(Press-News.org) Marilyn Monroe famously sang that diamonds are a girl's best friend, but they are also very popular with quantum scientists - with two new research breakthroughs poised to accelerate the development of synthetic diamond-based quantum technology, improve scalability, and dramatically reduce manufacturing costs.
While silicon is traditionally used for computer and mobile phone hardware, diamond has unique properties that make it particularly useful as a base for emerging quantum technologies such as quantum supercomputers, secure communications and sensors.
However there are two key problems; cost, and difficulty in fabricating the single crystal diamond layer, which is smaller than one millionth of a metre.
A research team from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Transformative Meta-Optics at the University of Technology Sydney (UTS), led by Professor Igor Aharonovich, has just published two research papers, in Nanoscale and Advanced Quantum Technologies, that address these challenges.
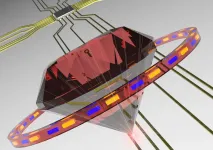
"For diamond to be used in quantum applications, we need to precisely engineer 'optical defects' in the diamond devices - cavities and waveguides - to control, manipulate and readout information in the form of qubits - the quantum version of classical computer bits," said Professor Aharonovich.
"It's akin to cutting holes or carving gullies in a super thin sheet of diamond, to ensure light travels and bounces in the desired direction," he said.
To overcome the "etching" challenge, the researchers developed a new hard masking method, which uses a thin metallic tungsten layer to pattern the diamond nanostructure, enabling the creation of one-dimensional photonic crystal cavities.
"The use of tungsten as a hard mask addresses several drawbacks of diamond fabrication. It acts as a uniform restraining conductive layer to improve the viability of electron beam lithography at nanoscale resolution," said lead author of paper in Nanoscale, UTS PhD candidate Blake Regan.
To the best of our knowledge, we offer the first evidence of the growth of a single crystal diamond structure from a polycrystalline material using a bottom up approach - like growing flowers from seed.
"It also allows the post-fabrication transfer of diamond devices onto the substrate of choice under ambient conditions. And the process can be further automated, to create modular components for diamond-based quantum photonic circuitry," he said.
The tungsten layer is 30nm wide - around 10,000 times thinner than a human hair - however it enabled a diamond etch of over 300nm, a record selectivity for diamond processing.
A further advantage is that removal of the tungsten mask does not require the use of hydrofluoric acid - one of the most dangerous acids currently in use - so this also significantly improves the safety and accessibility of the diamond nanofabrication process.
To address the issue of cost, and improve scalability, the team further developed an innovative step to grow single crystal diamond photonic structures with embedded quantum defects from a polycrystalline substrate.
"Our process relies on lower cost large polycrystalline diamond, which is available as large wafers, unlike the traditionally used high quality single crystal diamond, which is limited to a few mm2" said UTS PhD candidate Milad Nonahal, lead author of the study in Advanced Quantum Technologies.
"To the best of our knowledge, we offer the first evidence of the growth of a single crystal diamond structure from a polycrystalline material using a bottom up approach - like growing flowers from seed," he added.
"Our method eliminates the need for expensive diamond materials and the use of ion implantation, which is key to accelerating the commercialisation of diamond quantum hardware" said UTS Dr Mehran Kianinia, a senior author on the second study.
INFORMATION:
'Nanofabrication of high Q, transferable diamond resonators' is published in Nanoscale.
'Bottom-Up Synthesis of Single Crystal Diamond Pyramids Containing Germanium Vacancy Centres' is published in Advanced Quantum Technologies
. END
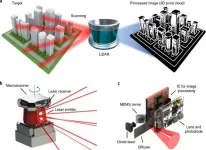
The nanophotonics-based LiDAR technology developed by a POSTECH research team was presented as an invited paper in Nature Nanotechnology, the leading academic journal in the field of nanoscience and nanoengineering.
In this paper, a POSTECH research team (led by Professor Junsuk Rho of the departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering, postdoctoral researcher Dr. Inki Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Ph.D. candidate Jaehyuck Jang of the Department of Chemical Engineering) in cooperation with the French National Science Institute (CNRS-CRHEA) focused on the LiDAR device developed through studying the metamaterials based ultralight nanophotonics.
In addition, the paper ...
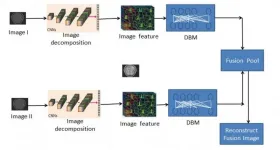
Image fusion is a process that can enhance the clinical value of medical images, improving the accuracy of medical diagnoses and the quality of patient care.
Researchers at the College of Data Science Software Engineering at China's Qingdao University, have developed a new 'multi-modal' image fusion method based on supervised deep learning that enhances image clarity, reduces redundant image features and supports batch processing. Their END ...
