Clean water and toilets for healthy shelters
2021-05-24
(Press-News.org) Regular, standardized assessments of evacuation shelters can help keep people healthy following natural disasters, according to research published by Tohoku University scientists and colleagues in the journal Heliyon. The study found that a clean tap water supply and hygienic toilets were especially important for protecting evacuees from the spread of infectious diseases.
"A clean water supply and maintaining hygiene are important for reducing environmental health risks among victims of natural disasters," says Tadashi Ishii, who specializes in disaster medicine at Tohoku University. "But scientists have
not yet established a strong evidence base that describes the relationship between damage in resource supplies and infrastructure on the one hand and disaster victims' health status on the other."
Ishii led the Ishinomaki Zone Joint Relief Team following the Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011. More than 15,000 people died and 2,500 went missing following the disaster, with some 500,000 evacuated to shelters across Japan. It took nearly a year before all shelters were shut down.
The team conducted regular visits to the shelters in order to assess resource availability, infrastructure, and the health status and needs of people residing in the shelters. Now, Ishii and his research team have analysed these 2011 records to evaluate the impacts of resource supply levels and infrastructure damage on the physical health of evacuees.
Their study included 28 mid- to large-sized shelters regularly assessed in the weeks following the earthquake. The study looked specifically at changes made to resources and infrastructure between days 14 and 25 after the earthquake.
The team found that inadequate clean tap water and toilets were insufficiently improved during the assessment period in about half the shelters. Clinical symptoms of common respiratory and gastrointestinal infections were more prevalent in shelters where these two resources had not improved. Shelters that were able to improve the supply of clean tap water and toilet hygiene witnessed significant reductions in the prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms among evacuees.
"Our study demonstrated the difficulty of quickly collecting objective assessment data from evacuation shelters during the acute phase of a massive disaster," says Ishii. "It also shows the validity of quick visual assessments of resources by trained staff. Importantly, the study reveals the importance of rapidly restoring clean water supply and toilet hygiene in shelters to reduce environmental health risks among evacuees."
Ishii and his team next plan to develop easy, reliable and quick assessment tools for evaluating resource damage and health status in evacuation shelters. He also stresses the importance of collaborating with local governments to set up effective supply chains that can rapidly deploy clean water and hygienic rescue toilets in the aftermath of natural disasters.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-24
HOUSTON - (May 24, 2021) - U.S. and Austrian physicists searching for evidence of quantum criticality in topological materials have found one of the most pristine examples yet observed.
In an open access paper published online in Science Advances, researchers from Rice University, Johns Hopkins University, the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) present the first experimental evidence to suggest that quantum criticality -- a disordered state in which electrons waver between competing states of order -- may give rise to topological phases, "protected" quantum states that are of growing interest ...
2021-05-24
A diverse microbial community has adapted to an extremely salty environment deep in the Red Sea. The microbes, many unknown to science, occupy a one-meter-thick area overlying the Suakin Deep, an expansive 80-meter-deep brine lake, 2,771 meters below the central Red Sea. The chemical properties of this thin "brine-seawater interface," along with the composition of microbial communities, change surprisingly rapidly across a sharp gradient.
"Our study sheds light on how microorganisms in the Suakin Deep's brine-seawater interface make an oasis of life in the desert of the deep Red Sea," says microbial ...
2021-05-24
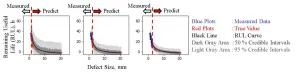
Osaka, Japan - Scientists from the Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research, and NTN Next Generation Research Alliance Laboratories at Osaka University developed a machine learning method that combines convolutional neural networks and Bayesian hierarchical modeling to precisely predict the remaining useful life of rolling bearings. This work may lead to new industrial monitoring methods that help manage maintenance schedules and maximize efficiency and safety under defect progression.
A rolling bearing consists of two rings separated by rolling elements (balls or rollers). Because of the ease of rolling, the rings can rotate relative to each other with very little friction. Rolling bearings are essential to almost all automated machinery with rotating elements. The bearings ...
