(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA--A five-year community outreach and engagement effort by the Abramson Cancer Center at the University of Pennsylvania (ACC) to increase enrollment of Black patients into cancer clinical trials more than doubled the percentage of participants, improving access and treatment for a group with historically low representation in cancer research. The percentage of patients enrolled into a treatment clinical trial, for example, increased from 12 to 24 percent. A significant increase was also observed in non-therapeutic interventional and non-interventional trials.
The findings were published today in an abstract to be presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting on June 5. (Abstract #100). [ADD LINK https://meetinglibrary.asco.org/record/196644/abstract]
"An important goal of the Abramson Cancer Center is to serve and engage our community --and that includes improving access to clinical trials for all patients," said senior author Robert H. Vonderheide, MD, DPhil, director of the ACC and vice president for Cancer Programs in the University of Pennsylvania Health System. "Aligning the number of Black patients with cancer we care for with the number enrolled in our trials is how we can help bring more equitable care to the community, close gaps in disparities, and sustain trust. There's more work to be done to improve access and inclusion of minority groups, and the impact of this outreach and engagement effort is an important step forward."
Despite making up 13.4 percent of the U.S. population, only five percent of Black patients with cancer are enrolled in clinical trials. Of 8,700 patients who participated in trials nationwide related to the 28 oncology drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2018 and 2019, only 4 percent were Black, according to FDA Drug Trial Snapshot reports.
In 2014, Black residents comprised 19 percent of the population and 16.5 percent of cancer cases in the 12-county catchment area surrounding Philadelphia, but only 11.1 percent of ACC patients were Black. The percentages of Black participants accrued into treatment, non-therapeutic interventional, and non-interventional trials at the ACC were 12.2 percent, 8.3 percent, and 13.0 percent, respectively.
To address these gaps, the ACC established a center-wide program with community guidance and engagement that included: culturally tailored marketing strategies; new partnerships with faith-based organizations serving Black communities to conduct educational events; establishment of an ACC community Advisory Board and community educational forums; pilot programs with Lyft and Ride Health to address transportation barriers; and patient education by nurse navigators regarding cancer and clinical trials.
The efforts reached more than 10,000 individuals in churches, neighborhoods, community parks and centers, and health centers with formats ranging from educational forums to wellness fairs. In addition, ACC promoted clinical trials that address the cancer burden in Black residents of the catchment area, required that each protocol have a minority accrual plan to obtain approval, and increased access to language-tailored consent forms and translation services for patients.
By 2018, the researchers found that the percentage of Black patients seen at ACC had increased to 16.2 percent. The percentages of Black participants accrued onto treatment, non-therapeutic interventional, and non-interventional trials were 23.9 percent, 33.1 percent, and 22.5 percent, respectively -- a 1.7- to 4.0-fold increase and higher than the percentage of Black patients seen at the ACC.
As part of its long-term strategy to improve access, the ACC has also collaborated with the Lazarex Cancer Foundation to implement its IMPACT program (IMproving Patient Access to Cancer Clinical Trials), a first-of-its-kind effort at the ACC combining financial reimbursement for travel related expenses, outreach, and educational programs to help patients with cancer learn about and access advanced treatment in clinical trials. Reimbursement covers plane tickets, hotels, gas, tolls, cabs, and parking for the patient, and a companion.
"We've shown here that a multifaceted, community-based engagement initiative works to improve access to cancer clinical trials by Black patients with cancer," said first author Carmen E. Guerra, MD, MSCE, FACP, an associate professor of Medicine and associate director for Diversity and Outreach in the ACC. "We will continue to work with collaborators such as Lazarex that share in our vision to increase participation of underrepresented patients in trials, while at the same time engage with the community to develop strategies that address needs and barriers, from different social determinants of health to solidifying their trust."
INFORMATION:
Penn co-authors Vicki Sallee, Wei-Ting Hwang, Brenda Bryant, Armenta L. Washington, Samuel U. Takvorian, Robert Schnoll, Karen Glanz, Roger B. Cohen, and Katherine L. Nathanson.
Vonderheide will present the findings during a ASCO special session, "Novel Initiatives to Address Disparities in Cancer," on June 5 at 8:30 am EST.
New York, NY (May 21, 2021) --Women who were highly exposed to ultra-fine particles in air pollution during their pregnancy were more likely to have children who developed asthma, according to a study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine in May. This is the first time asthma has been linked with prenatal exposure to this type of air pollution, which is named for its tiny size and which is not regulated or routinely monitored in the United States.
Slightly more than 18 percent of the children born to these mothers developed asthma in their preschool years, compared ...
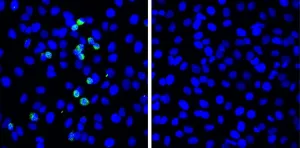
Scientists from Hokkaido University have discovered a novel defensive response to SARS-CoV-2 that involves the viral pattern recognition receptor RIG-I. Upregulating expression of this protein could strengthen the immune response in COPD patients.
