New species formed when the Mediterranean dried up
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) A new study may have uncovered why wall lizards have become the most successful reptile in the Mediterranean region. The results reveal how drastic changes in sea levels and climate 6 million years ago affected species formation in the area. The researchers believe they can now explain why the lizards became so diverse and widespread, something that has puzzled biologists since the 19th century. The study is published in Nature Communications.
The evolution of wall lizards offers clues on how major events in the Mediterranean climate and geology millions of years ago affected how species formed or became extinct, and also paved the way for biodiversity.
Wall lizards date back around 20 million years. However, species formation seems to have picked up speed shortly after the Messinian Salinity Crisis 6 million years ago. During this period the Mediterranean almost dried out, only to rapidly fill up with water again as the Strait of Gibraltar opened.
"Our results show that the dramatic changes at the time probably contributed to the emergence of new species. They also shed light on why biodiversity looks the way it does today", says Tobias Uller, professor of evolutionary ecology at Lund University who led the international study.
The research indicates that species isolated from each other for millions of years occasionally have found each other and shared genes. By comparing DNA sequences from 26 species and 8 subspecies, the team successfully mapped the major features of the evolution of wall lizards. This included what parts of the genome were transferred from other species through hybridization.
One example is the wall lizards found in Ibiza. Half of their genes come from wall lizards that today live on the Iberian Peninsula, and the other half from those found in the Balkans and among the Greek islands. The species in Ibiza thus originated as a hybrid, which provided evolution with great opportunities to combine old genes in new ways.
According to the researchers, this probably explains why species like the Ibiza wall lizard are so strikingly variable in colouration: despite close relationships and geographic proximity, they are a single colour on one island, but a variety of colours on the next, for example.
"We believe that hybridization has fuelled evolution, promoting biodiversity and extraordinary adaptability among certain species", concludes Tobias Uller.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-18
A University of Surrey project has revealed innovative methods that could dramatically improve the performance of future electrical vehicles (e-vehicles).
As part of the European Union's STEVE* project, Surrey has developed several pioneering approaches to torque vectoring in electric vehicles.
In e-vehicles with multiple motors, it is possible to deliver different amounts of drive power to each wheel. This benefits the vehicles' power consumption, safety and driveability. The process of calculating and optimising the precise amount of power needed while the vehicle ...
2021-05-18
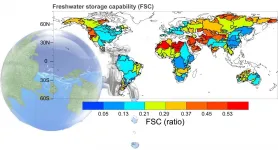
To support growing human and animal life, freshwater sources must continuously supply water. Freshwater from lakes, rivers, and underground is mainly recharged by rainfall. Ground reservoirs can store rainwater over time, depending on that location's storage capability. However, estimating freshwater storage capability (FSC) is still a challenge due to few observation opportunities and methods to measure and quantify FSC.
Prof. Xing Yuan and his Ph.D. student Enda Zhu, from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed and applied a new metric that characterizes the "inertia" of water after rainfall. This method allows better ...
2021-05-18
A research group at the University of Córdoba studied the molecular properties of the holm oak (Quercus ilex) in search of trees that are more resistant to drought and root rot.
One of the biggest problems affecting holm oaks is drought. The holm oak (Quercus ilex) boasts a high natural adaptability and resistance to inclement weather conditions in dry environments with high temperatures. However, drought is one of the main causes of mortality in holm oak plantations, with "drought stress" also an important factor contributing to root rot.
This is a multifactorial syndrome that causes the decay and death of holm oaks, consisting of a combination ...
2021-05-18
Scientists have developed a mathematical model that predicts how the number and effects of bacterial mutations leading to drug resistance will influence the success of antibiotic treatments.
Their model, described today in the journal eLife, provides new insights on the emergence of drug resistance in clinical settings and hints at how to design novel treatment strategies that help avoid this resistance occurring.
Antibiotic resistance is a significant public health challenge, caused by changes in bacterial cells that allow them to survive drugs that ...
2021-05-18
Researchers of Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) developed a new approach to determine the best electrode materials composition for Solid-state lithium-ion batteries. The results of the study were published in the first quartile journal Nanomaterials, MDPI. The Russian Science Foundation supports the project.
The development of miniature devices such as sensors and Internet of things (IoT) devices requires establishing small and complex power supplies with a high energy density. According to experts, traditional technologies for lithium-ion battery production reach their limits. It is difficult to reduce the size and control the shape of the power ...
2021-05-18
Analysing the forces at work behind the obstructions that cause heart attacks is crucial for identifying patients at risk of these events, says a study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest that bringing such biomechanical analyses into clinical practice could allow cardiologists to predict a future heart attack in patients by simulating the distribution of stress within diseased heart vessels.
A myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when the supply of blood to the heart is blocked by a blood clot or similar obstruction. A build-up of fatty deposits (lipids) over time forms plaques in the heart's arteries. If the plaque ruptures, it can form a blood clot that blocks the arteries and causes a heart attack.
Previous ...
2021-05-18
A research group led by Prof. LUO Tianzhi from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborating with Prof. WANG Zhengzhi's team from Wuhan University, explored the natural defenses in the tail spike of mantis shrimps and left chela of hermit crabs.
They revealed the chemical gradients from nanometer to centimeter and the correlation between micro-structure and mechanical properties. Also, they confirmed toughening mechanism and optimized structure principles through a 3D printing technique and finite-element analysis. The results were published in ACS Applied Materials ...
2021-05-18
HERSHEY, Pa. -- According to the World Health Organization, cervical cancer is the fourth most common form of cancer affecting women worldwide, and those in developing countries face a higher risk of dying from it. If detected early, cervical cancer responds well to treatment, however not everyone receives cancer screenings.
A team of researchers, including those from Penn State College of Medicine, took a closer look at cervical cancer in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) to determine the prevalence and key factors that influence cancer screenings. The group found that despite high mortality rates, cancer screenings are substantially low, and there are multiple reasons why.
In a new study, published in Cancer ...
2021-05-18
Autism spectrum disorder is a neurodevelopmental condition involving impaired social abilities, and this makes it a fascinating subject for neuroscientists like Prof. Teiichi Furuichi of the Tokyo University of Science who study the neuroscience of social behavior. Prof. Furuichi and his colleagues have previously worked on developing mouse models of autism to unravel the condition's neurochemical mechanisms, and in a paper recently published in the prestigious Journal of Neuroscience, they provide evidence that a genetic mutation associated with autism can impair the release of a peptide called oxytocin that plays an important role in regulating social behavior. This finding promises to broaden our understanding of the neurobiology of social behavior.
The gene that Prof. ...
2021-05-18
In the field of international business research, lobbying is considered a legitimate and legal political action conducted in a developed economy. Bribery, on the other hand, is seen as an outright corrupt practice in an emerging economy.
In a study published in the March issue of the journal Business & Society, a researcher from The University of Texas at Dallas examined the gray area between lobbying and bribery among multinational companies, especially in countries where lobbying is not regulated strongly or institutional development is insufficient.
The analysis found that firms based in developed countries, as opposed to developing countries or transition economies, are more likely to influence the institutional ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New species formed when the Mediterranean dried up