INFORMATION:
Virus infection cycle revealed in dynamic detail
2021-05-24
(Press-News.org) A critical process in the infection cycle of viruses has been revealed for the first time in dynamic detail using pioneering plant-based technology.
Evidence about the process of virus maturation revealed in the research could help us develop new methods for treating viral infections.
Maturation plays a critical role for all animal and bacterial viruses and is required to produce infectious virions or particles. Though the outlines of the process have been determined for many groups of viruses, detailed mechanistic studies have not been reported.
To provide the first detailed mechanistic study of maturation, Roger Castells-Graells, a rotation Ph.D. student working in Professor. George Lomonossoff's laboratory at the John Innes Centre infiltrated genetic material of the insect virus Nudaurelia capensis omega virus (N?V) into dwarf tobacco plants N.benthamiana.
This transient expression technique uses Virus Like Particles (VLPs) which are mimics of the authentic virus. The capsid or protein coat of the virus is produced by plant cells and the research team then analyses the material purified from infiltrated leaves.
The research demonstrated that maturation of procapsids - immature viral structures - can occur within plant cells to yield fully functional mature capsids. This has not been observed previously in the absence of a natural infection and is a new application for the transient expression system pioneered by Professor Lomonossoff at the John Innes Centre.
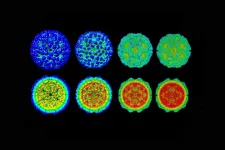
Comparative cryo-EM analysis of the structures of the procapsids and mature capsids revealed the large structural rearrangements both inside and between the protein subunits of the capsid that accompany maturation. These shape changes enable the chemical reactions that are necessary for the virus to infect the host.
Professor Lomonossoff, a group leader at the John Innes Centre, said: "Most structural studies of virus particles to date have given a static picture of the particles. By isolating particles from plants that are undergoing the process of maturation, we have managed to obtain a picture of the dynamics of an essential part of a virus infection cycle."
The present study, a collaboration involving scientists at the University of Leeds, in Brazil and the USA, as well as at the John Innes Centre, reveals details of the structures at the beginning and the end of the maturation process. What is now required is an analysis of intermediate steps to get a complete understanding of the dynamics.
This will enable the research team to determine the 3-D structures of intermediates in the maturation process to create a "movie."
"We have shown that maturation occurs over time within plant cells and that means we have discovered a valuable tool for studying virus maturation. We hope it will be of interest to potential collaborators and industry," said Professor Lomonossoff.
Plant-expressed virus-like particles reveal the intricate maturation process of a eukaryotic virus appears in Communications Biology
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers first synthesize conjoined bismacrocycle with all phenylene units
2021-05-24
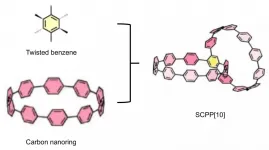
The research team led by Prof. DU Pingwu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) first successfully synthesized an all-phenylene bismacrocycle (bis- means two) with Siamese-twin structure and used fullerene as guest molecules to assemble a peanut-shaped supramolecular complex. This study was published in Angewandte Chemie.
As a new type of carbon material, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have attracted widespread attention because of their outstanding mechanical and photophysical properties. However, the synthesis of CNTs or CNTs fragments with selective simple structure is still a challenge.
This study reported a conjugated highly strained all-phenylene Siamese-twin bismacrocycle, SCPP[10]. Two phenylene nanorings, [10]CPP, conjoined ...
New study shows never before seen nutrient exchanges between algae and bacteria
2021-05-24
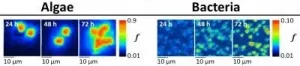
Research co-led by Newcastle University has shed new light on important microscopic scale interactions between algae and bacteria predicated on the mutually beneficial exchange of nutrients.
The research was carried out at the University of Cambridge and the Nordsim laboratory at the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm by Dr Hannah Laeverenz Schlogelhofer, now at the University of Exeter, and a team led by Dr Ottavio Croze, of Newcastle University's School of Mathematics, Statistics and Physics.
They have used an advanced high-spatial resolution isotope mapping technique called 'SIMS' (secondary ion mass spectrometry) to chart for the first time how long it takes for labelled carbon produced by microalgae to be transferred ...
Supersensitive connection causes hatred of noises
2021-05-24
A supersensitised brain connection has been identified in people who suffer from misophonia, an extreme reaction to "trigger" sounds.
