(Press-News.org) Scientists are investigating whether rising global temperatures may lead to more stillbirths, saying further study is needed on the subject as climates change.
Researchers from The University of Queensland's School of Earth and Environmental Science and the Mater Research Institute reviewed 12 studies, finding extreme ambient temperature exposures throughout pregnancy appeared to increase risk of stillbirth, particularly late in pregnancy.
UQ PhD candidate Jessica Sexton said while this was very early research, it did show a possible link between stillbirth and high and low ambient temperature exposures during pregnancy.
"Overall, risk of stillbirth appears to increase when the ambient temperature is below 15 degrees Celcius and above 23.4 degrees Celsius, with the highest risk being above 29.4 degrees Celsius," Ms Sexton said.
"An estimated 17 to 19 per cent of stillbirths are potentially attributable to chronic exposure to extreme hot and cold temperatures during pregnancy.
"And, as the world's temperatures rise due to climate change, this link will potentially increase stillbirth likelihood globally.
"But these findings are from the very limited research currently available, so expectant mothers shouldn't be anxious - there's still plenty of follow-up research that needs to happen."
Environmental scientist Dr Scott Lieske said the findings suggested that as temperatures rise, women in the developing world would feel the effects..
"More than two million stillbirths occur every year around the world, with the most occurring in low resource settings," Dr Lieske said.
"Not only are these poorer countries already affected disproportionately by stillbirth, they're now going to be disproportionately affected by climate change as well.
"If the link apparent in this research bears out upon further scrutiny, the majority of new stillbirths will occur invariably in the nations already suffering the most."
Professor Vicki Flenady, Director of the Centre of Research Excellence in Stillbirth (Stillbirth CRE) at Mater Research, said the research highlighted the importance of research to reduce global stillbirth rates.
"Even in 2021, a stillbirth occurs somewhere in the world every 16 seconds," Professor Flenady said.
"Stillbirth has a traumatic long-lasting impact on women and their families, who often endure profound psychological suffering as well as stigma, even in high-income countries.
"Here in Australia, stillbirth is still a major public health problem.
"As outlined in my recent research, in 2015 Australia's late gestation stillbirth rate was over 30 per cent higher than that of the best-performing countries globally.
"Further work is needed to understand the role that temperature plays in keeping women and babies safe during pregnancy.
"To fully understand the effects of maternal exposure to ambient temperatures and stillbirth, future studies should focus on the biological mechanisms involved and contributing factors, in addition to improving measurement of ambient temperature exposure.
"In the meantime, we would encourage pregnant women to talk to their healthcare providers about staying safe during the cold days of winter and hot days of summer."
INFORMATION:
The research is published in Environmental Research (DOI: j.envres.2021.111037).
It was conducted with the input of the above researchers, as well as Dr Christine Andrews, Professor Sailesh Kumar and SEES Winter Research Program researcher Selina Carruthers.
DALLAS, Sunday, May 23, 2021 - Late last week, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) alerted health care professionals that they are monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of young adults developing the rare heart-related complication myocarditis, after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine manufactured by Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna. The COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) of the CDC's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) is reviewing several dozen cases of myocarditis that ...
A 23 year study being presented at the 23rd European Congress of Endocrinology (e-ECE 2021), on Monday 24 May 2021 at 14:40 CET (http://www.ece2021.org), has found that women who experience gestational diabetes (GDM) when they are pregnant, are more prone to developing type-1 and type-2 diabetes later in life. The long-term study suggests that autoantibody testing should be considered for women who experience GDM in order to have a better understanding of their prognosis.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Globally, the number of people with diabetes rose from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in ...
Press release - Abstract 743: Effects of a very low-calorie ketogenic diet on androgen levels in overweight/obese men: a single-arm uncontrolled study
New research reveals that a low-calorie ketogenic diet can help testosterone levels in overweight men, reducing overall levels of obesity
A very low-calorie ketogenic diet can help testosterone and sex hormone (SHBG) levels in overweight men, according to a study being presented at the 23rd?European Congress of Endocrinology (e-ECE 2021), on Monday 24 May 2021 at 14:06 CET (http://www.ece2021.org). The study found that after following a recommended low-calorie ketogenic diet for four weeks, body weight, fat mass and body mass index (BMI) significantly decreased and a substantial increase of total ...
