(Press-News.org) Next-generation sequencing technology has made it easier than ever for quick diagnosis of plant diseases. "It's really exciting to see how sequencing technologies have evolved and how this new technology facilitates sequencing of entire genomes in such a short amount of time," said Yazmín Rivera, a plant pathologist with the United States Department of Agriculture's Plant Protection and Quarantine program, who recently published a research paper on the efficacy of Oxford Nanopore Technologies protocols.
"We wanted to provide an unbiased assessment of the technology and protocols available for long read sequencing," Rivera explained. Along with other plant pathologists, Rivera used the company's protocols to prepare RNA and DNA libraries from virus-infected plant material and from a plant pathogenic bacterium, respectively. After one hour of data sequencing, scientists had enough data to assemble small genomes.
"Diagnosticians will welcome an objective review of this technology," Rivera said. Rivera and her colleagues published their findings in END
New technology enables rapid sequencing of entire genomes of plant pathogens
2021-05-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
People at high genetic risk for colorectal cancer benefit more from lifestyle changes
2021-05-14
People with a high polygenic risk score for colorectal cancer could benefit more at preventing the disease by leading healthy lifestyles than those at lower genetic risk, according to a study by Vanderbilt researchers published in the April issue of The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Analyzing data from participants in the UK Biobank, the researchers estimated that maintaining a healthy lifestyle was associated with a nearly 40% reduction in colorectal cancer risk among those with a high genetic risk of developing the disease. The percentage dropped to only about 25% among people at ...
Compound may prevent risk of a form of arrhythmia from common medications
2021-05-14
Dozens of commonly used drugs, including antibiotics, antinausea and anticancer medications, have a potential side effect of lengthening the electrical event that triggers contraction, creating an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrhythmia called acquired Long QT syndrome. While safe in their current dosages, some of these drugs may have a more therapeutic benefit at higher doses, but are limited by the risk of arrhythmia.
Through both computational and experimental validation, a multi-institutional team of researchers has identified a compound that prevents the lengthening of the heart's electrical event, or action potential, resulting in a major step toward safer use and expanded therapeutic efficacy of these ...
Etching process enhances the extraction of hydrogen during water electrolysis
2021-05-14
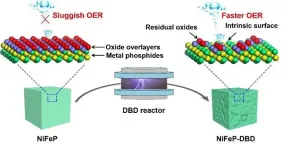
Extracting hydrogen from water through electrolysis offers a promising route for increasing the production of hydrogen, a clean and environmentally friendly fuel. But one major challenge of water electrolysis is the sluggish reaction of oxygen at the anode, known as the oxygen evolution reaction (OER).
A collaboration between researchers at Hunan University and Shenzhen University in China, has led to a discovery that promises to improve the OER process. In their recent paper, published in the KeAi journal Green Energy & Environment, they report that etching - or, in other words, chemically removing - the oxide overlayers that form on the surface of the metal phosphide electrocatalysts regularly used in electrolysis, can increase ...
Terpen-tales: The mystery behind the unique fragrance of the lovely lavender
2021-05-14
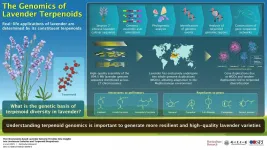
Even the mention of lavender evokes the distinct fragrance of the flower. This beautiful flower has been used to make perfumes and essential oils since time immemorial. The aesthetics of the flower have captured the imagination of hundreds, worldwide. So, what makes this flower so special? What are the "magical" compounds that gives it its unique fragrance? What is the genetic basis of these compounds? These questions have long puzzled scientists.
To find out the answers, a group of scientists from China have sequenced the genome of lavender, which is known in the scientific world as Lavandula angustifolia. The team headed by Dr. Lei Shi, Professor at the Key Laboratory of Plant Resources and Beijing Botanical Garden, Institute of Botany, Chinese ...
Cataloging breast cells to find cancer origins
2021-05-14
What if you could predict which cells might become cancerous? Breast tissue changes dramatically throughout a woman's life, so finding markers for sudden changes that can lead to cancer is especially difficult. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Associate Professor Camila dos Santos and her team identified and cataloged thousands of normal human and mouse breast cell types. The new catalog redefines healthy breast tissue so that when something goes awry, scientists can pinpoint its origin.
Any breast cell could become cancerous. Dos Santos says:
"To understand breast cancer risk, you have to understand normal breast cells first, so when we think about preventive and even targeting therapies, ...
Heart attack recovery aided by injecting heart muscle cells that overexpress cyclin D2
2021-05-14
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - In a large-animal study, researchers have shown that heart attack recovery is aided by injection of heart muscle cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cell line, or hiPSCs, that overexpress cyclin D2. This research, published in the journal Circulation, used a pig model of heart attacks, which more closely resembles the human heart in size and physiology, and thus has higher clinical relevance to human disease, compared to studies in mice.
An enduring challenge for bioengineering researchers is the failure of the heart to regenerate muscle tissue after a heart attack has killed part of its muscle wall. That dead tissue can strain the surrounding muscle, leading to a lethal heart enlargement.
Heart experts thus have sought to create new tissue -- applying ...
Harvesting light like nature does
2021-05-14
Inspired by nature, researchers at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), along with collaborators from Washington State University, created a novel material capable of capturing light energy. This material provides a highly efficient artificial light-harvesting system with potential applications in photovoltaics and bioimaging.
The research provides a foundation for overcoming the difficult challenges involved in the creation of hierarchical functional organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Nature provides beautiful examples of hierarchically structured hybrid materials such as bones and teeth. These materials typically showcase a precise atomic ...
Bio-inspired scaffolds help promote muscle growth
2021-05-14
HOUSTON - (May 14, 2021) - Rice University bioengineers are fabricating and testing tunable electrospun scaffolds completely derived from decellularized skeletal muscle to promote the regeneration of injured skeletal muscle.
Their paper in Science Advances shows how natural extracellular matrix can be made to mimic native skeletal muscle and direct the alignment, growth and differentiation of myotubes, one of the building blocks of skeletal muscle. The bioactive scaffolds are made in the lab via electrospinning, a high-throughput process that can produce single micron-scale fibers.
The research could ease the burden of performing an estimated ...
Fibre-optics used to take the temperature of Greenland Ice Sheet
2021-05-14
Scientists have used fibre-optic sensing to obtain the most detailed measurements of ice properties ever taken on the Greenland Ice Sheet. Their findings will be used to make more accurate models of the future movement of the world's second-largest ice sheet, as the effects of climate change continue to accelerate.
The research team, led by the University of Cambridge, used a new technique in which laser pulses are transmitted in a fibre-optic cable to obtain highly detailed temperature measurements from the surface of the ice sheet all the way to the base, more than 1000 metres below.
In contrast to previous studies, which measured temperature from separate sensors located tens or even hundreds of metres apart, the new approach allows temperature ...
New research shows: Antoni van Leeuwenhoek led rivals astray
2021-05-14
A microscope used by Antoni van Leeuwenhoek to conduct pioneering research contains a surprisingly ordinary lens, as new research by Rijksmuseum Boerhaave Leiden and TU Delft shows. It is a remarkable finding, because Van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) led other scientists to believe that his instruments were exceptional. Consequently, there has been speculation about his method for making lenses for more than three centuries. The results of this study were published in Science Advances on May 14.
Previous research carried out in 2018 already indicated that some of Van Leeuwenhoek's microscopes contained common ground lenses. Researchers have now examined ...