ATS 2021, New York, NY - The COVID-19 pandemic has, and will continue to have, a tremendous impact on ICU nurses' mental health and willingness to continue in the critical care work force, according to research presented at the ATS 2021 International Conference.
Jill Guttormson, PhD, RN, associate dean for Academic Affairs and associate professor, College of Nursing, Marquette University, and colleagues sought to describe the impact of COVID-19 on ICU nurses through a survey using valid and reliable measures of burnout, moral distress, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress symptoms.
The researchers recruited a national sample of nurses who have worked in the ICU during the COVID-19 pandemic between October and ...
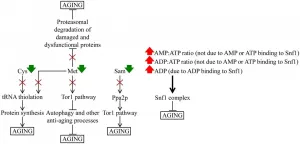
The cover for issue 7 of Oncotarget features Figure 14, "A hypothetical model of how a specific remodeling of cellular metabolism by CR slows down yeast chronological aging," published in "Caloric restriction creates a metabolic pattern of chronological aging delay that in budding yeast differs from the metabolic design established by two other geroprotectors" by Mohammad, et al. which reported that caloric restriction and the tor1Δ mutation are robust geroprotectors in yeast and other eukaryotes.
The authors demonstrate that caloric restriction generates a unique metabolic pattern.
Unlike the tor1Δ mutation or lithocholic acid, it slows down the metabolic pathway ...
A team of McMaster University researchers who studied heart patients found that stair-climbing routines, whether vigorous or moderate, provide significant cardiovascular and muscular benefits.
The findings, published in closely related studies in the journals Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise and Frontiers, address the most frequently cited barriers to exercise: time, equipment and access to gym facilities.
"Brief, vigorous stair-climbing and traditional moderate intensity exercise both changed fitness, which is a key predictor of mortality after a cardiac event," says Maureen MacDonald, one of the lead researchers on both studies and a professor in McMaster's Department ...
Oncotarget published "The cancer testis antigens CABYR-a/b and CABYR-c are expressed in a subset of colorectal cancers and hold promise as targets for specific immunotherapy" which reported that Calcium-binding tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated protein is expressed in the human germ line but not in adult human tissues, thus, it is considered a cancer testis protein.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the CABYR isoforms: a/b and c mRNA expression in colorectal cancer and to determine if these proteins hold promise as vaccine targets.
CABYR mRNA expression in a set of normal human tissues, including the testis, were determined ...
A rare syndrome has been observed in people following vaccination against Covid-19. This involves thrombosis at unusual sites in the body, associated with a low thrombocyte (blood platelet) count and a clotting disorder. In medical jargon, this syndrome is referred to as VITT (vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia). Doctors at the Department of Medicine I of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital (Division of Hematology and Hemastaseology) have now successfully treated an acute instance of this syndrome.
VITT is most probably caused by a defective immune response, whereby thrombocyte-activating antibodies are produced resulting ...
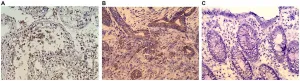
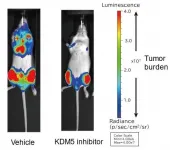
An international team of researchers from Japan, the US and the UK has analyzed the function of the histone demethylase KDM5A in multiple myeloma, one of the three major hematological cancers, and clarified the mechanism by which it promotes myeloma cell proliferation. They also developed a novel KDM5 inhibitor and showed that it inhibits cancer cell growth in a myeloma mouse model. The researchers expect that new therapies targeting KDM5A will be developed in the future.
The prognosis for multiple myeloma is improving every year with the introduction of new ...
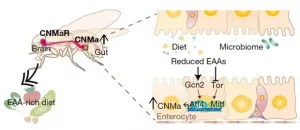
A new study led by KAIST researchers using fruit flies reveals how protein deficiency in the diet triggers cross talk between the gut and brain to induce a desire to eat foods rich in proteins or essential amino acids. This finding reported in the May 5 issue of Nature can lead to a better understanding of malnutrition in humans.
"All organisms require a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats for their well being," explained KAIST neuroscientist and professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh. "Taking in sufficient calories alone won't do the job, as it can still lead to severe forms of malnutrition including kwashiorkor, if the diet does not include enough proteins," he added.
Scientists already knew that inadequate ...
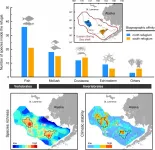
Scientists from Hokkaido University have used species survey and climate data to identify two marine biodiversity refugia in the Eastern Bering Sea - regions where species richness, community stability and climate stability are high.
Marine biodiversity, the diversity of life in the seas and oceans, supports ecosystem services of immense societal benefits. However, climate change and human activities have been adversely affecting marine biodiversity for many decades, resulting in population decline, community shifts, and species loss and extinction. Developing effective means to mitigate ...