(Press-News.org) COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Passports are a tangible way of showing where one has traveled, as the stamps provide a chronological order that traces an individual's journey across international borders. When an object's origins are not readily apparent, a variety of sources can be relied upon to learn more, which might include labels, sales receipts, foreign translations, oral histories, GPS coordinates and itemized personal possessions.
That documentation is an example of provenance, or the origins of an object and where it has traveled throughout history. Sarah Buchanan, an assistant professor in the University of Missouri's College of Education, is an archivist, a professional who assesses, collects and preserves various artifacts and archives them to better understand their origin and cultural heritage.
With a three-year grant, Buchanan is investigating ways to conduct provenance research more efficiently, inclusively and transparently, both on MU's campus and abroad. In a recently published study, Buchanan collaborated with Sara Mohr, a doctoral student at Brown University who reads and translates Assyrian, to create an online bibliography and corresponding map of ancient tablets located in universities throughout the United States, including six tablets inside MU's Ellis Library.
The tablets were written in cuneiform, the first writing system ever used by humans. It was first developed by the ancient Sumerians of Mesopotamia around 3,200 B.C.E in modern-day Iraq. Written on clay tablets, the writing system was used to document things like trade, business and religious activities at ancient temples.
"We identified cuneiform tablets at Brown University that complement the six we have here at Mizzou, and when we look at all of them together, we have a fuller, more compelling story about the societal context of their creation," Buchanan said. "If we only look at ours, it is like reading a page of a book that is half cut out. Their combination shows how powerful digitizing these artifacts can be, as it allows us to analyze two tablets side by side online that are otherwise thousands of miles apart."
The importance of provenance extends well beyond cuneiform tablets. Buchanan's research also includes studying rare books and manuscripts, audio recordings, Native American and indigenous collections, artwork, photos, and videos.
"Provenance shapes the stories that are told about objects and their owners," Buchanan said. "Artifacts and archives are a form of our history. They shed light on our cultural heritage that roots us as humans in where we have been and where we are going."
Museums can use provenance to assess the authenticity of collections on display. In Washington, D.C., officials from the Museum of the Bible accepted donated antiquities, including alleged fragments of the Dead Sea Scrolls-- ancient Jewish manuscripts with significant religious ties to the Hebrew Bible and Judaism-- that turned out to be fake.
After suspicions that the fragments were created recently, an investigation by independent researchers, which was funded by the museum itself, confirmed in November 2019 that all of the displayed fragments were modern forgeries.
"Unfortunate situations like this show why provenance research is so important, as there is a real accountability issue when artifacts, photographs or artwork are found to be doctored or forged," Buchanan said. "This work will help give a wider range of artifacts a clearer provenance so that we can be sure when pieces are exhibited in museums, that they truly are what we say they are and can be attributed back to a specific time and place."
Provenance can also help play a role in repatriation, or the return of a valued item to its place of origin. In 2018, Bowling Green State University announced that ancient mosaics housed in the university's Wolfe Center for the Arts purchased in good faith with the belief that they were excavated from ancient Antioch had actually been looted in the 1960s from Zeugma and later sold on the black market.
After years of talks between the university and the Turkish government, the 12 mosaics were returned to Turkey, where they are now on display at the Zeugma Mosaic Museum, the largest mosaic museum in the world.
"As archivists, we are tasked with determining how, where and when these historic objects traveled across land and time," Buchanan said. "Traditionally, institutions tend to display only items that have clear provenance. As we refine our methods of researching provenance, we will be able to narrate a greater number and variety of previously unstudied artifacts and share them with new audiences."
Because America's history is closely intertwined with immigration and the oppression of minority groups, provenance research can help archivists tell more complete stories -- the good, the bad and the ugly -- surrounding artifacts with murky history.
"Provenance can help us confront our history when it comes to topics like war, colonialism and land acknowledgments," Buchanan said. "By uncovering a greater number of artifacts, we can properly tell more stories so that more cultures are represented, particularly the cultures of traditionally marginalized groups like Native Americans."
Through conversations with Native American tribes, Buchanan has learned the power of collaboration and civil discourse in facilitating more inclusive storytelling.
"There is always the potential for repatriation," Buchanan said. "However, we have also learned that several Native American tribes are open to particular artifacts remaining here at Mizzou's Museum of Anthropology, where climate controls and procedures are in place to properly care for the artifacts."
As a professor in the College of Education's School of Information Science & Learning Technologies, Buchanan teaches graduate students in the archival studies emphasis of MU's Master of Library and Information Science program.
In 2018, she supervised graduate students in the program as they inventoried and digitized audio recordings with KOPN, a community radio station in Columbia, Missouri. The recordings cover interviews with political figures such as Angela Davis, and social topics such as the feminist movement in the 1970s. The collection of recordings was recently featured by GBH, the NPR radio affiliate in Boston, and the Library of Congress in March for Women's History Month.
"This grant will help us get tools into the hands of archivists so we can be more responsive to our communities and make our collections meaningful to their work." Buchanan said.
As technology has advanced, the value of provenance in documenting ownership of rare items has transferred to the digital world online. Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, have become increasingly popular and raised more than a few eyebrows in mainstream media. They are digital tokens attached to online items such as videos, photos or artwork that document their authenticity and original ownership, a clear way to show that they have not been altered or faked.
"I am passionate about teaching the next generation of archivists," Buchanan said. "Studying cuneiform in America is just the tip of the iceberg. The more we learn going forward, the better we can tell stories about a wide variety of items' origin in a clear and compelling way."
Editor's note: "A Bibliography of Cuneiform Tablet Editions in United States Colleges and Universities through 2020" was recently published in the Journal of Open Humanities Data. Funding for the study and Buchanan's Early Career Development grant was provided by the Institute of Museum and Library Services. The cuneiform tablets located in Ellis Library can be viewed and read further here.
