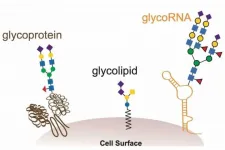
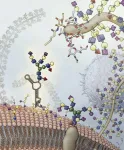
The novel biomolecule, dubbed glycoRNA, is a small ribbon of ribonucleic acid (RNA) with sugar molecules, called glycans, dangling from it. Up until now, the only kinds of similarly sugar-decorated biomolecules known to science were fats (lipids) and proteins. These glycolipids and glycoproteins appear ubiquitously in and on animal, plant and microbial cells, contributing to a wide range of processes essential for life.
The newfound glycoRNAs, neither rare nor furtive, were hiding in plain sight simply because no one thought to look for them - understandably so, given that their existence flies in the face of well-established cellular biology.
A study in the journal Cell, published May 17, describes the findings.
"This is a stunning discovery of an entirely new class of biomolecules," said Carolyn Bertozzi, the Anne T. and Robert M. Bass professor at Stanford's School of Humanities and Sciences, the Baker Family Director of Stanford Chemistry, Engineering and Medicine for Human Health and the study's senior author. "It's really a bombshell because the discovery suggests that there are biomolecular pathways in the cell that are completely unknown to us."
"What's more," Bertozzi added, "some of the RNAs modified by glycans to form glycoRNA have a sordid history of association with autoimmune diseases."
Bertozzi gives credit for the discovery to the study's lead author Ryan Flynn, who worked for months in her lab as a postdoctoral fellow chasing down glycoRNA, based mostly on a hunch.
"I came into Carolyn's lab asking, 'what if glycans can bind to RNA?', which turned out to be something that hadn't been explored before," said Flynn, now an assistant professor at Boston Children's Hospital in the Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology. "I just like wondering and asking questions and it was immensely gratifying to arrive at this unexpected answer."
Approaching research with an open mind Over the course of her trailblazing career, Bertozzi has brought the once-fringe field of glycobiology into the mainstream. For the past 25 years, her work has helped biologists appreciate how glycans, the long-overlooked sugar structures that stud our cells, are every bit as important as proteins and nucleic acids such as RNA and DNA.
Flynn admits he knew little about glycans when he joined Bertozzi's lab. His area of expertise is RNA, which was the focus of his medical degree and PhD. Flynn earned those degrees under the mentorship of Howard Chang, the Virginia and D. K. Ludwig Professor of Cancer Research and Professor of Genetics at Stanford.
"Ryan is RNA, I'm glycans," said Bertozzi. "We have completely different backgrounds."
The fields of RNA and glycan research are traditionally distinct because the biomolecules form and operate in different cellular places. Most types of RNA live in a cell's nucleus as well as in the cytosol, where the genome is kept and protein synthesis occurs, respectively. Glycans, in contrast, originate in subcellular structures bound by membranes and are thus separated from spaces where RNAs occupy. Glycoproteins and glycolipids localize to the cell's surface, acting as binding sites for extracellular molecules and communicating with other cells. (An example of glycolipids are those that define our blood type.)
"RNA and glycans live in two separate worlds if you believe the textbooks," said Bertozzi.
An odd bit of outlying biology had initially piqued Flynn's interest and got him wondering if those worlds might in fact overlap. He had taken note in the scientific literature of an enzyme, little-studied in the RNA field, that glycosylates (adds glycans to) certain proteins and which can also bind to RNAs. Based on this enzyme's mutual affinity for proteins and RNA, Flynn decided to see if there was a more direct connection between RNA and glycans.
"When Ryan started exploring a possible connection between glycosylation and RNA, I thought the chances of finding anything were very low," said Bertozzi. "But I figured it doesn't hurt to snoop around."
On the hunt Flynn wielded an array of techniques in his search for hypothetical glycoRNAs. Among the most effective was bioorthogonal chemistry, originally pioneered by Bertozzi for enabling studies of living cells without disturbing naturally occurring processes. One common method involves attaching an inobtrusive "reporter" chemical to a biomolecule that emits light when engaging in certain reactions.
Flynn outfitted many different glycans with reporting "lightbulbs" to see what biomolecules the sugars bound to and where the sugar-bonded biomolecules ended up in and on cells. Relying on his experiences preparing and working with RNA, Flynn went beyond the protein- and lipid-containing compartments inside cells as had theretofore been probed.
"Ryan is the first person we know of that actually looked at glycans and RNA in this way," said Bertozzi.
After many frustrating months of negative and confusing results, Flynn reassessed his data. He noticed that one labeled sugar, incorporated into a precursor molecule for sialic acid, kept popping up.
"Once I saw that signal, I felt like something was actually there," Flynn said.
"It was really important that Ryan did not come at this topic with preconceived notions and unconscious bias," Bertozzi said. "His mind was open to possibilities that violate what we think we know about biology."
Life's origins and operations After documenting the presence of the apparently novel glycoRNA in human cells, Flynn and colleagues searched for it in other cells. They found glycoRNAs in every cell type they tested - human, mouse, hamster and zebrafish.
The presence of glycoRNAs in different organisms suggests they perform fundamentally important functions. Furthermore, the RNAs are structurally similar in creatures that evolutionarily diverged hundreds of millions to billions of years ago. This suggests glycoRNAs could have ancient origins and may have had some role in the emergence of life on Earth, explained Bertozzi.
The function of glycoRNAs is not yet known, but it merits further study as they may be linked to autoimmune diseases that cause the body to attack its own tissues and cells, Flynn explained. For example, the immune systems of people suffering from lupus are known to target several of the specific RNAs that can compose glycoRNAs.
"When you find something brand-new like these glycoRNAs, they're so many questions to ask," Flynn said.
INFORMATION:
Bertozzi is also a member of Stanford Bio-X, the Maternal & Child Health Research Institute (MCHRI), the Stanford Cancer Institute, Stanford ChEM-H and Stanford's Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute. Other current and former Stanford authors include Kayvon Pedram, now a group leader at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute; Stacy Malaker, now an assistant professor at Yale University; former graduate students Benjamin "Benjie" Smith, Alex Johnson, Benson George; Karim Majzoub, now a researcher at INSERM in Strasbourg, France; and Jan Carette, associate professor in Stanford's Department of Microbiology and Immunology. Carette is also a member of Stanford Bio-X and the Stanford Maternal & Child Health Research Institute and is a faculty fellow at Stanford ChEM-H.
This work was supported by grants from Damon Runyon Cancer Research, the Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career Award for Medical Scientists, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, the National Science Foundation, the Stanford ChEM-H Chemistry/Biology Interface Predoctoral Training Program, National Cancer Institute and Center for Cancer Research of the United States of America.