New study shows never before seen nutrient exchanges between algae and bacteria
Research co-led by Newcastle University has shed new light on important microscopic scale interactions between algae and bacteria predicated on the mutually beneficial exchange of nutrients.
2021-05-24
(Press-News.org) Research co-led by Newcastle University has shed new light on important microscopic scale interactions between algae and bacteria predicated on the mutually beneficial exchange of nutrients.
The research was carried out at the University of Cambridge and the Nordsim laboratory at the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm by Dr Hannah Laeverenz Schlogelhofer, now at the University of Exeter, and a team led by Dr Ottavio Croze, of Newcastle University's School of Mathematics, Statistics and Physics.
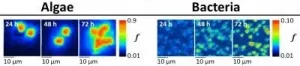
They have used an advanced high-spatial resolution isotope mapping technique called 'SIMS' (secondary ion mass spectrometry) to chart for the first time how long it takes for labelled carbon produced by microalgae to be transferred to the bacteria they are growing with.
The study reveals the details of important nutrient exchanges between algae and bacteria. Such exchanges determine the functioning of microbial communities in the environment, relevant to climate change cycles and agricultural productivity. Microbial interactions within microbial communities are important on many levels, ranging from the ecology of aquatic and terrestrial food webs, to wastewater treatment. A key characteristic of the interactions within these communities is the exchange of nutrients between species.
Publishing their findings in the journal PLOS ONE, the research team, involving also scientists from Stockholm University, Sweden, also used a mathematical model to predict how the concentrations of nutrients exchanged between the microbes change with time, including vitamin B12, which occurs in very low concentrations and is not easily trackable.
Many species of algae and bacteria share mutually beneficial resources. In this study, the algae depend on bacteria as a source of vitamin B12, as they can't make it themselves. On the other hand, bacteria rely on carbon produced by algae for their growth. The research combines SIMS and mathematical modelling to show what happens when microbial partners able to exchange nutrients are initially brought together.
Principal investigator of the study, Dr Croze said: "The paper concerns the onset of the mutualistic interaction between microalgae and bacteria, that is microbes that need each other to grow and survive, and the transfer of nutrients between them.
"Our results allow establishing when the microbial partners first form a 'relationship' by growing exclusively on the nutrients they respectively produce. The method we have developed is widely applicable to other microbial systems, and we hope it will contribute to furthering a mechanistic understanding of interactions within microbial communities in the environment and biotechnological applications."
Dr Laeverenz Schlogelhofer added: "It is the interdisciplinary nature of our approach to studying microbial interactions that I think will have broad applications. While the single-cell technique SIMS allowed us to visualise and measure the carbon exchange between algae and bacteria, mathematical modelling provided a link between the experimental observations and our understanding of the underlying nutrient kinetics."
Co-author Dr Rachel Foster, from Stockholm University, said: "I appreciate most that the work takes highly resolved single cell measurements and directly applies them for predicting nutrient acquisitions between cells. Hence we can use calculated rate measurements based on the SIMS measures instead of assuming an activity rate, and this approach should be far-reaching and applicable to many other microbial populations-free and/or symbiotic."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-24
A supersensitised brain connection has been identified in people who suffer from misophonia, an extreme reaction to "trigger" sounds.
For the first time, researchers led by Newcastle University, have discovered increased connectivity in the brain between the auditory cortex and the motor control areas related to the face, mouth and throat.
Publishing today, in the Journal of Neuroscience, lead author Dr Sukhbinder Kumar, Newcastle University Research Fellow in the Biosciences Institute said: "Our findings indicate that for people with misophonia there is abnormal communication between the auditory and motor ...
2021-05-24
Posts to Reddit forum "SuicideWatch" spike in the early hours of Monday morning
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King's College London has found that people on a social media suicide support forum are most likely to post to the site during the early hours of Monday morning.
The study, which has been published in BMC Psychiatry, suggests that there is a clear variation in behaviour throughout the week and throughout the day. The researchers hope that this means that targeted support to at risk populations can be made more readily available to those most in need.
The researchers looked at the timings at which users of the Reddit ...
