Nuclear terrorism could be intercepted by neutron-gamma detector that pinpoints source
2021-05-19
(Press-News.org) Scanning technology aimed at detecting small amounts of nuclear materials was unveiled by scientists in Sweden today, with the hope of preventing acts of nuclear terrorism.
Bo Cederwall, a professor of physics at KTH Royal Institute of Technology, says the technology can be used in airports and seaports for routine inspection of passengers and goods. The research is published and featured in the journals Science Advances and Science, respectively.
A form of tomography, the system enables quick 3D imaging of the source of neutron and gamma ray emissions from weapons-grade plutonium and other special nuclear materials, Cederwall says.
The so-called Neutron-Gamma Emission Tomography (NGET) system goes beyond the capabilities of existing radiation portal monitors, by measuring the time and energy correlations between particles emitted in nuclear fission, and using machine learning algorithms to visualize where they're coming from. The system looks for coincidences of neutron and gamma ray emissions--which when mapped together in real-time allow pinpointing their origin.
"The technology has a very high sensitivity and can within a few seconds detect gram-amounts of plutonium depending on the application and the plutonium isotope composition," Cederwall says. "It takes a little longer to get a really good picture so you can see exactly where the plutonium is. However, this can be done completely automatically."
But NGET isn't only for nuclear weapons and radiation-dispersing "dirty bombs"--it can be used to detect environmental radiation too, such as leaks from nuclear facilities or even natural sources. Cederwall says the research group is looking into equipping drones with the NGET system for this purpose.
"In case of a radiological emergency, It is extremely important to be able to quickly map the radioactive contamination in the environment in order to protect the population in the best possible way," he says.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-19
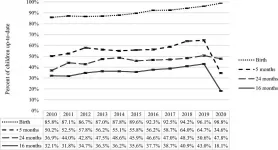
Despite expert recommendations that children continue to get regularly scheduled vaccines during the pandemic, vaccination rates have decreased in several states.
A new study by researchers from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health and several other research institutions looked at childhood immunization rates in Texas to see what effect the COVID-19 pandemic may have had on childhood immunizations in 2020. In the study, led by public health doctoral student Tasmiah Nuzhath and published in the journal Vaccine, the researchers used data from a statewide immunization registry ...
2021-05-19
May 19, 2021 - For patients with severe arthritis of the ankle, total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) provides better long-term function than ankle arthrodesis (AA), reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
"Both established treatments for end-stage ankle arthritis are effective at pain relief and improved patient-reported outcomes," according to the research by Bruce Sangeorzan MD, and colleagues at the University of Washington and VA Puget Sound Health Care System. "However, it appears TAA leads to greater improvement in most patient-reported outcome measures at 48 months after surgery."
Study adds to evidence supporting TAA for ankle arthritis
End-stage ankle arthritis is characterized ...
2021-05-19
The continued growth of wireless and cellular data traffic relies heavily on light waves. Microwave photonics is the field of technology that is dedicated to the distribution and processing of electrical information signals using optical means. Compared with traditional solutions based on electronics alone, microwave photonic systems can handle massive amounts of data. Therefore, microwave photonics has become increasingly important as part of 5G cellular networks and beyond. A primary task of microwave photonics is the realization of narrowband filters: the selection of specific data, at specific frequencies, out of immense volumes that are carried over light.
Many microwave photonic systems are built ...
2021-05-19
Scientists at SPECIFIC Innovation and Knowledge Centre, Swansea University, have found a way to replace the toxic, unsustainable solvents currently needed to make the next generation of solar technology.
Printed carbon perovskite solar cells have been described as a likely front runner to the market because they are extremely efficient at converting light to electricity, cheap and easy to make.
A major barrier to the large-scale manufacture and commercialisation of these cells is the solvents used to control crystallisation of the perovskite during fabrication: this is because they are ...
2021-05-19
ITHACA, N.Y. - For the first time, Cornell University researchers have developed a technique for studying the neuroscience of motor control in mice ¬- by focusing on a mouse's tongue when it licks a water spout.
The technique incorporates high-speed cameras and machine learning in a tractable experimental setup that opens the door for revealing mysteries of how the motor cortex works, understanding the neural basis of related disorders like Parkinson's disease, and informing robots.
"We now have an approach in a mouse where we can bring all the tools of modern neuroscience to bear on this really classic problem of motor control," said senior author Jesse Goldberg, associate professor of neurobiology and behavior.
The field of motor control neuroscience has made advancements ...
2021-05-19
Updated Criteria Also Released for Legius Syndrome and Mosaic NF
NF2 and Schwannomatosis Diagnostic Criteria to Be Released Later This Year
The Children's Tumor Foundation (CTF) today announced the publication of updated diagnostic criteria for the genetic disorder neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) in Genetics in Medicine, the official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. The new publication is the result of an extensive, multi-year collaborative effort of over 90 leading neurofibromatosis (NF) experts from around the globe, and is aimed at improving the accuracy and earlier diagnosis of NF1 in patients, thus ultimately leading to improved care and quality of life for those patients. ...
2021-05-19
Open up Scott Roy's Twitter bio and you'll see a simple but revealing sentence: "The more I learn the more I'm confused." Now the rest of the scientific world can share in his confusion. The San Francisco State University associate professor of Biology's most recent research, published earlier this month in one of the scientific world's most prestigious journals, catalogues a strange and confounding system of genes in a tiny rodent that scientists have ignored for decades.
"This is basically the weirdest sex chromosome system known to science," Roy said. "Nobody ordered this." But he's serving it anyway.
The owner of those chromosomes is the creeping vole, a burrowing rodent native to the Pacific Northwest. Scientists ...
2021-05-19
In recent years, foresters have been able to observe it up close: First, prolonged drought weakens the trees, then bark beetles and other pests attack. While healthy trees keep the invaders away with resin, stressed ones are virtually defenseless. Freiburg scientist Sylvie Berthelot and her team of researchers from the Faculty of Environment and Natural Resources and the Faculty of Biology are studying the importance of tree diversity on bark beetle infestation. They are investigating whether the composition of tree species affects bark beetle feeding behavior. The team recently published their findings in the Journal of Ecology.
In a 1.1 hectare experimental set-up in Freiburg, six native deciduous and coniferous tree species from Europe and six deciduous and coniferous ...
2021-05-19
SAN ANTONIO (May 19, 2021) -- Four months of multi-drug therapy that included rifapentine and moxifloxacin treated active tuberculosis (TB) as effectively as the standard six-month regimen in a multinational study, cutting treatment time by a third. Coauthors including Marc Weiner, MD, of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, reported the findings May 6 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"Shorter treatment would be easier for people to complete without missing doses, and ultimately may be cost-effective," said Dr. Weiner, associate professor in the health science center's Joe R. and Teresa Lozano END ...
2021-05-19
A team of researchers at the Centre Spatial de Liège (CSL) of the University of Liège has just developed a method to identify the contributors and origins of stray light on space telescopes. This is a major advance in the field of space engineering that will help in the acquisition of even finer space images and the development of increasingly efficient space instruments. This study has just been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Space telescopes are becoming more and more powerful. Technological developments in recent years have made it possible, for example, to observe objects further and further into the universe or to measure the composition of the Earth's atmosphere with ever greater precision. However, there is still one factor limiting the performance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nuclear terrorism could be intercepted by neutron-gamma detector that pinpoints source