(Press-News.org) University of California scientists have discovered genetic data that will help food crops like tomatoes and rice survive longer, more intense periods of drought on our warming planet.
Over the course of the last decade, the research team sought to create a molecular atlas of crop roots, where plants first detect the effects of drought and other environmental threats. In so doing, they uncovered genes that scientists can use to protect the plants from these stresses.
Their work, published today in the journal Cell, achieved a high degree of understanding of the root functions because it combined genetic data from different cells of tomato roots grown both indoors and outside.
"Frequently, researchers do lab and greenhouse experiments, but farmers grow things in the field, and this data looks at field samples too," said Neelima Sinha, a UC Davis professor of plant biology and the paper's co-author.
The data yielded information about genes that tell the plant to make three key things.
Xylem are hollow, pipe-like vessels that transport water and nutrients from the roots all the way up to the shoots. Without transport in xylem, the plant cannot create its own food via photosynthesis.
"Xylem are very important to shore up plants against drought as well as salt and other stresses," said lead study author Siobhan Brady, a professor of plant biology at UC Davis.
In turn, without plant mineral transport in xylem, humans and other animals would have fewer vitamins and nutrients essential for our survival. In addition to some typical players needed to form the xylem, new and surprising genes were found.
The second key set of genes are those that direct an outer layer of the root to produce lignin and suberin. Suberin is the key substance in cork and it surrounds plant cells in a thick layer, holding in water during drought.
Crops like tomatoes and rice have suberin in the roots. Apple fruits have suberin surrounding their outer cells. Anywhere it occurs, it prevents the plant from losing water. Lignin also waterproofs cells and provides mechanical support.
"Suberin and lignin are natural forms of drought protection, and now that the genes that encode for them in this very specific layer of cells have been identified, these compounds can be enhanced," said study co-author Julia Bailey-Serres, a UC Riverside professor of genetics.
"I'm excited we've learned so much about the genes regulating this moisture barrier layer. It is so important for being able to improve drought tolerance for crops," she said.
Genes that encode for a plant's root meristem also turned out to be remarkably similar between tomato, rice, and Arabidopsis, a weed-like model plant. The meristem is the growing tip of each root, and it's the source of all the cells that make up the root.
"It's the region that's going to make the rest of the root, and serves as its stem cell niche," said Bailey-Serres. "It dictates the properties of the roots themselves, such as how big they get. Having knowledge of it can help us develop better root systems."
Brady explained that when farmers are interested in a particular crop, they select plants that have features they can see, such as bigger, more attractive fruits. Much more difficult is for breeders to select plants with properties below ground they can't see.
"The 'hidden half' of a plant, below ground, is critical for breeders to consider if they want to grow a plant successfully," Brady said. "Being able to modify the meristem of a plant's roots will help us engineer crops with more desirable properties."
Though this study analyzed only three plants, the team believes the findings can be applied more broadly.
"Tomato and rice are separated by more than 125 million years of evolution, yet we still see similarities between the genes that control key characteristics," said Bailey-Serres. "It's likely these similarities hold true for other crops too."
INFORMATION:
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that adults ages 45 to 75 be screened for colorectal cancer, lowering the age for screening that was previously 50 to 75. The USPSTF also recommends that clinicians selectively offer screening to adults 76 to 85 years of age. Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death for both men and women in the United States. In 2016, 26% of eligible adults had never been screened and nearly one-third were not up to date with screening in 2018. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this statement replaces its 2016 recommendation.
To access the embargoed study: ...
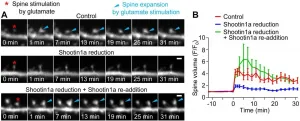
Ikoma, Japan - In neurons, changes in the size of dendritic spines - small cellular protrusions involved in synaptic transmission - are thought to be a key mechanism underlying learning and memory. However, the specific way in which these structural changes occur remains unknown. In a study published in Cell Reports, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have revealed that the binding of cell adhesion molecules with actin, via an important linker protein in the structural backbone of synapses, is vital for this process of structural plasticity.
