Anisotropic zoning in the upper crust of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt
2021-05-17
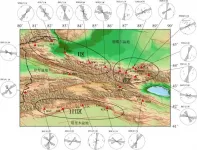
(Press-News.org) The collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates resulted in the formation of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt; however, the formation mechanism of Tianshan and the construction of a dynamic model explaining it remain to be achieved and an integrated understanding has not been reached. A new study adopted shear-wave splitting system to collect and analyze shear-wave splitting parameters of 33 stations in the Tianshan area, it provides new evidence for potentially enhance the understanding the dynamic mechanism of the Tianshan tectonic belt.
The research paper is titled:"Anisotropic zoning in the upper crust of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt, Published in Science China Earth Sciences Issue 4, 2021, Corresponding author of the paper is Yuan Gao, Institute of Earthquake Prediction, China Earthquake Administration. Li Jin, works in the Earthquake Administration of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, is the first author. This study investigates the spatial distribution of seismic anisotropy in the upper crust at 33 stations measured during 2009-2019 in the Tianshan Tectonic Belt.
Current research on the anisotropy of Tianshan is insufficient due to the lack of observational data, the research found that the polarization directions of fast waves at various stations in the Tianshan Tectonic Belt show obvious zoning in terms of spatial distribution. In the area with the strong surface piedmont deformation in the Tianshan Tectonic Belt, the polarization directions are consistent with the tectonic stress field. The obvious stress extrusion observations could be related to dynamic models such as "interlayer insertion and reduction" and "intraplate subduction". The Tianshan Orogenic Belt is relatively softer compared to the basins located on both sides of the north and the south. As the main crustal shortening area, the Tarim Basin thrusts and subducts beneath the Tianshan into the crust and the upper mantle, due to the long-range influences of the convergence between the Indian Plate and Siberian Plate.
Time delays of slow waves exhibit spatial differences. The time delays in the Tianshan Tectonic Belt, regardless of North Tianshan or South Tianshan, increase from east to west. These results are consistent with the north-south convergence deformations across the Tianshan Mountains, where the deformation rate increased from east to west. The average values of time delays in northeastern Pamir are significantly higher than that in the other areas due to the occurrence of the most intensive tectonic movements suggesting that the anisotropy of the zone is significantly stronger than that of the other zones in the Tianshan Tectonic Belt.
This research successfully deciphered the seismic anisotropy in the upper crust and provided a comprehensive and systematic understanding of the dynamic mechanisms of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt.
This research was funded by the Science for Earthquake Resilience Project (No. XH17041Y, XH21041) and the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (No. 2020D01A83).
See the article: Li J, Gao Y, Wang Q. 2021. Anisotropic zoning in the upper crust of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt. Science China Earth Sciences, 64(4): 651-666.
https://www.sciengine.com/doi/10.1007/s11430-020-9709-0
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-17
In our ongoing quest to transform into a more eco-friendly society, hydrogen (H2) is heralded as the clean fuel of tomorrow. Because H2 can be produced from water (H2O) without generating carbon emissions, developing H2-compatible technologies has become a top priority. However, the road ahead is bumpy, and many technical limitations must be ironed out. "Hydrogen is the smallest molecule in nature, and finding feasible ways to store it is a critical issue to realize a hydrogen economy," states Associate Professor Youngjune Park from the Gwangju Institute of Science ...
2021-05-17
WASHINGTON, DC--People with cardiovascular disease (CVD) taking aspirin to lower their chances of suffering a heart attack or stroke experienced similar health benefits, including reduced death and hospitalization for heart attack and stroke, whether they took a high or low dose of aspirin, according to a study presented today at ACC.21, the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session and published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
CVD--and atherosclerosis, in particular, which is a narrowing and hardening of the arteries--is a leading cause of death for men, women, and most racial and ethnic groups in the United States, with estimated direct costs of END ...
2021-05-17
New research has shown that people with type 1 diabetes may have features of premature heart disease induced by the condition often before they even get their diagnosis.
