Errors in large-scale and convective tropical precipitation simulations using current global models may impact climate feedback
2021-05-17
(Press-News.org) Heavy precipitation can cause large economic, ecological, and human life losses. Both its frequency and intensity have increased due to climate change influences. Therefore, it is becoming increasingly critical to accurately model and predict heavy precipitation events. However, current global climate models (GCMs) struggle to correctly model tropical precipitation, particularly heavy rainfall. Atmospheric scientists are working to identify and minimize model biases that arise when attempting to model large-scale and convective precipitation.
"Unrealistic convective and large-scale precipitation components essentially contribute to the biases of simulated precipitation." said Prof. Jing Yang, a faculty member in the Geographical Science department at Beijing Normal University.
Prof. Yang and her postgraduate student Sicheng He, along with Qing Bao from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, explored the challenges and barriers to achieving realistic rainfall modeling from the perspective of convective and large-scale precipitation.
"Although sometimes total rainfall amounts can be simulated well, the convective and large-scale precipitation partitions are incorrect in the models." remarked Yang.
To clarify the status of convective and large-scale precipitation components within current GCMs, researchers comprehensively classified 16 CMIP6 models focusing on tropical heavy rainfall. In most cases, results show a much more rainfall resolved from large-scale rainfall rather than convective components of CMIP6 model simulations, which is not realistic.
The research team divided model components into three distinct groups to better assess based on the percentage of large-scale precipitation: (1) whole mid-to-lower tropospheric wet biases (60%-80% large-scale rainfall); (2) mid-tropospheric wet peak (50% convective/large-scale rainfall); and (3) lower-tropospheric wet peak (90%-100% large-scale rainfall).
These classifications are closely associated with the vertical distribution of moisture and clouds within the tropical atmosphere. Because the radiative effects of low and high clouds differ, the associated differences in vertical cloud distributions can potentially cause different climate responses, therefore considerable uncertainties in climate projections.
The study is recently published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences. "The associated vertical distribution of unique clouds potentially causes different climate feedback, suggesting accurate convective/large-scale rainfall partitions are necessary to reliable climate projection." noted Yang.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-17
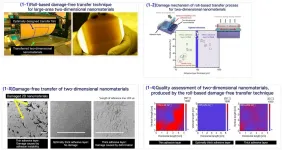
The Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) under the Ministry of Science and ICT developed a roll-based damage-free transfer technique that allows two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials to be transferred into wafer scale without damage. The proposed technique has a variety of applications from transparent displays and semiconductors to displays for self-driving cars, and is expected to accelerate the commercialization of 2D nanomaterial-based high-performance devices.
Dr. Kwang-Seop Kim, principal researcher of the Department of Nano-Mechanics at KIMM, succeeded in developing a technique ...
2021-05-17
(SYDNEY, Monday 17th May 2021) The early immune response in a person who has been vaccinated for COVID-19 can predict the level of protection they will have to the virus over time, according to analysis from Australian mathematicians, clinicians, and scientists, and published today in Nature Medicine.
The researchers from UNSW's Kirby Institute, the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, and the University of Sydney have identified an 'immune correlate' of vaccine protection. This has the potential to dramatically cut development times for new vaccines, by measuring neutralising antibody levels as a 'proxy' for immune protection from COVID-19.
"Neutralising antibodies are tiny Y-shaped proteins produced by our body in response to infection or vaccination. They ...
2021-05-17
A weather pattern that pushes snowfall away from parts of Greenland's ice sheet is causing the continent to become darker and warmer, according to Dartmouth research published in Geophysical Research Letters.
The reduction in the amount of fresh, light-colored snow exposes older, darker snow on the surface of the ice sheet. The resulting decrease in reflectivity, known as albedo, causes the ice to absorb more heat, also likely contributing to faster melting.
"As snow ages, even over hours to a few days, you get this reduction in reflectivity, and that's why the fresh snow is so important," said Erich Osterberg, associate professor of earth sciences at Dartmouth and the principal investigator of the study.
According to the ...