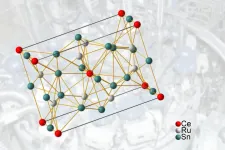
In everyday life, phase transitions usually have to do with temperature changes - for example, when an ice cube gets warmer and melts. But there are also different kinds of phase transitions, depending on other parameters such as magnetic field. In order to understand the quantum properties of materials, phase transitions are particularly interesting when they occur directly at the absolute zero point of temperature. These transitions are called "quantum phase transitions" or a "quantum critical points".
Such a quantum critical point has now been discovered by an Austrian-American research team in a novel material, and in an unusually pristine form. The properties of this material are now being further investigated. It is suspected ...
A membrane made from threads of a polymer commonly used in vascular sutures can be loaded with therapeutic drugs and implanted in the body, where mechanical forces activate the polymer's electric potential and slowly release the drugs.
The novel system, developed by a group led by bioengineers at UC Riverside and published in ACS Applied Bio Materials, overcomes the biggest limitations of conventional drug administration and some controlled release methods, and could improve treatment of cancer and other chronic diseases.
The drawbacks of conventional drug administration include repeated administration, nonspecific biodistribution ...
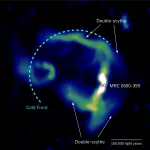
For the first time, researchers have observed plasma jets interacting with magnetic fields in a massive galaxy cluster 600 million light years away, thanks to the help of radio telescopes and supercomputer simulations. The findings, published in the journal Nature, can help clarify how such galaxy clusters evolve.
Galaxy clusters can contain up to thousands of galaxies bound together by gravity. Abell 3376 is a huge cluster forming as a result of a violent collision between two sub-clusters of galaxies. Very little is known about the magnetic fields that exist within this and similar galaxy clusters.
"It is generally difficult to directly examine the structure of intracluster magnetic fields," says Nagoya University astrophysicist ...
DALLAS, May 24, 2021 -- Having a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA), sometimes called a "mini-stroke," increases the risk for a stroke in the future. Identifying the cause of the stroke or TIA can lead to specific prevention strategies to reduce the risk of additional strokes, according to an updated guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. The guideline is published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association.
Ischemic strokes account for 87% of strokes in the United States. An ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow in a vessel leading to the brain is blocked, by either clots or plaques. ...
CRISPR technology allows researchers to edit genomes by altering DNA sequences and by thus modifying gene function. Its many potential applications include correcting genetic defects, treating and preventing the spread of diseases and improving crops.
Genome editing tools, such as the CRISPR-Cas9 technology, can be engineered to make extremely well-defined alterations to the intended target on a chromosome where a particular gene or functional element is located. However, one potential complication is that CRISPR editing may lead to other, unintended, genomic changes. These are known as off-target activity. ...
While many might consider a walk in the woods to be a quiet, peaceful escape from their noisy urban life, we often don't consider just how incredibly noisy some natural environments can be. Although we use soothing natural sounds in our daily lives - to relax or for meditation - the thunder of a mountain river or the crash of pounding surf have likely been changing how animals communicate and where they live for eons. A new experimental study published in the journal Nature Communications finds that birds and bats often avoid habitat swamped with loud whitewater river noise.
Dr. Dylan Gomes, a recent PhD graduate of Boise State University ...
For centuries, pelagic Sargassum, floating brown seaweed, have grown in low nutrient waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, supported by natural nutrient sources like excretions from fishes and invertebrates, upwelling and nitrogen fixation. Using a unique historical baseline from the 1980s and comparing it to samples collected since 2010, researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute and collaborators have discovered dramatic changes in the chemistry and composition of Sargassum, transforming this vibrant living organism into a toxic "dead zone."
Their findings, published in Nature Communications, suggest that increased nitrogen availability from natural and anthropogenic sources, including sewage, is supporting blooms of ...