INFORMATION:
See the article:
Pathways of China's PM2.5 air quality 2015-2060 in the context of carbon neutrality. Cheng J et al. National Science Review, https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwab078
China's PM2.5 pathways under carbon neutrality goals
2021-05-21
(Press-News.org) China's clean air policies have substantially reduced PM2.5 air pollution in recent years. Yet >99% of Chinese population is still exposed to PM2.5 concentrations in excess of the World Health Organization (WHO) Air Quality Guidelines of 10 μg/m3. Climate actions targeting to reduce fossil fuel consumption also have substantial air quality benefits. The announcement of ambitious climate commitment to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 may fuel the power to long-term air quality improvement in China.
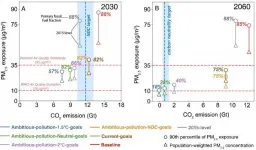
Combining Global/China's climate mitigation pathways (i.e. global 2°C- and 1.5°C-pathways, NDC pledges, and carbon neutrality goals) and local clean air policies, Chinese energy system, anthropogenic emissions and PM2.5 air quality pathways from 2015 to 2060 are assessed. If the government improves the source treatment--promote the renewable energy fraction, push the production peaks of high consumption industries (e.g., iron, steel, cement), accelerate the phasing out of scattered coal; meanwhile continue to promote the in-depth end-of-pipe control in high-polluted industries, diesel-fueled vehicles and engines, and VOC-related industries, China would meet the NDC climate target in 2030, as well as mitigate the national population-weighted PM2.5 concentrations to ~28 μg/m3, achieving the national air quality standards.
However, the benefits of end-of-pipe control reductions are mostly exhausted by 2030, and reducing PM2.5 exposure of the majority of the Chinese population to below 10 μg/m3 by 2060 will likely require more ambitious climate mitigation efforts such as China's carbon neutrality goals and global 1.5°C-pathways. As the solution, by 2060, China will complete the transformation of low-carbon energy, with the dominate role of renewable energy (i.e. the renewable energy power generation would account for more than 70%, the fraction of coal would be less than 15% in industry sector, electricity and hydrogen vehicles would account higher than 60%). Such in-depth energy transition would lower China's carbon emissions by 90%. As a result, the average annual exposure level of PM2.5 will be around 8 μg/m3, lower than the WHO guideline and the air pollution problem has been fundamentally solved.
Cheng et al. proposes practical strategies to address both air pollution and GHGs emissions in the near-term, in which co-control measures focusing on co-emitted sources (i.e. fossil fuel consumption), co-management mechanism on PM2.5 and O3 pollution, and co-development plan on low carbon economy and clean energy transition are prioritized. China's future clean air pathways should transform from end-of-pipe control to energy and economic system optimization. Meanwhile, China should proactively promote the air quality standards to gradually integrate with the relevant WHO standards 10 μg/m3 as a new long-term goal, to accelerate the implementation of carbon neutrality strategy.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New mechanism to control tomato ripening discovered
2021-05-21
An international research group involving the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Plants (IBMCP), a joint centre of the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), has discovered that a genetic mechanism, called CHLORAD, which is involved in the ageing of plant leaves, also plays a decisive role in the tomato ripening process. Thus, tomatoes with an activated CHLORAD system turn red more quickly, and accumulate more lycopene, a compound beneficial to health. The results, which have been published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Plants, will lead to better quality tomatoes.
The ripening of most fleshy fruits gives them attractive colours and smells, which is a trick of the plant to spread its seeds ...
Nanoparticles: The complex rhythm of chemistry
2021-05-21
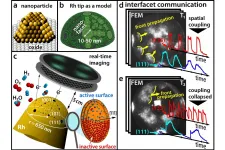
Most of commercial chemicals are produced using catalysts. Usually, these catalysts consist of tiny metal nanoparticles that are placed on an oxidic support. Similar to a cut diamond, whose surface consists of different facets oriented in different directions, a catalytic nanoparticle also possesses crystallographically different facets - and these facets can have different chemical properties.
Until now, these differences have often remained unconsidered in catalysis research because it is very difficult to simultaneously obtain information about the chemical reaction itself and about the surface structure of the catalyst. At TU Wien (Vienna), this has now been achieved by combining different microscopic methods: with ...
Scientists discover gene signature for plaque-eating microglia in Alzheimer's Disease
2021-05-21
SINGAPORE, 21 May 2021 - Alzheimer's Disease is the most common form of dementia and is characterised by the build-up of amyloid plaques in the brain. Microglia, the immune sentinels of the brain, are not only responsible for eliminating foreign invaders, but also maintaining brain homeostasis by clearing toxic waste such as the amyloid plaques.