For the first time, researchers led by Newcastle University, have discovered increased connectivity in the brain between the auditory cortex and the motor control areas related to the face, mouth and throat.
Publishing today, in the Journal of Neuroscience, lead author Dr Sukhbinder Kumar, Newcastle University Research Fellow in the Biosciences Institute said: "Our findings indicate that for people with misophonia there is abnormal communication between the auditory and motor ...
Posts to Reddit forum "SuicideWatch" spike in the early hours of Monday morning
2021-05-24
Posts to Reddit forum "SuicideWatch" spike in the early hours of Monday morning
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King's College London has found that people on a social media suicide support forum are most likely to post to the site during the early hours of Monday morning.
The study, which has been published in BMC Psychiatry, suggests that there is a clear variation in behaviour throughout the week and throughout the day. The researchers hope that this means that targeted support to at risk populations can be made more readily available to those most in need.
The researchers looked at the timings at which users of the Reddit ...
Link between local oxygen depletion in the brain and Alzheimer's disease
2021-05-24
The study, published in the journal Nature Aging and led by the laboratories of Dr. Alberto Pascual (CSIC), from the Neuronal Maintenance Mechanisms Group, and Prof. Javier Vitorica (University of Seville/CIBERNED) of the Physiopathology of Alzheimer's Disease Group at IBiS, demonstrates for the first time that low oxygen levels in the so-called senile plaques in the brain reduces the immune system's defensive capacity against the disease.
The study also suggests that this lack of oxygen in the brain enhances the action of disorders associated with Alzheimer's disease that are characterised by low systemic oxygen levels, such as atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases.
What happens ...
Forensic archaeologists begin to recover Spanish Civil War missing bodies
2021-05-24
Forensic archaeologists and anthropologists from Cranfield University have started to recover the bodies of victims executed by the Franco regime at the end of the Spanish Civil War during an excavation in the Ciudad Real region of Spain.
The team from Cranfield is working with partners from the University Complutense of Madrid (UCM) and social anthropologists from Mapas de Memoria (Maps of Memory) to search for, exhume and identify those executed and buried in the civil cemetery at Almagro between 1939 and 1940.
Several bodies with gunshot wounds to the head, personal effects and parts of clothing ...
Obesity protects against death in severe bacterial infection
2021-05-24
For many diseases, overweight and obesity are risk factors. But now a study shows that a higher BMI may be linked to higher survival rates in patients hospitalized for severe bacterial infections.
Scientists at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, and Skaraborg Hospital in Skövde carried out the research, and their study has now been published in the journal PLOS ONE. The data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic.
The population-based study involved observations, over a nine-month period, of all 2,196 individual adults receiving care for suspected severe bacterial ...
Using waste heat to power an environmentally sustainable future
2021-05-24
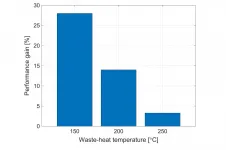
In his most recent published research, appearing in Applied Thermal Engineering, City, University of London's Dr Martin White explores a novel organic Rankine cycle system, based on a two-phase expansion through numerical simulations of the system.
His paper, Cycle and turbine optimisation for an ORC operating with two-phase expansion, considers the use of modern fluids whose properties could help to mitigate concerns around turbine damage, whilst allowing the benefits of two-phase expansion to be realised.
Waste heat from a range of industries, ranging from iron and steel to food and drink, ...
Electromagnetic anomalies that occur before an earthquake
2021-05-24
It has been documented over hundreds of years that various electromagnetic anomalies occur during a few weeks before the occurrence of a large earthquake. These electromagnetic anomalies are variations that appear in telluric current, geomagnetism, electromagnetic waves etc. before the earthquake.
Although there are various models to explain the mechanism, the large current generated at the source was not fully explained. For example, many researchers thought that the stress applied to the fault produced an electric current, but the stress applied to the fault takes place over hundreds or thousands of years before the occurrence of the earthquake. It is a common belief among seismologists ...
Telomere length, a longevity measure, may be determined early in life
2021-05-24
Telomeres are protective caps on DNA that shorten as we grow older. Now, one of the first studies to examine telomere length (TL) in childhood finds that the initial setting of TL during prenatal development and in the first years of life may determine one's TL throughout childhood and potentially even into adulthood or older age. The study also finds that TL decreases most rapidly from birth to age 3, followed by a period of maintenance into the pre-puberty period, although it was sometimes seen to lengthen.
The study, which followed children from birth to age 9, was led by researchers ...