INFORMATION:
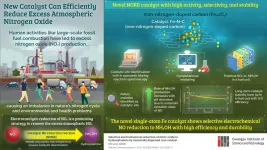
Our reliance on fossil fuels as a primary energy source has pushed air pollution to an all-time high, resulting in several environmental and health concerns. Among the major pollutants, nitrogen oxide (NOx) accumulation can cause severe respiratory diseases and imbalance in the Earth's nitrogen cycle. Reducing NOx accumulation is, therefore, an issue of utmost importance.
Recently, the conversion of NOx into harmless or even useful nitrogen products has emerged as a promising strategy. Particularly appealing to scientists is the reduction of NOx to hydroxylamine (NH2OH), which can be utilized ...
A large-scale research project at the University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute has revealed insight into the relationship between surface debris on glaciers and the rate at which they melt.
The work is the first global assessment of Earth's 92,033 debris-covered glaciers and shows that debris, taken as a whole, substantially reduces glacier mass loss.
The results will affect sea level rise calculations and allow for improved assessment of hazards faced by nearby communities.
"This is the first step to enable us to start projecting how these debris-covered glaciers are going to evolve in the future and how they're going to affect glacial runoff and sea level rise," said glaciologist ...
May 20, 2021 - Comets that circle the Sun in very elongated orbits spread their debris so thin along their orbit or eject it out of the solar system altogether that their meteor showers are hard to detect. From a new meteor shower survey published in the journal Icarus, researchers now report that they can detect showers from the debris in the path of comets that pass close to Earth orbit and are known to return as infrequent as once every 4,000 years.
"This creates a situational awareness for potentially hazardous comets that were last near-Earth orbit as far back as 2,000 BC," said meteor astronomer and lead author Peter Jenniskens of the SETI Institute.
Jenniskens is the ...
Building more homes and buildings with wood has been on the radar for years as a way to offset carbon emissions, though construction companies have been hesitant to take the material in broader use. A study at Aalto University in Finland is now the first to show that building with wood can be a sound investment.
The team analysed statistical data from real estate sales in the Finnish capital of Helsinki and two suburbs, from 1999 to 2018. Of these, timber-built homes made up 2.23% of cases. The findings show that multi-storied buildings made out of wood sold for an average of 8.85% more than those made from other materials.
Previous research has pointed to perceptions of higher costs in wood construction, ...
Biologist Sasha Mendjan at the Austrian Academy of Sciences in Vienna and his team have used human pluripotent stem cells to grow sesame-seed-sized heart models, called cardioids, that spontaneously self-organize to develop a hollow chamber without the need of experimental scaffolds. This advance, which allows for the creation of some of the most realistic heart organoids to date, appears on May 20th in the journal Cell.
Previously, scientists have built 3D cardiac organoids via tissue engineering, an approach that generally involves assembling cells and scaffolds like building a house out of brick and mortar. But these engineered organoids do not have the same physiological responses to damages as human ...
Swifts aren't called "swifts" for nothing. They're known for being among the fastest migrating small birds around. When they aren't breeding, common swifts stay in the air most of the time--up to 10 months of the year. Scientists had thought they travel about 500 kilometers per day on average. Now, new evidence reported in the journal iScience on May 20 shows that's a conservative estimate.
According to new tracking data, common swifts travel 570 kilometers (more than 350 miles) on an average day--but they are capable of going much farther and faster. The maximum recorded distance in the study was more than 830 kilometers (more than 500 miles) per day over nine days.
"We have discovered that common swifts breeding in the most northern part of the European ...
A common factor called "decision acuity" underpins diverse decision-making abilities in adolescents and young adults, suggests a study appearing May 20th in the journal Neuron. A large set of behavioral and neuroimaging data revealed that decision acuity is stable over time, distinct from IQ, and reduced in individuals with low general social functioning.
"We describe a new cognitive construct that captures global decision-making ability across multiple domains," says senior study author Raymond Dolan of University College London. "This construct may be important for understanding mental health, particularly regarding poor social function and aberrant thought patterns."
Decision-making is ...
DALLAS, May 20, 2021 — While death rates from cardiovascular disease (CVD) nationwide have steadily declined over the past few decades, the overall trend masks significant disparities between high- and low-mortality counties, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Heart Association’s Epidemiology, Prevention, Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health Conference 2021. The meeting is virtual, May 20-21, and offers the latest science on population-based health and wellness and implications for lifestyle.
The researchers examined mortality data from the National Center for Health Statistics collected from 1980 to 2014 from all 3,133 ...
DALLAS, May 20, 2021 — Women who are menopausal by the age of 40 had a 40% increased risk of developing coronary heart disease over their lifetime compared to women who did not go through early menopause, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Heart Association’s Epidemiology, Prevention, Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health Conference 2021. The meeting is virtual, May 20-21 and offers the latest science on population-based health and wellness and implications for lifestyle.
Coronary heart disease is a very common type of heart disease in which arteries around the heart become blocked due to a buildup of plaque, which develops over time. Left undetected and untreated, women can suffer ...
DALLAS, May 20, 2021 — Taking more steps per day, either all at once or in shorter spurts, may help you live longer, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Heart Association’s Epidemiology, Prevention, Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health Conference 2021. The meeting is virtual, May 20-21, and offers the latest science on population-based health and wellness and implications for lifestyle.
Walking is one of the safest and easiest ways to improve fitness and health including heart health. The American Heart Association’s fitness guidelines for adults recommend at least 150 minutes per week of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous physical activity, or a combination of both. Popular fitness ...