However, the role of microglia in Alzheimer's Disease and its relationship to amyloid plaque accumulation remain unclear. Now, a team of scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School and Monash University have found the gene expression signatures underlying microglia associated ...
Pu particles from nuclear testing more complex than previously thought
2021-05-21
More than 100 kg of highly toxic uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu) was dispersed in the form of tiny 'hot' radioactive particles after the British detonated nine atomic bombs in remote areas of South Australia, including Maralinga.
Scientists say that these radioactive particles persist in soils to this day, more than 60 years after the detonations. Previously, we had limited understanding of how Pu was released from these "hot" particles into the environment for uptake by wildlife around Maralinga.
But now, a new study published today in Scientific Reports and led by Monash University researchers warns that the particles are actually more ...
Biodiversity devastation: Human-driven decline requires millions of years of recovery
2021-05-21
A new study shows that the current rate of biodiversity decline in freshwater ecosystems outcompetes that at the end-Cretaceous extinction that killed the dinosaurs: damage now being done in decades to centuries may take millions of years to undo.
The current biodiversity crisis, often called the 6th mass extinction, is one of the critical challenges we face in the 21st century. Numerous species are threatened with extinction, mostly as a direct or indirect consequence of human impact. Habitat destruction, climate change, overexploitation, pollution and invasive species are among the main causes for Earth's biota to decline rapidly.
To investigate the tempo of extinction and predict recovery times, an international team of evolutionary biologists, paleontologists, geologists and modelers ...
New nondestructive broadband imager is the next step towards advanced technology
2021-05-21
One of the key aspects of academic and industrial research today is non-destructive imaging, a technique in which an object or sample is imaged (using light) without causing any damage to it. Often, such imaging techniques are crucial to ensuring safety and quality of industrial products, subsequently leading to growing demands for high-performance imaging of objects with arbitrary structures and locations.
On one hand, there has been tremendous advancements in the scope of non-destructive imaging regarding the region of electromagnetic (EM) spectrum it can access, which now ranges from visible light to as far as millimeter waves! On the other, imaging devices have become flexible and wearable, enabling stereoscopic (3D) visualization ...
Green light on gold atoms
2021-05-21
Because individual atoms or molecules are 100 to 1000 times smaller than the wavelength of visible light, it is notoriously difficult to collect information about their dynamics, especially when they are embedded within larger structures.
In an effort to circumvent this limitation, researchers are engineering metallic nano-antennas that concentrate light into a tiny volume to dramatically enhance any signal coming from the same nanoscale region. Nano-antennas are the backbone of nanoplasmonics, a field that is profoundly impacting biosensing, photochemistry, solar energy harvesting, and photonics.
Now, researchers at EPFL led by Professor Christophe Galland at the School of Basic Sciences ...
Study on intermittency in gang membership underscores value of preventing youth from rejoining gangs
2021-05-21
Research has shown that joining a gang is associated with increased criminal behavior. A new study examined whether the intermittent nature of gang membership affects offending. Researchers sought to determine whether the association with increased offending was a consistent attribute or, since people enter and exit and re-enter gangs, whether the intermittent nature of membership affected members' likelihood of offending. The study found that first-time membership was associated with increases in criminal behavior from when gang members were not in gangs, and that joining for a second ...
First-of-its-kind flower smells like dead insects to imprison 'coffin flies'
2021-05-21
The plant Aristolochia microstoma uses a unique trick: its flowers emit a fetid-musty scent that seems to mimic the smell of decomposing insects. Flies from the genus Megaselia (family Phoridae) likely get attracted to this smell while searching for insect corpses to mate over and lay their eggs in. When they enter a flower, they are imprisoned and first pollinate the female organs, before being covered with pollen by the male organs. The flower then releases them unharmed.
"Here we show that the flowers of A. microstoma emit an unusual mix of volatiles that includes alkylpyrazines, which are otherwise rarely produced by flowering plants. Our results suggest that this is the first known case of a flower that tricks pollinators by smelling like dead and rotting insects rather than vertebrate ...
Doctors have nothing to fear from a central register of interests, say experts
2021-05-21
UK doctors have nothing to fear from the introduction of a central register listing money or benefits they receive in addition to their NHS salary, say experts today ahead of a public meeting on the issue hosted by the All-Party Parliamentary Group for First Do No Harm and The BMJ.
Last year the Independent Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Review, chaired by Baroness Julia Cumberlege, investigated harmful side effects caused by the hormone pregnancy test Primodos, the anti-epileptic drug sodium valproate, and pelvic mesh.
During the review, she heard from patients who were concerned that clinicians ...