2021-05-24
The study, published in the journal Nature Aging and led by the laboratories of Dr. Alberto Pascual (CSIC), from the Neuronal Maintenance Mechanisms Group, and Prof. Javier Vitorica (University of Seville/CIBERNED) of the Physiopathology of Alzheimer's Disease Group at IBiS, demonstrates for the first time that low oxygen levels in the so-called senile plaques in the brain reduces the immune system's defensive capacity against the disease.
The study also suggests that this lack of oxygen in the brain enhances the action of disorders associated with Alzheimer's disease that are characterised by low systemic oxygen levels, such as atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases.
What happens ...
2021-05-24
Forensic archaeologists and anthropologists from Cranfield University have started to recover the bodies of victims executed by the Franco regime at the end of the Spanish Civil War during an excavation in the Ciudad Real region of Spain.
The team from Cranfield is working with partners from the University Complutense of Madrid (UCM) and social anthropologists from Mapas de Memoria (Maps of Memory) to search for, exhume and identify those executed and buried in the civil cemetery at Almagro between 1939 and 1940.
Several bodies with gunshot wounds to the head, personal effects and parts of clothing ...
2021-05-24
For many diseases, overweight and obesity are risk factors. But now a study shows that a higher BMI may be linked to higher survival rates in patients hospitalized for severe bacterial infections.
Scientists at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, and Skaraborg Hospital in Skövde carried out the research, and their study has now been published in the journal PLOS ONE. The data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic.
The population-based study involved observations, over a nine-month period, of all 2,196 individual adults receiving care for suspected severe bacterial ...
2021-05-24
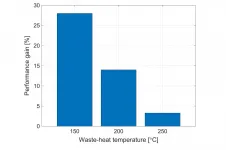
In his most recent published research, appearing in Applied Thermal Engineering, City, University of London's Dr Martin White explores a novel organic Rankine cycle system, based on a two-phase expansion through numerical simulations of the system.
His paper, Cycle and turbine optimisation for an ORC operating with two-phase expansion, considers the use of modern fluids whose properties could help to mitigate concerns around turbine damage, whilst allowing the benefits of two-phase expansion to be realised.
Waste heat from a range of industries, ranging from iron and steel to food and drink, ...
2021-05-24
It has been documented over hundreds of years that various electromagnetic anomalies occur during a few weeks before the occurrence of a large earthquake. These electromagnetic anomalies are variations that appear in telluric current, geomagnetism, electromagnetic waves etc. before the earthquake.
Although there are various models to explain the mechanism, the large current generated at the source was not fully explained. For example, many researchers thought that the stress applied to the fault produced an electric current, but the stress applied to the fault takes place over hundreds or thousands of years before the occurrence of the earthquake. It is a common belief among seismologists ...
2021-05-24
Telomeres are protective caps on DNA that shorten as we grow older. Now, one of the first studies to examine telomere length (TL) in childhood finds that the initial setting of TL during prenatal development and in the first years of life may determine one's TL throughout childhood and potentially even into adulthood or older age. The study also finds that TL decreases most rapidly from birth to age 3, followed by a period of maintenance into the pre-puberty period, although it was sometimes seen to lengthen.
The study, which followed children from birth to age 9, was led by researchers ...
2021-05-24
AMHERST, Mass. - New developments in recreational fishing technology--from the use of aerial drones and social media scouting reports to advances in hook design--are creating challenges for fisheries management and effective policy making, according to a new study co-authored by University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher Andy Danylchuk.
With the opening of the spring fishing season, millions of recreational fishing aficionados across North America are dusting off their tackleboxes, fitting together their rods, and heading to the bait and tackle shop to purchase the latest ...
2021-05-24
(Boston)--Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is caused by diabetes and hypertension. In 2017, the global prevalence of CKD was 9.1 percent, which is approximately 700 million cases. Chronic kidney damage is assessed by scoring the amount of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) in a renal biopsy sample. Although image digitization and morphometric (measuring external shapes and dimensions) techniques can better quantify the extent of histologic damage, a more widely applicable way to stratify kidney disease severity is needed.
Now, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have developed a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool to predict the grade of IFTA, a known structural ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study shows never before seen nutrient exchanges between algae and bacteria
Research co-led by Newcastle University has shed new light on important microscopic scale interactions between algae and bacteria predicated on the mutually beneficial exchange of nutrients.