2021-05-17
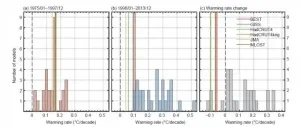
A new study led by Dr. Wei and Dr. Qiao from the First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources provides an evaluation of the performance of the newly released CMIP6 models in simulating the global warming slowdown observed in the early 2000s. This study reveals that the key in simulating and predicting near-term temperate change is to correctly separate and simulate the two distinct signals, i.e., the human-induced long-term warming trend and natural variabilities, especially those at interannual, interdecadal and multidecadal scales. This work was online published in SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences on April 15th, 2021.
After the unprecedented warming over the last quarter of the 20th century, the global surface temperature growth slowed unexpectedly during ...
2021-05-17
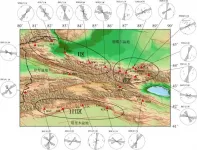
The collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates resulted in the formation of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt; however, the formation mechanism of Tianshan and the construction of a dynamic model explaining it remain to be achieved and an integrated understanding has not been reached. A new study adopted shear-wave splitting system to collect and analyze shear-wave splitting parameters of 33 stations in the Tianshan area, it provides new evidence for potentially enhance the understanding the dynamic mechanism of the Tianshan tectonic belt.
The research paper is titled:"Anisotropic zoning in the upper crust of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt, Published in Science China Earth Sciences Issue 4, 2021, Corresponding author ...
2021-05-17
In our ongoing quest to transform into a more eco-friendly society, hydrogen (H2) is heralded as the clean fuel of tomorrow. Because H2 can be produced from water (H2O) without generating carbon emissions, developing H2-compatible technologies has become a top priority. However, the road ahead is bumpy, and many technical limitations must be ironed out. "Hydrogen is the smallest molecule in nature, and finding feasible ways to store it is a critical issue to realize a hydrogen economy," states Associate Professor Youngjune Park from the Gwangju Institute of Science ...
2021-05-17
WASHINGTON, DC--People with cardiovascular disease (CVD) taking aspirin to lower their chances of suffering a heart attack or stroke experienced similar health benefits, including reduced death and hospitalization for heart attack and stroke, whether they took a high or low dose of aspirin, according to a study presented today at ACC.21, the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session and published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
CVD--and atherosclerosis, in particular, which is a narrowing and hardening of the arteries--is a leading cause of death for men, women, and most racial and ethnic groups in the United States, with estimated direct costs of END ...
2021-05-17
New research has shown that people with type 1 diabetes may have features of premature heart disease induced by the condition often before they even get their diagnosis.
Early markers for this heart disease could be used to ensure patients get targeted therapies as soon as they are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes to slow down or even halt cardiovascular problems.
The findings, published in Stem Cell Research and Therapy, show that tiny pieces of genetic material, called miR-424-5p, increased in early stages of heart disease - these could be targeted to help reduce inflammation in order to compensate for elevated risk.
Early heart disease
Dr Jolanta Weaver, from Newcastle University's Faculty of Medical Sciences, UK, ...
2021-05-17
There's been a breakthrough in the case of the missing planets.
While planet-hunting missions have discovered thousands of worlds orbiting distant stars, there's a severe scarcity of exoplanets that measure between 1.5 and two times Earth's radius. That's the middle ground between rocky super-Earths and larger, gas-shrouded planets called mini-Neptunes. Since discovering this 'radius gap' in 2017, scientists have been sleuthing out why there are so few midsize heavenly bodies.
The new clue arose from a fresh way of looking at the data. A team of researchers led by the Flatiron Institute's Trevor David investigated whether the radius gap changes as planets age. They divvied up exoplanets into two groups -- young and old -- and reassessed the gap. The ...
2021-05-17
The blood thinner apixaban was not superior to standard of care following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), according to findings from a new trial called ATLANTIS presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session. Researchers found that while apixaban reduced the formation of blood clots (thrombosis) around the implanted valve with no increased bleeding risk, a subset of patients taking apixaban who did not have an indication for anticoagulation apart from the TAVR procedure showed a tendency toward a higher rate of non-cardiovascular death--a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Errors in large-scale and convective tropical precipitation simulations using current global models may impact climate feedback