INFORMATION:
The research was funded by grants from the National Geographic Society and the National Science Foundation in the United States and the European Research Council and the Natural Environment Research Council in the United Kingdom.
Pre-Columbus climate change may have caused Amazon population decline
Indigenous Amazonia populations may have been in decline prior to 'Great Dying'
2021-05-24
(Press-News.org) Climate change impacts felt in the Amazon rainforest prior to the arrival of European settlers after 1492 may have meant populations of indigenous people were already in decline before the 'Great Dying', new research has suggested.
Scientists studying fossil pollen and charcoal data from across the Amazon say it appears to show that human management of the rainforest may have peaked around 1200 AD, before some sites were abandoned, allowing reforestation of these areas.
The new research, involving University of Reading scientists and published in the journal Science, challenges the prior assumption that the largest population decrease in the Americas - known as the Great Dying - did not start until after European settlers carried new diseases to the continent.
Professor Frank Mayle, a tropical palaeoecology researcher at the University of Reading, and co-author of the study, said: "Our analysis raises the possibility that climate change caused the decline of some Amazonian societies several centuries before the Europeans arrived, especially the more complex societies which may have been too rigid to adapt.
"Although the introduction of European diseases, such as small pox, is still likely to have been the reason for the major population decline subsequently seen in the Americas, the research is a warning of the threat climate change poses to society. Knowledge of how different types of ancient society responded to past climate change may provide valuable clues to understanding the fate of today's diverse societies under 21st century global warming."
The research was led by Professor Mark Bush at Florida Tech, and included a team of international collaborators who are investigating how pre- and post-European people modified and managed Amazonian forests.
Analysis of fossilised pollen and charcoal revealed that many previously deforested lands have been recovering for over 800 years, rather than the 400 years previously supposed, indicating a pre-European population decline. The research team is now looking to assess the drivers and mechanisms of this population drop-off.
Finding signatures of initial forest regrowth following ancient human disturbance is important to ongoing discussions about the impact of Pre-Columbian people on Amazon rainforests and the extent to which modern forests exhibit legacies of past human activity.
This research also has implications for atmospheric and biosphere science. It was previously believed that the indigenous population collapse in Amazonia following European Contact, and subsequent reforestation, led to the sequestration of so much carbon dioxide that global atmospheric CO2 levels decreased markedly, an event known as the 'Orbis Spike'. Yet the team found no evidence that the Orbis Spike was caused by Amazonian reforestation.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Generating electricity from heat using the spin Seebeck device
2021-05-24
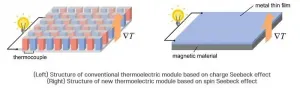
Thermoelectric (TE) conversion offers a carbon-free power generation from geothermal, waste, body or solar heat, and shows promise to be the next-generation energy conversion technology. At the core of such TE conversion, there lies an all solid-state thermoelectric device which enables energy conversion without the emission of noise, vibrations, or pollutants. To this, a POSTECH research team proposed a way to design the next-generation thermoelectric device that exhibits remarkably simple manufacturing process and structure compared to the conventional ones, while displaying ...
Oregon State University research shows two invasive beachgrasses are hybridizing
2021-05-24
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Two species of sand-stabilizing beachgrasses introduced to the Pacific Northwest starting in the early 1900s are hybridizing, raising new questions about impacts to the coastal ecosystems the non-native plants have been engineering for more than a century.
Researchers in the Oregon State University College of Science identified the hybrid in a paper published in Ecosphere.
In addition to their ecological implications, the findings are important in the context of coastal vulnerability to the effects of climate change, including increasing ...
New use of imaging technique could allow early detection of aortic aneurysms
2021-05-24
Ibaraki, Japan - Ascending thoracic aortic aneurisms (aTAAs) occur when the walls of the aorta, the largest blood vessel in the body, weaken and begin to bulge. This can result in rupture or dissection (a tear in the aortic wall), leading to life-threatening bleeding and death. Sometimes these complications can occur before any symptoms of the aneurysm appear. However, an international team led by Hiromi Yanagisawa at the University of Tsukuba and Katja Schenke-Layland at Eberhard Karls University, Tübingen have used Raman microspectroscopy (an analysis technique that uses Raman scattering to probe ...
