Researchers develop novel raman method to capture target molecules in small gaps actively
2021-05-24
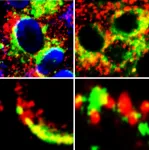
(Press-News.org) Recently, Professor YANG Liangbao, from the Institute of Health and Medical Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), developed a general surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) method for actively capturing target molecules in small gaps based on nano-capillary pumping model. Relevant results were detailed in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
SERS is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules. It's commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.
In this research, using the principle of capillary suction, they constructed a nanocapillary pumping model, for the first time, with ubiquitous hot spots, leading to the first systematic study of small gaps to actively capture molecules.
"What makes this method stand out is the highly universal characteristic of it," said YANG, a scientist of medicine.
It could be used for highly sensitive detection of almost all types of molecules, including plasticizers, organic contaminants, antitumor drugs, poisons, toxins, pesticide residues, dyes, antibiotics, explosives, and amino acids.
On top of that, they successfully analyzed the changes in single A549 cells at the molecular level during photothermal stimulation with this method, which proved that it could be applied to actively capture target molecules in small gaps to study the death of a single cell resulting from photothermal stimulation.
This general method has provided a new way for stimulating active transport of target molecules to optimal hot spots to achieve ultrasensitive detection and real-time monitoring of cell behavior or chemical kinetics.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-24
Talk of a graduate student mental health crisis is abundant in academic and popular media, but a University of Otago study has found no evidence of one in New Zealand.
The study, published in Frontiers in Psychology, used data from the Graduate Longitudinal Study New Zealand to compare the mental wellbeing of students who did, and did not, transition into PhD study after completing their undergraduate degree.
Co-author Dr Damian Scarf, from the Department of Psychology, says the researchers found poor mental health is not an inevitable consequence of PhD study in New Zealand.
This is despite ...
2021-05-24
ATLANTA - MAY 24, 2021 - A new study underscores the importance of health insurance coverage continuity in access to and receipt of care and care affordability in the United States. Researchers found that health insurance coverage disruptions were consistently associated with worse healthcare access and problems with care affordability. The study appears in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Decades of research has demonstrated that health insurance coverage is associated with better access to care and health outcomes in the U.S. However, less research has addressed coverage disruptions ...
2021-05-24
A strange phenomenon happens with modern blue whales, humpback whales and gray whales: they have teeth in the womb but are born toothless. Replacing the teeth is baleen, a series of plates composed of thin, hair- and fingernail-like structures growing from the roof of their mouths that act as a sieve for filter feeding small fish and tiny shrimp-like krill.
The disappearing embryonic teeth are testament to an evolutionary history from ancient whales that had teeth and consumed larger prey. Modern baleen whales on the other hand use their fringed baleen ...
2021-05-24
The swift development of vaccines has provided a vital tool to combat the spread of the deadly SARS-CoV-2 virus, but challenges to reaching herd immunity posed by the rise of new mutations and the inability of immunosuppressed people to develop an effective immune response following vaccination point to a need for additional solutions to maximize protection.
A new USC study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry reveals how therapies targeting a molecular chaperone called GRP78 might offer additional protection against COVID-19 and other coronaviruses that emerge in the future.
Chaperones like GRP78 are molecules that help regulate the correct folding of proteins, especially when a cell is under ...
2021-05-24
Reduced levels of a metabolic hormone known as leptin is linked to poor vaccine antibody responses in the general population, a University of Queensland study has found.
The researchers made the discovery while investigating several cohorts' responses to the influenza vaccine or hepatitis B vaccine pre-COVID.
UQ's Professor Di Yu identified a link between the metabolic and immune systems that could be used to develop new strategies for improving vaccine protection in vulnerable populations.
"Using multiple advanced techniques in immunology, genetics ...
2021-05-24
Women taking 1,000 mg of docosohexanoic acid (DHA) daily in the last half of pregnancy had a lower rate of early preterm birth than women who took the standard 200 mg dose, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. Women who entered the study with the lowest DHA level had the greatest reduction in early preterm birth, which is birth before 34 weeks of pregnancy and which increases the risk of infant death and disability
The study was conducted by Susan E. Carlson, Ph.D., at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, and colleagues. It appears in EClinicalMedicine. Funding was provided by NIH's Eunice Kennedy Shriver National ...
2021-05-24
Among the powerful biochemicals of the human immune system, peptides are one of the best.
Most commonly found in the places where microbes love to take root - mucous membranes of the eye, mouth, nose and lungs - they're known to kill all sorts of tiny invaders, such as viruses, bacteria and fungi.
Given their power, one might think peptides would represent promising drug treatments, perhaps even a cure, for many infectious diseases. But, alas, they are fundamentally flawed: They are vulnerable to a myriad of enzymes whose job is to rapidly break them down in a way that robs them of their therapeutic properties.
"Because of their vulnerability to enzymatic breakdown, ...
2021-05-24
A clinical study led by Linköping University and financed by pharmaceuticals company Diamyd Medical has investigated whether immunotherapy against type 1 diabetes can preserve the body's own production of insulin. The results suggest that injection of a protein, GAD, into lymph nodes can be effective in a subgroup of individuals. The results have been published in Diabetes Care.
In type 1 diabetes, the body's immune system attacks the cells that produce insulin. When the insulin-producing cells have disappeared, the body can no longer regulate blood sugar level, and a person with type 1 diabetes must take exogenous ...
2021-05-24
Regular, standardized assessments of evacuation shelters can help keep people healthy following natural disasters, according to research published by Tohoku University scientists and colleagues in the journal Heliyon. The study found that a clean tap water supply and hygienic toilets were especially important for protecting evacuees from the spread of infectious diseases.
"A clean water supply and maintaining hygiene are important for reducing environmental health risks among victims of natural disasters," says Tadashi Ishii, who specializes in disaster medicine at Tohoku University. "But scientists have
not yet established a strong evidence base that describes the relationship between damage in resource supplies and infrastructure ...
2021-05-24
HOUSTON - (May 24, 2021) - U.S. and Austrian physicists searching for evidence of quantum criticality in topological materials have found one of the most pristine examples yet observed.
In an open access paper published online in Science Advances, researchers from Rice University, Johns Hopkins University, the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) present the first experimental evidence to suggest that quantum criticality -- a disordered state in which electrons waver between competing states of order -- may give rise to topological phases, "protected" quantum states that are of growing interest ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers develop novel raman method to capture target molecules in small gaps actively