Early markers for this heart disease could be used to ensure patients get targeted therapies as soon as they are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes to slow down or even halt cardiovascular problems.
The findings, published in Stem Cell Research and Therapy, show that tiny pieces of genetic material, called miR-424-5p, increased in early stages of heart disease - these could be targeted to help reduce inflammation in order to compensate for elevated risk.
Early heart disease
Dr Jolanta Weaver, from Newcastle University's Faculty of Medical Sciences, UK, ...
2021-05-17
There's been a breakthrough in the case of the missing planets.
While planet-hunting missions have discovered thousands of worlds orbiting distant stars, there's a severe scarcity of exoplanets that measure between 1.5 and two times Earth's radius. That's the middle ground between rocky super-Earths and larger, gas-shrouded planets called mini-Neptunes. Since discovering this 'radius gap' in 2017, scientists have been sleuthing out why there are so few midsize heavenly bodies.
The new clue arose from a fresh way of looking at the data. A team of researchers led by the Flatiron Institute's Trevor David investigated whether the radius gap changes as planets age. They divvied up exoplanets into two groups -- young and old -- and reassessed the gap. The ...
2021-05-17
The blood thinner apixaban was not superior to standard of care following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), according to findings from a new trial called ATLANTIS presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session. Researchers found that while apixaban reduced the formation of blood clots (thrombosis) around the implanted valve with no increased bleeding risk, a subset of patients taking apixaban who did not have an indication for anticoagulation apart from the TAVR procedure showed a tendency toward a higher rate of non-cardiovascular death--a ...
2021-05-17
Transcatheter left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with a WATCHMAN device was associated with a low rate of stroke at one year even among older patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who faced a high risk for stroke or bleeding based on their previous health history, according to new data presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
The WATCHMAN device, which blocks a small portion of the heart to help reduce the risk of a dangerous clot forming, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2015. The device is used to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with AFib, a heart rhythm disorder, that is not caused by problems with the heart valve. ...
2021-05-17
Patients with an elevated risk of stroke due to heart rhythm problems, or atrial fibrillation (AFib), were much less likely to suffer a stroke after undergoing heart surgery if doctors concurrently performed an additional procedure, called left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), according to the results of a trial presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
AFib increases a person's risk of stroke or systemic embolism, which are life-threatening conditions caused by blood clots blocking an artery. It has been hypothesized that the blood clots that cause these conditions often originate in the left atrial appendage, a small sac on the upper left chamber of the heart. LAAO is a procedure to ...
2021-05-17
The heart failure drug sacubitril/valsartan did not significantly reduce the rate of heart failure or cardiovascular death following a heart attack compared to ramipril, an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor proven effective in improving survival following heart attacks. Findings from the PARADISE-MI trial were presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
The study is the first large trial to examine whether sacubitril/valsartan can reduce heart failure and associated hospitalizations and deaths in patients post-heart attack who face a high risk of developing heart failure. Patients taking sacubitril/valsartan were about 10% less likely than those ...
2021-05-17
Researchers found no significant differences in cardiovascular events or major bleeding in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease who were taking 81 milligrams (mg), also called baby aspirin, versus 325 mg of daily aspirin, according to new data presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
Aspirin is the most common medication for people with established cardiovascular disease--for example, those who have had a heart attack, a stent placed or bypass surgery--to help prevent another heart attack, stroke or premature death. But despite aspirin's proven and widespread use, there has been no evidence as to whether low-dose aspirin (81 mg) or regular-strength (325 mg) aspirin is ...
2021-05-17
Two months after undergoing renal denervation (RDN), patients with high blood pressure who did not respond to treatment with multiple medications had a greater reduction in daytime systolic blood pressure than patients who did not receive RDN, with no difference in major adverse effects, according to research presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
Patients who received RDN--a procedure that delivers energy to overactive nerves in the kidneys to decrease their activity--saw a median reduction of 8 mmHg in their daytime ambulatory systolic blood ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Anisotropic zoning in the upper crust of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt



