Nearly half of COVID-19 patients left hospital in worse physical condition
The results fill in a knowledge gap about how patients recover from the disease.
2021-05-25
(Press-News.org) Over a year after the novel coronavirus cemented its grip on the world, much of the conversation surrounding the disease remains simple: how many people died and how many survived?
But researchers at Michigan Medicine say a devastating side effect lurks, underreported, between those extremes - the loss of ability caused by the virus.
In a study published in the journal PM&R, investigators found that 45% of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 experienced significant functional decline after being discharged.
"Rehabilitation needs were really, really common for these patients," says lead author Alecia K. Daunter, M.D., a pediatric physiatrist at Michigan Medicine. "They survived, but these people left the hospital in worse physical condition than they started. If they needed outpatient therapy or are now walking with a cane, something happened that impacted their discharge plan."
The team of researchers reviewed charts of nearly 300 adult patients hospitalized for COVID-19 at Michigan Medicine during the pandemic's first wave between March and April 2020. They analyzed patients' discharge locations, therapy needs at the time of release and if they needed durable medical equipment or other services.
Of survivors who experienced functional decline, 80% were referred for additional therapy after being discharged. Nearly 20% of all patients lost so much ability, they were not able to live independently after their release.
"These patients may have needed to move to a subacute facility, or they might have needed to move in with a family member, but they were not able to go home," Daunter says. "This has a massive impact on patients and their families - emotionally and physically."
The study period occurred in the pandemic's infancy, as health care providers sought best practices to minimize exposures and manage patient overflow. As a result, 40% of patients never had a rehabilitation evaluation while hospitalized. That likely means, Daunter explains, that the number of patients losing ability is underreported.
"Physicians and others in the health care system were working appropriately to discharge patients," she says. "They needed to keep patients safe while maximizing available beds and minimizing exposure to staff. I think that contributed to many people not being assessed by a therapist or PM&R physician. So, the things we do to in the hospital to maximize functioning, like mobility interventions and assessing activities of daily living were, not happening as often."
COVID-19 can systematically damage various organ systems, causing neurological and musculoskeletal impairments. Michigan Medicine recently opened two clinics to address the growing population of "long COVID" patients.
However, the virus' effect on daily functioning is not frequently described, which, given the magnitude of the current public health crisis, can't be ignored any longer, says Edward Claflin, M.D., a Michigan Medicine physiatrist and co-author of the paper.
"These results help to highlight the true impact of the COVID-19 disease on our patients," Claflin says. "They fill in that gap in knowledge about how patients with COVID recover and what kind of rehabilitation needs they have."
The "first wave" study is a snapshot look at acute therapy needs during a time when knowledge of the unique virus was even more limited. The team hopes for additional research examining the long-term effects COVID has on functionality. However, health systems can use the current data to optimize rehabilitation evaluations and prepare resources for this underserved population, Daunter says.
"These problems are frequent, and the stakes are pretty high if we miss them, or allow them to progress during hospitalization," she says. "Some of these people were working and many were living independently. To lose that level of function is meaningful. We want to make sure we're addressing those needs, not just looking at the black and white, survival or death."
INFORMATION:
Paper cited: "Functional Decline in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in the Early Months of the Pandemic," PM&R. DOI: 10.1002/pmrj.12624
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-25
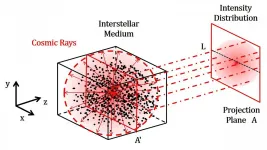
WASHINGTON, May 25, 2021 -- Cosmic rays are high-energy atomic particles continually bombarding Earth's surface at nearly the speed of light. Our planet's magnetic field shields the surface from most of the radiation generated by these particles. Still, cosmic rays can cause electronic malfunctions and are the leading concern in planning for space missions.
Researchers know cosmic rays originate from the multitude of stars in the Milky Way, including our sun, and other galaxies. The difficulty is tracing the particles to specific sources, because the turbulence of interstellar gas, plasma, and dust causes them to scatter and rescatter in different directions.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, University of Notre Dame researchers developed a simulation model ...
2021-05-25
Fusarium Head Blight (FHB), also known as scab, is a significant disease of small grain cereals, such as wheat and barley, that impacts farmers around the world. The disease has been reducing acreage and increasing the price of wheat production in the United States since the early 1990s, which in turn increases costs for downstream producers, such as millers and brewers.
The disease is caused by a fungus that produces heat-stable trichothecene mycotoxins, which help the disease spread. To stop the spread, plant breeders are working to develop cultivars with improved resistance to FHB. A team of plant pathologists primarily based at Rutgers University recently generated ...
2021-05-25
What started as the preliminary analysis of routine laboratory data has since evolved into the largest-ever study of viral load levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2. A team of researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin have now analyzed the PCR samples of more than 25,000 persons with COVID-19. Working under the leadership of Prof. Dr. Christian Drosten, the team determined the viral loads of each individual sample and used their results to estimate levels of infectiousness. The research, which has been published in Science*, provides a clear idea of the infectiousness of the disease in different age groups and at different levels of disease severity. It also provides new insights into the ...
2021-05-25
LA JOLLA--(May 25, 2021) One of the many effects of aging is loss of muscle mass, which contributes to disability in older people. To counter this loss, scientists at the Salk Institute are studying ways to accelerate the regeneration of muscle tissue, using a combination of molecular compounds that are commonly used in stem-cell research.
In a study published on May 25, 2021, in Nature Communications, the investigators showed that using these compounds increased the regeneration of muscle cells in mice by activating the precursors of muscle cells, called myogenic progenitors. Although more work is needed before this approach can be applied in humans, the ...
2021-05-25
Childhood abuse and trauma are linked to many health issues in adulthood. New research from the University of Georgia suggests that a history of childhood mistreatment could have negative ramifications for the children of people who experienced abuse or neglect in childhood.
Teaching your children how to manage their emotions is an integral part of parenting. For people who experienced childhood abuse, that can become a difficult task. People who were frequently mistreated as children may find it hard to identify their emotions and implement strategies to regulate them. This difficulty, in turn, can harm their kids' emotional development.
The study, published ...
2021-05-25
Recently, the eROSITA (extended Roentgen Survey with an Imaging Telescope Array) x-ray telescope, an instrument developed by a team of scientists at Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), has gained attention among astronomers. The instrument performs an all-sky survey in the x-ray energy band of 0.2-8 kilo electron volts aboard the Spectrum-Roentgen-Gamma (SRG) satellite that was launched in 2019 from the Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
"The eROSITA has been designed to study the large-scale structure of the universe and test cosmological models, including dark energy, by detecting galaxy clusters with redshifts greater than 1, corresponding to a cosmological expansion ...
2021-05-25
Plants contain several types of specialized light-sensitive proteins that measure light by changing shape upon light absorption. Chief among these are the phytochromes.
Phytochromes help plants detect light direction, intensity and duration; the time of day; whether it is the beginning, middle or end of a season; and even the color of light, which is important for avoiding shade from other plants. Remarkably, phytochromes also help plants detect temperature.
New research from Washington University in St. Louis helps explain how the handful of phytochromes found in every plant respond differently to light intensity and temperature, thus ...
2021-05-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- When the worsening COVID-19 pandemic prompted colleges to shutter their campuses and shift to remote learning in spring 2020, concerns arose that many underrepresented students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics disciplines would be demotivated and drop out in even greater numbers.
However, a study of 182 undergraduate students in a biology course at one university found little evidence to support that belief. Instead, across all demographic groups, the impact varied: Some students were more motivated, some were less so, and some saw no changes ...
2021-05-25
(10 a.m. EDT May 25, 2021 Denver)-- Adding sintilimab to a regimen of gemcitabine and platinum demonstrates clinical benefit over gemcitabine and platinum alone as first-line therapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic squamous cell non-small cell lung cancer, according to a study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
The standard chemotherapy for squamous NSCLC (sqNSCLC), includes platinum plus gemcitabine. sintilimab, an anti-PD-1 antibody, plus platinum/gemcitabine, has shown encouraging efficacy as first-line therapy for sqNSCLC in the phase III study ECOG 1594. Platinum/gemcitabine is another standard regimen of chemotherapy for sqNSCLC and is commonly used in ...
2021-05-25
China has made remarkable gains in reducing the number of women who die during childbirth and boosting child survival rates over the past 70 years, according to new review.
The Lancet report brought together China's health research institutions alongside its international colleagues from Australia, the UK and the US to review the country's progress in maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health and nutrition since 1949.
Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) Professor George Patton, one of the international researchers, said over the past 70 years China had made a remarkable transition from where the survival of women and children was the priority to one where children ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nearly half of COVID-19 patients left hospital in worse physical condition
The results fill in a knowledge gap about how patients recover from the disease.