In the 18 months since the first report of COVID-19 and the spread of the pandemic, there has been a large amount of research into understanding it and developing menas to treat it. COVID-19 does not affect all infected individuals equally. Many individuals are asymptomatic; of those who are symptomatic, the large majority have mild symptoms, and only a small number have severe cases. The reasons for this are not fully understood and are an important area of ongoing research.
A team of scientists ...
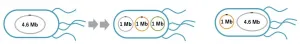
The issue of concern was that the Escherichia coli (E. coli) genome, consisting of 4.6 million base pairs of a single circular DNA, is too large to manipulate following the extraction and transfer to other bacteria.
In the present study, a group of Rikkyo University researchers led by Assistant Professor Takahito Mukai and Professor Masayuki Su'etsugu has succeeded in splitting the E.coli genome into tripartite-genome of 1 million base pairs per genome (split-genome) using the smallest E. coli genome strain established so far. In addition, they successfully extracted the split-genome from bacteria and installed it in other E. ...
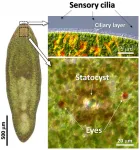
All living organisms are equipped with sensory organs to detect changes in their surrounding environment. It may not immediately strike us as obvious but, similar to how we can sense heat, cold, light, and darkness, we are also extremely adept at sensing gravity. In our case, it is our inner ear that does this job, helping us maintain balance, posture, and orientation in space. But, what about other organisms, for instance invertebrates that lack a backbone?
The gravity sensing organ in some aquatic invertebrates, known as a "statocyst," is, in fact, rather fascinating. The statocyst is essentially a fluid-filled sac with sensory cells lining its inner wall and a small, mineralized ...
[Highlights]
- Integrated cyber attack analysis platform "NIRVANA Kai" newly supports IPv6 and enhances its functions.
- Observation of IPv6 communications, collection of IPv6-related alerts, and real-time visualization of IPv6 networks.
- Expected to simplify security operations in IPv6 networks.
[Abstract]
The Cybersecurity Laboratory of the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT, President: TOKUDA Hideyuki, Ph.D.) has enhanced its cyber attack integrated analysis platform "NIRVANA Kai" to support the Internet Protocol version ...
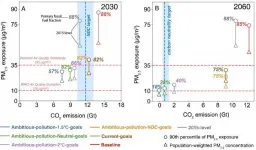
China's clean air policies have substantially reduced PM2.5 air pollution in recent years. Yet >99% of Chinese population is still exposed to PM2.5 concentrations in excess of the World Health Organization (WHO) Air Quality Guidelines of 10 μg/m3. Climate actions targeting to reduce fossil fuel consumption also have substantial air quality benefits. The announcement of ambitious climate commitment to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 may fuel the power to long-term air quality improvement in China.
Combining Global/China's climate mitigation pathways (i.e. global 2°C- and 1.5°C-pathways, NDC pledges, and carbon neutrality goals) and local clean ...
An international research group involving the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Plants (IBMCP), a joint centre of the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), has discovered that a genetic mechanism, called CHLORAD, which is involved in the ageing of plant leaves, also plays a decisive role in the tomato ripening process. Thus, tomatoes with an activated CHLORAD system turn red more quickly, and accumulate more lycopene, a compound beneficial to health. The results, which have been published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Plants, will lead to better quality tomatoes.
The ripening of most fleshy fruits gives them attractive colours and smells, which is a trick of the plant to spread its seeds ...
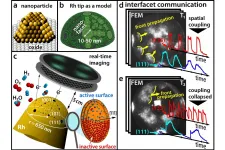
Most of commercial chemicals are produced using catalysts. Usually, these catalysts consist of tiny metal nanoparticles that are placed on an oxidic support. Similar to a cut diamond, whose surface consists of different facets oriented in different directions, a catalytic nanoparticle also possesses crystallographically different facets - and these facets can have different chemical properties.
Until now, these differences have often remained unconsidered in catalysis research because it is very difficult to simultaneously obtain information about the chemical reaction itself and about the surface structure of the catalyst. At TU Wien (Vienna), this has now been achieved by combining different microscopic methods: with ...
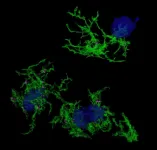
SINGAPORE, 21 May 2021 - Alzheimer's Disease is the most common form of dementia and is characterised by the build-up of amyloid plaques in the brain. Microglia, the immune sentinels of the brain, are not only responsible for eliminating foreign invaders, but also maintaining brain homeostasis by clearing toxic waste such as the amyloid plaques.
However, the role of microglia in Alzheimer's Disease and its relationship to amyloid plaque accumulation remain unclear. Now, a team of scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School and Monash University have found the gene expression signatures underlying microglia associated ...
More than 100 kg of highly toxic uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu) was dispersed in the form of tiny 'hot' radioactive particles after the British detonated nine atomic bombs in remote areas of South Australia, including Maralinga.
Scientists say that these radioactive particles persist in soils to this day, more than 60 years after the detonations. Previously, we had limited understanding of how Pu was released from these "hot" particles into the environment for uptake by wildlife around Maralinga.
But now, a new study published today in Scientific Reports and led by Monash University researchers warns that the particles are actually more ...