New study targets secrets of great entrepreneurial cities
2021-05-24
"If you build it, they will come," so says the idiom but it's the storytellers, knowledge-makers and an "agentic" or open-minded population who help create great entrepreneurial cities.
A new research study, conducted by QUT, RMIT and the University of Indiana, analysed data from 362 American cities with a focus on human agency, entrepreneurial spirit, and economic growth.
The study, based on geographic psychological profiles of millions of people based in the US, found people and an empowered city life matter in shaping urban vitality.
The research points to San Francisco and Austin as the zip codes that drive the highest-impact ...
Otago study helps explain how religious beliefs are formed
2021-05-24
Feeling anxious can direct our attention and memory toward supernatural beings such as gods, a University of Otago study has found.
Lead author Dr Thomas Swan, of the Department of Psychology, says the research may help explain how religious beliefs are formed.
For the study, published in the International Journal for the Psychology of Religion, 972 participants completed an online recall test to determine if a bias to recall supernatural agents was stronger in anxious people, rather than non-anxious people.
Those who felt anxious were more likely ...
Early research suggests climate change could lead to more stillbirths
2021-05-24
Scientists are investigating whether rising global temperatures may lead to more stillbirths, saying further study is needed on the subject as climates change.
Researchers from The University of Queensland's School of Earth and Environmental Science and the Mater Research Institute reviewed 12 studies, finding extreme ambient temperature exposures throughout pregnancy appeared to increase risk of stillbirth, particularly late in pregnancy.
UQ PhD candidate Jessica Sexton said while this was very early research, it did show a possible link between stillbirth and high and low ambient temperature exposures during pregnancy.
"Overall, risk of stillbirth appears ...
COVID-19 vaccine benefits still outweigh risks, despite possible rare heart complications
2021-05-24
DALLAS, Sunday, May 23, 2021 - Late last week, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) alerted health care professionals that they are monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of young adults developing the rare heart-related complication myocarditis, after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine manufactured by Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna. The COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) of the CDC's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) is reviewing several dozen cases of myocarditis that ...
A long-term study shows strong links between gestational diabetes during pregnancy and type-1 and type-2 diabetes later in life
2021-05-24
A 23 year study being presented at the 23rd European Congress of Endocrinology (e-ECE 2021), on Monday 24 May 2021 at 14:40 CET (http://www.ece2021.org), has found that women who experience gestational diabetes (GDM) when they are pregnant, are more prone to developing type-1 and type-2 diabetes later in life. The long-term study suggests that autoantibody testing should be considered for women who experience GDM in order to have a better understanding of their prognosis.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Globally, the number of people with diabetes rose from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in ...
New research reveals that a low-calorie ketogenic diet can help testosterone levels in overweight men
2021-05-24
Press release - Abstract 743: Effects of a very low-calorie ketogenic diet on androgen levels in overweight/obese men: a single-arm uncontrolled study
New research reveals that a low-calorie ketogenic diet can help testosterone levels in overweight men, reducing overall levels of obesity
A very low-calorie ketogenic diet can help testosterone and sex hormone (SHBG) levels in overweight men, according to a study being presented at the 23rd?European Congress of Endocrinology (e-ECE 2021), on Monday 24 May 2021 at 14:06 CET (http://www.ece2021.org). The study found that after following a recommended low-calorie ketogenic diet for four weeks, body weight, fat mass and body mass index (BMI) significantly decreased and a substantial increase of total ...
New quantum material discovered
2021-05-24
In everyday life, phase transitions usually have to do with temperature changes - for example, when an ice cube gets warmer and melts. But there are also different kinds of phase transitions, depending on other parameters such as magnetic field. In order to understand the quantum properties of materials, phase transitions are particularly interesting when they occur directly at the absolute zero point of temperature. These transitions are called "quantum phase transitions" or a "quantum critical points".
Such a quantum critical point has now been discovered by an Austrian-American research team in a novel material, and in an unusually pristine form. The properties of this material are now being further investigated. It is suspected ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Pre-Columbus climate change may have caused Amazon population declineIndigenous Amazonia populations may have been in decline prior to 'Great Dying'