Microscopic fossils record ancient climate conditions
2021-05-24
(Press-News.org) Fifty-six million years ago, as the Earth's climate warmed by five to eight degrees C, new land mammals evolved, tropical forests expanded, giant insects and reptiles appeared and the chemistry of the ocean changed. Through it all, bacteria in the ocean in what is now New Jersey kept a record of the changes in their environment through forming tiny magnetic particles. Now, those particles and their record are all that's left of these microorganisms. Thanks to new research tools, that record is finally being read.
In research published in the journal Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, researchers including University of Utah doctoral student Courtney Wagner and associate professor Peter Lippert report the climate clues that can be found by analyzing the magnetic fossil particles, or magnetofossils.
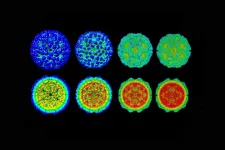
"We interpret the relative abundances of these different populations of magnetofossils based on shape and size, which are a function of bacteria species, to encode environmental changes that are not as apparent in other fossil data sets or geochemical proxies," Lippert says.
Using their FORC method (which stands for first-order reversal curves, a way of magnetically measuring and statistically describing the magnetic signatures in a sample of rock or sediment) they teased out three different subsets of magnetofossils from ancient coastal marine sediments.
"Each of the magnetofossil populations tells us something a little different about the environment," Wagner says. One consists of "giant needle-shaped" magnetofossils, associated with increased iron and an expansion of a gradient between oxygenated and deoxygenated seawater. Another contains "equant" magnetofossils, which may record more stable, long-term conditions in the ocean and the last contains "elongated" magnetofossils, which may indicate seasonal conditions.
The results are important because they allow researchers to track the chemistry of the ocean throughout a global warming event similar to what the Earth is currently experiencing. For example, the results seem to show that the New Jersey coast rapidly declined in oxygen near the beginning of the ancient warming event and then oxygen levels fluctuated thereafter.
"All this has potential implications for understanding how climate change will affect these sensitive coastal ecosystems today and in the future," Wagner says.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-24
By making a game out of getting their daily steps, new research points to the possibility that people with diabetes could be nudged toward increasing their physical activity, with changes lasting for a full year. Since many now use apps or other digital means to manage their diabetes, this program - which utilized tools like wearable step counters and electronic scales with personalized goals - could potentially be integrated to help individuals achieve greater success. Findings from the study, conducted by a team from the Perelman School of Medicine ...
2021-05-24
Carbon is vital to the existence of all living organisms, since it forms the basis of all organic molecules that, in turn, form the basis of all living beings. While that alone is pretty impressive, it has recently found surprisingly novel applications in disciplines such as aerospace and civil engineering with the development of carbon fibers that are stronger, stiffer, and lighter than steel. Consequently, carbon fibers have taken over steel in high-performance products like aircrafts, racecars, and sports equipment.
Carbon fibers are usually combined with other materials to form ...
2021-05-24
Scientists studying a special kind of semimetals have found a material with an unusually pristine nature that could be crucial for developing powerful new quantum technologies and discovering new phases of matter.
In an open access paper published in Science Advances, Johns Hopkins physicists and colleagues at Rice University, the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien), and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), present experimental evidence of naturally occurring quantum criticality in a material.
Criticality is the point at which a material hovers between two phases--like the slushy transition between water and ice--without ever settling. Useful materials often exploit this point. For example, air conditioners use compressors to change refrigerant ...
2021-05-24
In order to understand foodways and subsistence strategies of humans in the past, as well as distributions of ancient animal species, it is critical for archaeologists to accurately identify animal taxa in archaeological sites. Many sites across sub-Saharan Africa have fragmented and poorly preserved animal bones, leaving the majority of specimens unidentifiable. Sub-Saharan Africa is also home to the greatest diversity of bovids on Earth, including African buffalo, wildebeest, eland, and duikers, as well as domestic sheep, goat, and cattle. The sheer number of osteologically similar animals in Africa presents a major challenge for identifying animal bones.
During the past decade, archaeologists have increasingly used a bone ...
2021-05-24
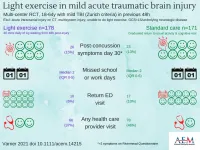
Des Plaines, IL - For acute mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), there were no differences in recovery or health care utilization outcomes with prescribed early light exercise compared to standard care. These are the results of a study titled A randomized trial comparing prescribed light exercise to standard management for emergency department patients with acute mild traumatic brain injury, to be published in the May issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM) journal, a peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
Findings of the study suggest that early light exercise may be encouraged as tolerated at emergency department discharge following mTBI, but this guidance is not sufficient ...
2021-05-24
HOUSTON ? Several Phase II clinical trials conducted by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center show promising results for patients with melanoma, breast cancer, HER2-positive tumors and ovarian cancer. The results of these studies, which will be presented at the virtual 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, highlight new advances in drug therapy research to improve patient outcomes.
Combination therapy of nivolumab and relatlimab before and after surgery is effective against melanoma (Abstract #9502)
In a Phase II study, MD Anderson researchers showed that a regimen of neoadjuvant and ...
2021-05-24
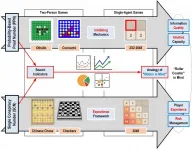
Iahikawa, Japan - Humans benefit from playing games more than some might realize. Games can be a relaxed approach to learning or honing our problem-solving skills while relieving stress. However, game playing generally carries a considerable amount of decision-making, involving mathematical and statistical considerations that we make to decide on what we think is the best move. Thus, games showcase many of the impressive faculties and inner workings of the human brain, which in turns makes them a great testbed and playground for research on artificial intelligence (AI).
One aspect common to many games is decision making based on uncertain information about current and potential ...
2021-05-24
Months after recovering from mild cases of COVID-19, people still have immune cells in their body pumping out antibodies against the virus that causes COVID-19, according to a study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such cells could persist for a lifetime, churning out antibodies all the while.
The findings, published May 24 in the journal Nature, suggest that mild cases of COVID-19 leave those infected with lasting antibody protection and that repeated bouts of illness are likely to be uncommon.
"Last fall, there were reports that antibodies wane quickly after infection with the virus that causes COVID-19, and mainstream media interpreted that to mean that immunity was not long-lived," said senior author Ali Ellebedy, PhD, an associate professor ...
2021-05-24
A critical process in the infection cycle of viruses has been revealed for the first time in dynamic detail using pioneering plant-based technology.
Evidence about the process of virus maturation revealed in the research could help us develop new methods for treating viral infections.
Maturation plays a critical role for all animal and bacterial viruses and is required to produce infectious virions or particles. Though the outlines of the process have been determined for many groups of viruses, detailed mechanistic studies have not been reported.
To provide the first detailed mechanistic study of maturation, Roger Castells-Graells, ...
2021-05-24
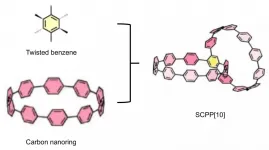
The research team led by Prof. DU Pingwu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) first successfully synthesized an all-phenylene bismacrocycle (bis- means two) with Siamese-twin structure and used fullerene as guest molecules to assemble a peanut-shaped supramolecular complex. This study was published in Angewandte Chemie.
As a new type of carbon material, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have attracted widespread attention because of their outstanding mechanical and photophysical properties. However, the synthesis of CNTs or CNTs fragments with selective simple structure is still a challenge.
This study reported a conjugated highly strained all-phenylene Siamese-twin bismacrocycle, SCPP[10]. Two phenylene nanorings, [10]CPP, conjoined ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Microscopic fossils record ancient climate conditions