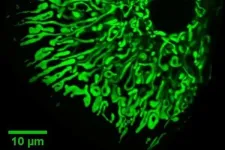
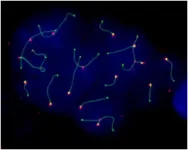
How plants leave behind their parents' genomic baggage
2021-05-20
(Press-News.org) Passing down a healthy genome is a critical part of creating viable offspring. But what happens when you have harmful modifications in your genome that you don't want to pass down? Baby plants have evolved a method to wipe the slate clean and reinstall only the modifications that they need to grow and develop. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor & HHMI Investigator Rob Martienssen and his collaborators, Jean-Sébastien Parent and Institut de Recherche pour le Développement Université de Montpellier scientist Daniel Grimanelli, discovered one of the genes responsible for reinstalling modifications in a baby plant's genome.
A plant's genomic modifications--called epigenetic modifications--help turn off genes at the right times. Epigenetic changes accumulate with age. Martienssen explains:
"If you think about a tree, the flowers that arise a hundred years after it germinated, they're obviously a long way from the original acorn, and an awful lot of epigenetic changes could happen in that period. And so, these are important resets for development so that you don't inherit this epigenetic collateral damage."
Martienssen's team discovered that after baby plants remove the epigenetic modifications, the SUVH9 protein puts back the ones they need to survive. Without SUVH9, plants develop poorly because the wrong genes turn on at the wrong time. Parent, a research scientist at Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, says:
"I remember this moment where we were like, 'Wow! This is not what we expected.' There was an opening for an actor that was not accounted for in the standard models, and that was the most innovative part of our story."
The SUVH9 protein uses small snippets of RNA to look for the right places to reinstall the beneficial modifications, which are on mobile genetic elements known as transposons. The SUVH9 protein adds the epigenetic modifications to them, and this ensures nearby genes are turned off at the right time. Reinstalling the beneficial modifications also stops the transposons from jumping around in the genome and disrupting other genes.
The scientists think SUVH9 protein contributed to today's plant diversity. By stopping harmful transposons from disrupting genes, the protein allowed different species to evolve. Parent says:
"One of the big mysteries about flowering plants is how they manage to become so diverse and to generate so many different species so quickly in evolutionary history. And, we believe that we are touching here a part of a molecular mechanism that can allow this sort of flexibility."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-20
The study sought to describe and explain gender pay differences in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services between 2010 and 2018. HHS comprises a quarter of the country's governmental public health workers, with over 80,000 employees.
Understanding what may be driving wage gaps at HHS provides opportunities for employers and legislators to take action to support women in the health care field, said lead author Zhuo "Adam" Chen, an associate professor of health policy and management at UGA's College of Public Health.
"A large percentage of the health care workforce are women," said Chen. "If you have underpaid women in the profession, I don't think it spells good things for the public health system."
Chen ...
2021-05-20
Maywood, Ill. - May 19, 2021 - A team of scientists from Loyola University Chicago's Stritch School of Medicine have discovered a critical component for renewing the heart's molecular motor, which breaks down in heart failure.
Approximately 6.2 million Americans have heart failure, an often fatal condition characterized by the heart's inability to pump enough blood and oxygen throughout the body. This discovery could represent a novel approach to repair the heart.
Their findings, published in the May 19 issue of Nature Communications, show how a protein called BAG3 helps replace "worn-out" components of the cardiac sarcomere. The sarcomere is a microscopic ...
2021-05-20
FINDINGS
A new multi-institution study led by a team of researchers at the David Geffen School of Medicine demonstrated that blocking a protein called ABCB10 in liver cells protects against high blood sugar and fatty liver disease in obese mice. Furthermore, ABCB10 activity prompted insulin resistance in human liver cells.
The findings are the first to show that ABCB10 transports biliverdin out of the mitochondria - the cell's "energy generating powerhouses." Biliverdin is the precursor of bilirubin, a substance with antioxidant properties. Consequently, ABCB10 transport ...
2021-05-20
So, you thought the problem of false information on social media could not be any worse? Allow us to respectfully offer evidence to the contrary.
Not only is misinformation increasing online, but attempting to correct it politely on Twitter can have negative consequences, leading to even less-accurate tweets and more toxicity from the people being corrected, according to a new study co-authored by a group of MIT scholars.
The study was centered around a Twitter field experiment in which a research team offered polite corrections, complete with ...
2021-05-20
Orangutans are closely related to humans. And yet, they are much less sociable than other species of great apes. Previous studies have showed that young orangutans mainly acquire their knowledge and skills from their mothers and other conspecifics. Social learning in orangutans occurs through peering, i.e. sustained observation of other members of the species at close range.
An international team led by the University of Zurich (UZH) has now studied peering behavior in young orangutans at two research stations on the islands of Sumatra and Borneo. The data was collected by researchers from the Department of Anthropology of UZH, the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior in Constance, the Universitas Nasional in Jakarta and Leipzig University, ...
2021-05-20
Do we have free choice or are our decisions predetermined? Is physical reality local, or does what we do here and now have an immediate influence on events elsewhere? The answers to these questions are sought by physicists in the Bell inequalities. It turns out that free choice and local realism can be skilfully measured and compared. The results obtained reveal surprising relationships of a fundamental and universal nature, going far beyond quantum mechanics itself.
Causality, locality, and free choice are related by a few simple formulas known as Bell's inequalities. The sophisticated experiments in quantum optics over the past few decades have unquestionably proved that these inequalities are broken. Today, physicists are ...
2021-05-20
The genome is tightly organised (packaged) within the cell nuclei. This three-dimensional (3D) genome organisation is fundamental, given that it regulates gene expression.
A study led by scientists at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) now demonstrates using mice models that the 3D organisation of the genome is extremely dynamic during the formation of male germ cells (precursors of spermatozoa) and that alterations in this structure can affect fertility.
The research, published in Nature Communications, describes the 3D genome organisation in germ cells of wild populations of house mice (Mus musculus domesticus) with chromosomal rearrangements, ...
2021-05-20
Since they are far more compact than today's accelerators, which can be kilometers long, plasma accelerators are considered as a promising technology for the future. An international research group has now made significant progress in the further development of this approach: With two complementary experiments at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and at the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munich (LMU), the team was able to combine two different plasma technologies for the first time and build a novel hybrid accelerator. The concept could advance accelerator development ...
2021-05-20
An international team, led by researchers from Pompeu Fabra University (UPF) in Barcelona, Spain, David Andreu and Rafael Maldonado, has developed a peptides family that allows delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main component of Cannabis sativa, to fight pain in mice without side effects. The study, published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, was carried out together with researchers from the Autonomous University of Barcelona, ??the University of Barcelona, and the University of Lisbon.
At present, there are two main types of pain relievers prescribed based on the severity of the pain. Nonsteroidal ...
2021-05-20
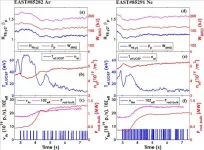
The high-power and long-pulse operation of tokamak will cause excessive particle flux and heat load on the divertor target plate. The surface of the target plate will be subject to intense sputtering, and the thermal load of the target plate will exceed the material/component limit.
The sputtered atoms generated by the damage of the target plate may be transported to the core plasma, degrading the quality of the fusion plasma and increasing the difficulty of plasma stability control.
Recently, the EAST group of Institute of Plasma Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), reported their new findings about the influence of different impurity gases ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How plants leave behind their parents' genomic baggage