2021-05-24
Scientists used to perform experiments by stirring biological and chemical agents into test tubes.
Nowadays, they automate research by using microfluidic chips the size of postage stamps. In these tiny devices, millions of microscopic particles are captured in droplets of water, each droplet serving as the "test tube" for a single experiment. The chip funnels these many droplets, one at a time, through a tiny channel where a laser probes each passing droplet to record thousands of experimental results each second.
These chips are used for such things as testing new antibiotics, screening drug compounds, sequencing the DNA and RNA of single cells, and otherwise speeding up the pace of scientific ...
2021-05-24
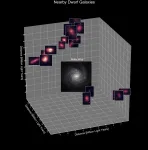
Three dozen dwarf galaxies far from each other had a simultaneous "baby boom" of new stars, an unexpected discovery that challenges current theories on how galaxies grow and may enhance our understanding of the universe.
Galaxies more than 1 million light-years apart should have completely independent lives in terms of when they give birth to new stars. But galaxies separated by up to 13 million light-years slowed down and then simultaneously accelerated their birth rate of stars, according to a Rutgers-led study published in the Astrophysical Journal.
"It appears that these galaxies are responding to a large-scale ...
2021-05-24
Ever since the existence of molecules was proven and molecular reactions were predicted, humans have wanted to visually observe how such events proceed. Such observations of single-molecule reactions are highly important for the fundamental understanding of chemical sciences, which would aid in the development of novel catalysts, materials, or drugs, and help us decipher the complex biochemical processes. However, this was not possible for the longest time in modern chemistry, and so far the information of dynamical processes on the nanometer scale was obtained only from indirect methods because molecules ...
2021-05-24
Healthcare and aerospace experts at King's College London, The Alan Turing Institute, the University of Cambridge, and the Oden Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences at UT Austin in Texas have said advances in digital twin technology make it a powerful tool for facilitating predictive and precision medicine and enhancing decision-making for aerospace systems. Their opinion piece was published today in Nature Computational Science.
When applied to healthcare, the digital twin, a virtual version of real-life objects that can be used to predict how that object will perform, could predict how a patient's disease will develop and how patients are likely to respond to different therapies.
It is also of huge benefit in aerospace, where, for example, the technology ...
2021-05-24
Climate change impacts felt in the Amazon rainforest prior to the arrival of European settlers after 1492 may have meant populations of indigenous people were already in decline before the 'Great Dying', new research has suggested.
Scientists studying fossil pollen and charcoal data from across the Amazon say it appears to show that human management of the rainforest may have peaked around 1200 AD, before some sites were abandoned, allowing reforestation of these areas.
The new research, involving University of Reading scientists and published in the journal Science, challenges the prior assumption that the largest population decrease in the Americas - known as the Great Dying - did not start until after European settlers carried new diseases to ...
2021-05-24
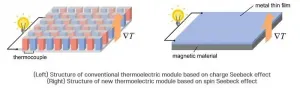
Thermoelectric (TE) conversion offers a carbon-free power generation from geothermal, waste, body or solar heat, and shows promise to be the next-generation energy conversion technology. At the core of such TE conversion, there lies an all solid-state thermoelectric device which enables energy conversion without the emission of noise, vibrations, or pollutants. To this, a POSTECH research team proposed a way to design the next-generation thermoelectric device that exhibits remarkably simple manufacturing process and structure compared to the conventional ones, while displaying ...
2021-05-24
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Two species of sand-stabilizing beachgrasses introduced to the Pacific Northwest starting in the early 1900s are hybridizing, raising new questions about impacts to the coastal ecosystems the non-native plants have been engineering for more than a century.
Researchers in the Oregon State University College of Science identified the hybrid in a paper published in Ecosphere.
In addition to their ecological implications, the findings are important in the context of coastal vulnerability to the effects of climate change, including increasing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Clean water and toilets for healthy shelters