Archaeologists teach computers to sort ancient pottery
2021-05-17
(Press-News.org) Archaeologists at Northern Arizona University are hoping a new technology they helped pioneer will change the way scientists study the broken pieces left behind by ancient societies.
The team from NAU's Department of Anthropology have succeeded in teaching computers to perform a complex task many scientists who study ancient societies have long dreamt of: rapidly and consistently sorting thousands of pottery designs into multiple stylistic categories. By using a form of machine learning known as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), the archaeologists created a computerized method that roughly emulates the thought processes of the human mind in analyzing visual information.
"Now, using digital photographs of pottery, computers can accomplish what used to involve hundreds of hours of tedious, painstaking and eye-straining work by archaeologists who physically sorted pieces of broken pottery into groups, in a fraction of the time and with greater consistency," said Leszek Pawlowicz, adjunct faculty in the Department of Anthropology. He and anthropology professor Chris Downum began researching the feasibility of using a computer to accurately classify broken pieces of pottery, known as sherds, into known pottery types in 2016. Results of their research are reported in the June issue of the peer-reviewed publication Journal of Archaeological Science.
"On many of the thousands of archaeological sites scattered across the American Southwest, archaeologists will often find broken fragments of pottery known as sherds. Many of these sherds will have designs that can be sorted into previously-defined stylistic categories, called 'types,' that have been correlated with both the general time period they were manufactured and the locations where they were made" Downum said. "These provide archaeologists with critical information about the time a site was occupied, the cultural group with which it was associated and other groups with whom they interacted."
The research relied on recent breakthroughs in the use of machine learning to classify images by type, specifically CNNs. CNNs are now a mainstay in computer image recognition, being used for everything from X-ray images for medical conditions and matching images in search engines to self-driving cars. Pawlowicz and Downum reasoned that if CNNs can be used to identify things like breeds of dogs and products a consumer might like, why not apply this approach to the analysis of ancient pottery?
Until now, the process of recognizing diagnostic design features on pottery has been difficult and time-consuming. It could involve months or years of training to master and correctly apply the design categories to tiny pieces of a broken pot. Worse, the process was prone to human error because expert archaeologists often disagree over which type is represented by a sherd, and might find it difficult to express their decision-making process in words. An anonymous peer reviewer of the article called this "the dirty secret in archaeology that no one talks about enough."
Determined to create a more efficient process, Pawlowicz and Downum gathered thousands of pictures of pottery fragments with a specific set of identifying physical characteristics, known as Tusayan White Ware, common across much of northeast Arizona and nearby states. They then recruited four of the Southwest's top pottery experts to identify the pottery design type for every sherd and create a 'training set' of sherds from which the machine can learn. Finally, they trained the machine to learn pottery types by focusing on the pottery specimens the archaeologists agreed on.
"The results were remarkable," Pawlowicz said. "In a relatively short period of time, the computer trained itself to identify pottery with an accuracy comparable to, and sometimes better than, the human experts."
For the four archaeologists with decades of experience sorting tens of thousands of actual potsherds, the machine outperformed two of them and was comparable with the other two. Even more impressive, the machine was able to do what many archaeologists can have difficulty with: describing why it made the classification decisions that it did. Using color-coded heat maps of sherds, the machine pointed out the design features that it used to make its classification decisions, thereby providing a visual record of its "thoughts."
"An exciting spinoff of this process was the ability of the computer to find nearly exact matches of particular snippets of pottery designs represented on individual sherds," Downum said. "Using CNN-derived similarity measures for designs, the machine was able to search through thousands of images to find the most similar counterpart of an individual pottery design."
Pawlowicz and Downum believe this ability could allow a computer to find scattered pieces of a single broken pot in a multitude of similar sherds from an ancient trash dump or conduct a region-wide analysis of stylistic similarities and differences across multiple ancient communities. The approach might also be better able to associate particular pottery designs from excavated structures which have been dated using the tree-ring method.
Their research is already receiving high praise.
"I fervently hope that Southwestern archaeologists will adopt this approach and do so quickly. It just makes so much sense," said Stephen Plog, emeritus professor of archaeology at the University of Virginia and author of the book "Stylistic Variation In Prehistoric Ceramics." "We learned a ton from the old system, but it has lasted beyond its usefulness, and it's time to transform how we analyze ceramic designs."
