Risk scores for predicting short-term outcomes for patients with unexplained syncope
2021-05-19
(Press-News.org) Des Plaines, IL - The Canadian Syncope Risk Score (CSRS) is an accurate validated prediction score for emergency department patients with unexplained syncope. These are the results of a study titled Multivariable risk scores for predicting short-term outcomes for emergency department patients with unexplained syncope: A systematic review, to be published in the May issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM) journal, peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
Syncope is a common presentation to an emergency department, with patients at risk of experiencing an adverse event within 30 days. Without a standardized risk stratification system of patients, there will be health care disparities and inconsistent patient care, which may lead to poor outcomes.
Overall, this systematic review provides an updated qualitative overview of the accuracy of nine risk stratification scores among adult patients following a syncopal event. Many scores in the study are not validated or not sufficiently accurate for clinical use. Other risk scores were not validated on an independent sample, had low positive likelihood ratios for identifying patients at high risk, or had high negative likelihood ratios for identifying patients at low risk.
While more longitudinal studies are required prior to changing guidelines, the Canadian Syncope Risk Score was the most accurate at classifying patients at low and high risk for adverse events. This provides a promising ability to assist physicians in determining whether patients warrant additional workup or admission to hospital. Its impact on clinical decision making, admission rates, cost, or outcomes of care is not known and therefore, further research is recommended.
The lead author of the report is Rachel A. L. Sweanor, BMBS, from the division of internal medicine, Sunnybrook Health Sciences, and the department of medicine, University of Toronto, both in Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Commenting on the study is Venkatesh Thiruganasambandamoorthy, CCFP-EM, MSc, associate professor in the department of emergency medicine and the School of Epidemiology and Public Health and senior scientist at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. Dr. Thiruganasambandamoorthy also serves as the clinical research chair in cardiovascular emergencies and as a mid-career clinical researcher at Physicians' Services Incorporated Foundation.
"While there have been significant advances in emergency department syncope risk stratification, this systematic review highlights the weaknesses of several risk tools previously published. Risk tools reduce uncertainty in medical decision-making by providing probabilities of serious outcome at a specified time and should have undergone the three major stages of development: derivation, validation, and implementation. Implementation to demonstrate true effect on patient care is the ultimate test for any clinical decision tool."
INFORMATION:
ABOUT ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
Academic Emergency Medicine, the monthly journal of Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, features the best in peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research relevant to the practice and investigation of emergency care. The above study is published open access and can be downloaded by following the DOI link: 10.1111/acem.14203. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Tami Craig at tcraig@saem.org.
ABOUT THE SOCIETY FOR ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
SAEM is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit organization dedicated to the improvement of care of the acutely ill and injured patient by leading the advancement of academic emergency medicine through education and research, advocacy, and professional development. To learn more, visit saem.org.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-19
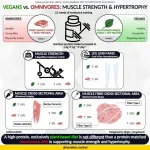
Protein intake is more important than protein source if the goal is to gain muscle strength and mass. This is the key finding of a study that compared the effects of strength training in volunteers with a vegan or omnivorous diet, both with protein content considered adequate.
In the study, which was conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil, 38 healthy young adults, half of whom were vegans and half omnivores, were monitored for 12 weeks. In addition to performing exercises to increase muscle strength and mass, the volunteers followed either a mixed diet with both ...
2021-05-19
Artificial intelligence is providing new opportunities in a range of fields, from business to industrial design to entertainment. But how about civil engineering and city planning? How might machine- and deep-learning help us create safer, more sustainable, and resilient built environments?
A team of researchers from the NSF NHERI SimCenter, a computational modeling and simulation center for the natural hazards engineering community based at the University of California, Berkeley, have developed a suite of tools called BRAILS -- Building Recognition ...
2021-05-19
Quality of life relating to physical and mental health can be a key element in the treatment of obese adults. For this reason, interdisciplinary clinical measures including cognitive and behavioral therapy may produce more significant outcomes for these people, reducing not just weight but also symptoms of depression.
This is the main conclusion of a study conducted in Brazil by the Obesity Research Group at the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) in Santos, São Paulo state, and published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition.
Considered one of the world’s major public health problems, obesity has ...
2021-05-19
EVANSTON, Ill. --- Self-affirmation, the practice of reflecting upon one's most important values, can aid Black medical students in reaching their residency goals. But conversely, it can lead to the perception that they are less qualified for a prestigious residency than their peers.
The pandemic has underscored the racial disparities in the quality of healthcare, a field in which Black Americans are vastly underrepresented as medical physicians.
New Northwestern University research aims to address the "leaky pipeline" preventing Black medical students from completing medical school to pursuing residencies in high-need and underrepresented areas.
Sylvia Perry, assistant professor of psychology in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences at Northwestern, is the ...
2021-05-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Though obesity in midlife is linked to an increased risk for Alzheimer's disease, new research suggests that a high body mass index later in life doesn't necessarily translate to greater chances of developing the brain disease.
In the study, researchers compared data from two groups of people who had been diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment - half whose disease progressed to Alzheimer's in 24 months and half whose condition did not worsen.
The researchers zeroed in on two risk factors: body mass index (BMI) and a cluster of ...
2021-05-19
BOSTON - In a major breakthrough, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have discovered how amyloid beta--the neurotoxin believed to be at the root of Alzheimer's disease (AD)--forms in axons and related structures that connect neurons in the brain, where it causes the most damage. Their findings, published in Cell Reports, could serve as a guidepost for developing new therapies to prevent the onset of this devastating neurological disease.
Among his many contributions to research on AD, Rudolph Tanzi, PhD, vice chair of Neurology and co-director of the McCance Center for Brain Health at MGH, led a team ...
2021-05-19
The development of antibodies to the COVID-19 virus has been the great long-term hope of ending the pandemic. However, immune system turncoats are also major culprits in severe cases of COVID-19, Yale scientists report in the journal Nature.
These autoantibodies target and react with a person's tissues or organs similar to ones that cause autoimmune diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. In COVID-19 cases they can attack healthy tissue in brain, blood vessels, platelets, liver, and the gastrointestinal tract, researchers report. The more autoantibodies detected, the greater the disease severity experienced ...
2021-05-19
A research team has found that a method commonly used to skirt one of metal 3D printing's biggest problems may be far from a silver bullet.
For manufacturers, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, provides a means of building complex-shaped parts that are more durable, lighter and more environmentally friendly than those made through traditional methods. The industry is burgeoning, with some predicting it to double in size every three years, but growth often goes hand in hand with growing pains.
Residual stress, a byproduct of the repeated heating and cooling inherent to metal printing processes, can ...
2021-05-19
During a 15-year study of wild bees visiting blueberry fields during their blooming season, researchers caught an unexpected glimpse of how extreme weather events can impact bee populations highlighting the need for more long-term studies, says a Michigan State University researcher.
"There are few bee studies in the U.S. that have sampled bees for many years at the same location," said Rufus Isaacs, a professor in the Department of Entomology within the College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, "There are even fewer that use the same methods over more than a decade."
The research ...
2021-05-19
The younger generation of workers, although raised with and on technology, are not as technology savvy as the older generations believe.
A new study by researchers in The University of Toledo John B. and Lillian E. Neff College of Business and Innovation published in the END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Risk scores for predicting short-term outcomes for patients with unexplained syncope