Actin proteins make up an important part of a cell's structure, or cytoskeleton, and allow for dynamic changes in this structure by forming ...
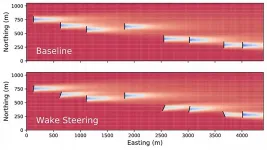
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- Wake steering is a strategy employed at wind power plants involving misaligning upstream turbines with the wind direction to deflect wakes away from downstream turbines, which consequently increases the net production of wind power at a plant.
In Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) illustrate how wake steering can increase energy production for a large sampling of commercial land-based U.S. wind power plants.
While some plants showed less potential for wake steering due to unfavorable meteorological conditions or turbine layout, several wind power plants were ideal candidates ...
What The Study Did: Telemedicine use grew rapidly during the COVID-19 pandemic but there was geographic variation in its use so researchers in this study examined the association of county-level telemedicine use with community factors among people with commercial or Medicare Advantage insurance.
Authors: Ateev Mehrotra, M.D., M.P.H., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10330)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and ...
What The Study Did: Demographic information from 105 randomized clinical trials for primary open-angle glaucoma was combined to compare the rate of participation between individuals from racial/ethnic minority groups with white individuals.
Authors: Deepkumar G. Patel, D.D.S., M.P.H., of New York Ophthalmology Associates in Manhattan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.8348)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
Research to be published tomorrow in the journal Nature Communications is the first study to quantify the costs of storm damage caused by sea level rise driven specifically by human-induced climate change. Researchers from Stevens Institute of Technology, Climate Central, Rutgers University and other institutions found this self-inflicted damage to be $8.1 billion of Hurricane Sandy's damage and an additional 71,000 people and 36,000 homes exposed to Sandy's flooding.
Hurricane Sandy struck the northeast U.S. coast in 2012, causing widespread destruction estimated at ...
BOSTON - Prompted by a recent alarming rise in cases of colorectal cancer in people younger than 50, an independent expert panel has recommended that individuals of average risk for the disease begin screening exams at 45 years of age instead of the traditional 50.
The guideline changes by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), published in the current issue of JAMA, updates its 2016 recommendations and aligns them with those of the American Cancer Society, which lowered the age for initiation of screening to 45 years in 2018.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most preventable malignancies, owing to its long natural history of progression and the availability ...
CLEVELAND - According to new study results, a team of researchers led by Cleveland Clinic's Thaddeus Stappenbeck, M.D., Ph.D., have found that a diet high in fat and sugar is associated with impaired intestinal immune cell function in mice. The findings, published in Cell Host & Microbe, provide novel insights into pathways linking obesity and disease-driving gut inflammation, and have implications for developing targets to treat inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) in patients.
Using data from more than 900 patients, the researchers found that elevated body mass index is associated with abnormal Paneth cells among patients with Crohn's disease and non-IBD patients.
Paneth cells are a type of anti-inflammatory immune cell found in ...
Eating a Western diet impairs the immune system in the gut in ways that could increase risk of infection and inflammatory bowel disease, according to a study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and Cleveland Clinic.
The study, in mice and people, showed that a diet high in sugar and fat causes damage to Paneth cells, immune cells in the gut that help keep inflammation in check. When Paneth cells aren't functioning properly, the gut immune system is excessively prone to inflammation, putting people at risk of inflammatory bowel disease and undermining effective control of disease-causing microbes. The findings, published May 18 in Cell Host & Microbe, open up new approaches to regulating gut immunity by restoring normal Paneth cell function.
"Inflammatory ...
Scientists led by Dr. Salvador Aznar-Benitah, head of the Stem Cells and Cancer laboratory at IRB Barcelona, have described the alterations that occur during mammary gland formation when heterochromatin (the part of DNA that does not actively produce proteins) is poorly regulated. The results, which have been published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, indicate that incorrect DNA packaging makes retrotransposons (a type of transposable element originated in ancestral fragments of viruses integrated into the cell genome) more accessible.
As these fragments are more accessible, they can be "read" and copied ...