High-intensity intermittent training improves spatial memory in rats
University of Tsukuba researchers show that both endurance and high-intensity intermittent training improve exercise capacity and brain function in rats
2021-05-17
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan--Researchers at the University of Tsukuba found that, despite only covering about one-third of the distance in HIIT compared with that covered in endurance training, similar improvements in exercise capacity and brain function were observed for both forms of exercise.
"We investigated how rats' muscles and brains--specifically, the region of the brain involved in spatial learning called the hippocampus--adapted to these types of exercise, and how the rats consequently learned and remembered navigating mazes," explains Professor Hideaki Soya, the principal investigator.
In the experiment, rats were assigned to 1 of 3 groups--resting, endurance running, or alternating intervals (short sprints and rest)--during training sessions on treadmills 5 days/week for 4 weeks.
Both endurance running and HIIT resulted in weight loss, greater muscle mass, and the ability to exercise longer compared with controls; however, increased cellular aerobic capacity was found in the soleus (a muscle with predominantly slow-twitch fibers that makes it functionally well suited to endurance) and in the plantaris (a muscle with predominantly fast-twitch fibers for meeting high-energy functional demands) in the endurance-running and HIIT groups, respectively.
Rats in both groups demonstrated having better memory of spatial learning trials in searching for an escape platform in a water maze. In the hippocampus, increased cell development--neurogenesis--was also observed for both forms of exercise; however, levels of a signaling protein that promotes neurogenesis (BDNF) were increased by HIIT but not by endurance running, whereas the levels of its receptor (TrkB) were increased by both.
Given that BDNF expression is known to be affected by exercise, why didn't endurance running increase BDNF expression? The answer may lie in the mediating role of stress on BDNF expression; exercise is a type of stress. While stress indicators in both exercise groups were found to be similar, this line of enquiry may lead to future studies:
"In this study, we showed that an HIIT exercise regimen with a low exercise volume nevertheless improves spatial memory, and we demonstrated that these improvements are supported by changes in neuronal plasticity in the hippocampus. In a previous study, we found that continuous light-intensity training had a similar beneficial effect, whereas continuous high-intensity training did not," Professor Soya summarizes. "Thus, it seems that the benefits yielded by exercise may actually depend on optimization, that is, a trade-off between exercise time and intensity."
A future where exercise regimens can be tailored to improve both physical and cognitive features may be on the horizon.
INFORMATION:
The article, "High-intensity Intermittent Training Enhances Spatial Memory and Hippocampal Neurogenesis Associated with BDNF Signaling in Rats," was published in Cerebral Cortex at DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhab093
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-17
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have found several grape varieties native to Cyprus, which tolerate drought conditions better than some international varieties popular in Australia, contain chemical compounds responsible for flavours preferred by Australian consumers.
The study published in OENO One follows earlier research with Cypriot grape varieties Maratheftiko and Xynisteri in particular, which showed they are well adapted to a hot climate and continue to perform well as the climate becomes hotter.
Lead author and PhD student Alexander Copper, from the University of ...
2021-05-17
ATLANTA - Yerkes National Primate Research Center researchers in collaboration with Institut Pasteur have determined a combination immunotherapy of Interleukin-21 (IL-21) and interferon alpha (IFN?) when added to antiviral therapy (ART) is effective in generating highly functional natural killer (NK) cells that can help control and reduce simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) in animal models. This finding, published online today in Nature Communications, is key for developing additional treatment options to control HIV/AIDS, which impacts 38 million people worldwide.
ART is the current leading treatment for HIV/AIDS. It is capable of reducing the virus to undetectable levels, but is ...
2021-05-17
The way in which banks react to climate risks and uncertainty could impact financial stability as well as the world's transition to a low-carbon economy. A new study by researchers from IIASA and the Vienna University of Economics and Business explored the role that banks' expectations about climate-related risks will play in fostering or hindering an orderly low-carbon transition.
According to the study published in a special issue on climate risks and financial stability of the Journal of Financial Stability, banks and their expectations about climate-related risks - and especially ...
2021-05-17
Scientists at Skoltech Center for Energy Science and Technology have developed an enriched and scalable approach for increasing the capacity of a broad range of metal-ion battery cathode materials. These findings, published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A, can be useful for developing a new generation of advanced rechargeable energy storage devices.
