlas' that details the different cells found in these tissues.
The atlas, which was described in EMBO Journal, ...
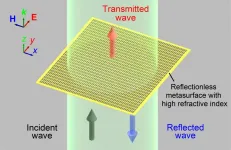
Japanese researchers successfully tested reflectionless, highly refractive index metasurface that may eventually be used in practical applications to send, receive, and manipulate light and radio waves in the terahertz waveband (THz). THz is measured in millionths of a meter, known as micrometers. The metasurface, an artificial two-dimensional flat material, was made of micro-sized cut metal wires of silver paste ink placed on both the front and back of a polyimide film. The team, led by Takehito Suzuki, Associate Professor at the Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) Institute of Engineering, published their findings on April 29, 2021 in Optics Express.
Such flat metasurfaces ...
Psychology researchers at UC Santa Cruz have found that playing games in virtual reality creates an effect called "time compression," where time goes by faster than you think. Grayson Mullen, who was a cognitive science undergraduate at the time, worked with Psychology Professor Nicolas Davidenko to design an experiment that tested how virtual reality's effects on a game player's sense of time differ from those of conventional monitors. The results are now published in the journal Timing & Time Perception.
Mullen designed a maze game that could be played in both virtual reality and conventional formats, then the research team recruited 41 UC Santa Cruz undergraduate ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has been shown to have caused a significant strain on the healthcare system and resources in the United States. However, data regarding the impact of the virus on hip fractures, primarily seen in elderly patients, is lacking.
Researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) sought to compare characteristics and outcomes of hip fracture patients admitted during the COVID-19 outbreak to patients admitted before the outbreak. They also examined characteristics and outcomes of hip fracture patients with and without the virus. Their findings were presented at the 2021 Spring American Society of Regional Anesthesia and ...
Interim results of a study conducted by researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) suggest that oral tranexamic acid (TXA) is non-inferior to intravenous (IV) TXA in preventing blood loss in total knee and total hip replacement surgery. These findings were presented at the 2021 Spring American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (ASRA) Annual Meeting.1
Previously available information suggests that oral, IV and topical TXA are all effective at reducing blood loss and drastically reducing blood transfusion rates during and after surgery, but research with direct comparisons for each method is limited.
"TXA in orthopedic surgery has become the standard ...
While it has been said that the eyes are a window to the soul, a new study shows they could be a means for understanding diseases of the brain. According to new research by scientists at the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, retinal scans can detect key changes in blood vessels that may provide an early sign of Alzheimer's, while offering important insights into how one of the most common Alzheimer's risk genes contributes to the disease.
"The most prevalent genetic risk for Alzheimer's disease is a variant of the APOE gene, known as APOE4," said lead author Fanny Elahi, MD, PhD. "We still don't fully understand how this variant increases risk of brain degeneration, we just know that it does, and that this risk is modified by sex, race, and lifestyle. "Our ...
Climate change is exacerbating problems like habitat loss and temperatures swings that have already pushed many animal species to the brink. But can scientists predict which animals will be able to adapt and survive? Using genome sequencing, researchers from McGill University show that some fish, like the threespine stickleback, can adapt very rapidly to extreme seasonal changes. Their findings could help scientists forecast the evolutionary future of these populations.
A popular subject of study among evolutionary ecologists, stickleback are known for their different shapes, sizes, and behaviours - they can even live in both seawater and freshwater, and under a wide range of temperatures. But what ...
Plants have evolved unique immunity mechanisms that they can activate upon detecting the presence of a pathogen. Interestingly, the presence of some nonpathogenic microorganisms can also prompt a plant to activate its systemic immunity mechanisms, and some studies have shown that pretreating agricultural crops with such "immunity-activating" nonpathogenic microorganisms can leave the crops better prepared to fight off infections from pathogenic microorganisms. In effect, this means that immunity-activating nonpathogenic microorganisms can function like vaccines for plants, providing a low-risk stimulus for the plant's immune system that prepares it for dealing with genuine threats. These are exciting findings for crop scientists because they suggest the ...
Researchers at UC San Francisco have observed a new feature of neural activity in the hippocampus - the brain's memory hub - that may explain how this vital brain region combines a diverse range of inputs into a multi-layered memories that can later be recalled.
Using a special "micro-grid" recording device developed by colleagues at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), the UCSF researchers were able to measure hippocampus activity in study participants undergoing surgery to treat severe epilepsy. They discovered that brain waves travel back and forth across this structure, integrating messages ...