The researchers are exploring practical applications of the CNN model's classification expertise and are working on additional journal articles to share the technology with other archaeologists. They hope this new approach to archaeological analysis of pottery can be applied to other types of ancient artifacts, and that archaeology can enter a new phase of machine classification that results in greater efficiency of archaeological efforts and more effective methods of teaching pottery designs to new generations of students.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-17
The development of dementia, often from Alzheimer's disease, late in life is associated with abnormal blood levels of dozens of proteins up to five years earlier, according to a new study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Most of these proteins were not known to be linked to dementia before, suggesting new targets for prevention therapies.
The findings are based on new analyses of blood samples of over ten thousand middle-aged and elderly people--samples that were taken and stored during large-scale studies decades ago as part of an ongoing study. The researchers linked abnormal blood levels of 38 proteins to higher risks of developing Alzheimers within ...
2021-05-17
May 16, 2021 -- In a study of low-income, urban youth in the U.S., researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health found that students exposed to Photovoice, an educational intervention, experienced greater improvements in STEM-capacity scores and environmental awareness scores compared to a group of youth who were not exposed to the activity. The results suggest that the Photovoice activities may be associated with improved learning outcomes. The study is published in the International Journal of Qualitative Methods.
"Our findings suggest that the Photovoice activities result in greater environmental awareness and may be associated with improved learning skills," said Nadav Sprague, doctoral fellow, ...
2021-05-17
Stanford researchers have discovered a new kind of biomolecule that could play a significant role in the biology of all living things.
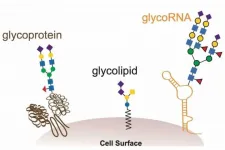
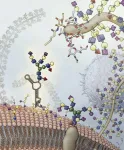
The novel biomolecule, dubbed glycoRNA, is a small ribbon of ribonucleic acid (RNA) with sugar molecules, called glycans, dangling from it. Up until now, the only kinds of similarly sugar-decorated biomolecules known to science were fats (lipids) and proteins. These glycolipids and glycoproteins appear ubiquitously in and on animal, plant and microbial cells, contributing to a wide range of processes essential for life.
The newfound glycoRNAs, neither ...
2021-05-17
FRANKFURT. There are currently only a few synthetic agents that bind to and block the widespread membrane transport proteins, ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC). Scientists at Goethe University and the University of Tokyo identified four of these macrocyclic peptides as models for a novel generation of active substances. They used methods for which the scientists involved are considered world leaders.
Thanks to deep sequencing, an extremely fast and efficient read-out procedure, the desired macrocyclic peptides could be filtered out of a "library" ...
2021-05-17
In a surprise find, scientists have discovered sugar-coated RNA molecules decorating the surface of cells.
These so-called "glycoRNAs" poke out from mammalian cells' outer membrane, where they can interact with other molecules. This discovery, reported May 17, 2021, in the journal Cell, upends the current understanding of how the cell handles RNAs and glycans.
"This was probably the biggest scientific shock of my life," says study author END ...
2021-05-17
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Washington State University researchers have developed an innovative way to convert plastics to ingredients for jet fuel and other valuable products, making it easier and more cost effective to reuse plastics.
The researchers in their reaction were able to convert 90% of plastic to jet fuel and other valuable hydrocarbon products within an hour at moderate temperatures and to easily fine-tune the process to create the products that they want. Led by graduate student Chuhua Jia and Hongfei Lin, associate professor in the Gene and Linda Voiland School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering, they report on their work in the journal, ...
2021-05-17
What The Study Did: Researchers assessed the feasibility of using positive behavior supports to promote the use of face coverings in school-aged children with autism spectrum disorders and/or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) attending a summer program during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Benjamin Aaronson, Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10281)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
2021-05-17
What The Study Did: Hospital discharge rates, hospitalization outcomes and demographic factors were examined among U.S. patients with ischemic stroke before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Adam de Havenon, M.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10314)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
2021-05-17
What The Study Did: Online search data were used to assess changes in home birth information seeking across the United States and United Kingdom during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Christina N. Schmidt, B.S., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10310)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access ...
2021-05-17
Early diagnosis and improvement of breast cancer treatments have reduced breast cancer mortality in recent years, with survival rates reaching 85% today. In spite of these data, breast cancer was still the most frequently diagnosed tumour in the world in 2020, mainly due to increased population screening and social factors such as ageing. RANK protein plays a key role in the development of these tumours. Located in the membrane of cells, when it binds to its partner RANKL, it sends signals that stimulate the development of the mammary gland. When these proteins do not work properly, breast cells begin to divide and multiply ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Archaeologists teach computers to sort ancient pottery