Creation of modern lithium-ion batteries became possible owing to several scientific breakthroughs. One of them, made by a Nobel laureate John B. Goodenough, was the development of cathode materials that contain reversibly extractable lithium ions. Implementation ...
2021-05-17
Devices that deliver nicotine without smoke inhalation have potential to help smokers who cannot or do not want to stop using nicotine to reduce dramatically the risk of smoking-related disease and death.
However, for smokers to switch to these alternatives, the products need to provide what smokers expect from cigarettes.
The newest study from Queen Mary University of London evaluates safety and effects of these products and has focused on the most popular "heat not burn" product, IQOS.
The researchers compared nicotine delivery and user ratings of IQOS with those of cigarettes, Juul (the US version of a 'pod' based e-cigarette with high nicotine content), and refillable e-cigarettes.
IQOS delivered less nicotine than cigarettes. ...
2021-05-17
Heavy precipitation can cause large economic, ecological, and human life losses. Both its frequency and intensity have increased due to climate change influences. Therefore, it is becoming increasingly critical to accurately model and predict heavy precipitation events. However, current global climate models (GCMs) struggle to correctly model tropical precipitation, particularly heavy rainfall. Atmospheric scientists are working to identify and minimize model biases that arise when attempting to model large-scale and convective precipitation.
"Unrealistic ...
2021-05-17
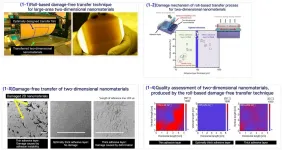
The Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) under the Ministry of Science and ICT developed a roll-based damage-free transfer technique that allows two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials to be transferred into wafer scale without damage. The proposed technique has a variety of applications from transparent displays and semiconductors to displays for self-driving cars, and is expected to accelerate the commercialization of 2D nanomaterial-based high-performance devices.
Dr. Kwang-Seop Kim, principal researcher of the Department of Nano-Mechanics at KIMM, succeeded in developing a technique ...
2021-05-17
(SYDNEY, Monday 17th May 2021) The early immune response in a person who has been vaccinated for COVID-19 can predict the level of protection they will have to the virus over time, according to analysis from Australian mathematicians, clinicians, and scientists, and published today in Nature Medicine.
The researchers from UNSW's Kirby Institute, the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, and the University of Sydney have identified an 'immune correlate' of vaccine protection. This has the potential to dramatically cut development times for new vaccines, by measuring neutralising antibody levels as a 'proxy' for immune protection from COVID-19.
"Neutralising antibodies are tiny Y-shaped proteins produced by our body in response to infection or vaccination. They ...
2021-05-17
A weather pattern that pushes snowfall away from parts of Greenland's ice sheet is causing the continent to become darker and warmer, according to Dartmouth research published in Geophysical Research Letters.
The reduction in the amount of fresh, light-colored snow exposes older, darker snow on the surface of the ice sheet. The resulting decrease in reflectivity, known as albedo, causes the ice to absorb more heat, also likely contributing to faster melting.
"As snow ages, even over hours to a few days, you get this reduction in reflectivity, and that's why the fresh snow is so important," said Erich Osterberg, associate professor of earth sciences at Dartmouth and the principal investigator of the study.
According to the ...
2021-05-17
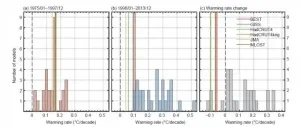
A new study led by Dr. Wei and Dr. Qiao from the First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources provides an evaluation of the performance of the newly released CMIP6 models in simulating the global warming slowdown observed in the early 2000s. This study reveals that the key in simulating and predicting near-term temperate change is to correctly separate and simulate the two distinct signals, i.e., the human-induced long-term warming trend and natural variabilities, especially those at interannual, interdecadal and multidecadal scales. This work was online published in SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences on April 15th, 2021.
After the unprecedented warming over the last quarter of the 20th century, the global surface temperature growth slowed unexpectedly during ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] High-intensity intermittent training improves spatial memory in rats
University of Tsukuba researchers show that both endurance and high-intensity intermittent training improve exercise capacity and brain function in rats