Protein tenascin-C important in retinal blood flow disorders
2021-05-26
(Press-News.org) Many eye diseases are associated with a restricted blood supply, known as ischaemia, which can lead to blindness. The role of the protein tenascin-C, an extracellular matrix component, in retinal ischaemia was investigated in mice by researchers from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB). They showed that tenascin-C plays a crucial role in damaging the cells responsible for vision following ischaemia. The results were published online by the team in the journal Frontiers in Neuroscience on 20 May 2021.
As part of the research, the team around Dr. Susanne Wiemann and Dr. Jacqueline Reinhard from the Department of Cell Morphology and Molecular Neurobiology at RUB collaborated with Professor Stephanie Joachim's research group from the Experimental Eye Research Institute at the University Eye Clinic in Bochum.
Tenascin-C after retinal ischaemia
Ischaemia occurs due to an interruption in the supply of blood and nutrients to the retina - similar to a stroke. This causes the cells responsible for vision to die, which can lead to impaired vision or even blindness. The research team showed in mice that retinal cells express increased levels of tenascin-C at a very early stage following ischaemia. The quantity of the protein then gradually reduces again as the damage to the retina progresses. "Tenascin-C could therefore be a biomarker for the early detection of ischaemic eye conditions," says Jacqueline Reinhard.
Improved retinal function in mice without tenascin-C following ischaemia
The researchers also conducted electroretinogram analyses, allowing them to measure the electrical signal flow of the retina after a light stimulus. They thus showed that retinal ischaemia impairs the function of certain cell types in the retina: both the rod-photoreceptors and the bipolar cells, which are involved in downstream visual processing.
In genetically modified mice, who were unable to form tenascin-C, the cells responsible for vision in the retina functioned considerably better following ischaemic damage than those in control animals, who had tenascin-C. In addition, fewer photoreceptors died without tenascin-C after ischaemia.
Possible changes between the neuron contact points
The researchers also demonstrated elevated levels of the vesicular glutamate transporter vGlut1 in the ischaemic retina. "These could be linked to impaired synaptic signal transmission between the cells and contribute to cell death as a result of retinal ischaemia. Tenascin-C could be an important modulator here," assumes Jacqueline Reinhard. "Based on this knowledge, future therapy approaches could be developed to improve the treatment of ischaemia."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-26
Included in the vast fallout stemming from the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists are paying closer attention to microbial infections and how life forms defend against attacks from pathogens.
Research led by University of California San Diego scientists has shed new light on the complex dynamics involved in how organisms sense that an infection is taking place.
UC San Diego Assistant Project Scientist Eillen Tecle in Professor Emily Troemel's laboratory (Division of Biological Sciences) led research focusing on how cells that are not part of the conventional immune system respond to infections when pathogens attack. Scientists have conducted extensive research on so-called "professional" immune cells that are defensive specialists. Much less is known about how "non-professional" cells ...
2021-05-26
Alzheimer's disease - also called dementia - where memory and cognitive functions gradually decline due to deformation and death of neurons, and Parkinson's disease that causes tremors in hands and arms impeding normal movement are major neurodegenerative diseases. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has identified the structure of the agent that causes Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases to occur together.
A research team led by Professor Joon Won Park and Ph.D. candidate Eun Ji Shin of the Department of Chemistry at POSTECH investigated the surface structure of hetero-oligomers found in the overlap of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, using an atomic force microscopy (AFM) to reveal their structural identity. This study was featured as the ...
2021-05-26
While the plates carry water to the Earth's interior, phase transitions of dry olivine, the main mineral in the plates, are thought to be responsible for deep-focus earthquakes and plate deformation. This study resolves the contradiction of the presence of dry olivine even in wet plates. Takayuki Ishii, a researcher at the Center for High Pressure Science & Technology Advanced Research (HPSTAR), China and the Bavarian Institute of Geosciences, University of Bayreuth, Germany, and Eiji Otani, a professor emeritus at Tohoku University, used high-pressure and high-temperature experiments to determine the water content of olivine under ...
2021-05-26
Tiny charged electrons and protons which can damage satellites and alter the ozone have revealed some of their mysteries to University of Otago scientists.
In a study, published in Geophysical Research Letters, the group looked at charged particles interacting with a type of radio wave called 'EMIC' - a wave generated in Earth's radiation belts (invisible rings of charged particles orbiting the Earth).
Lead author Dr Aaron Hendry, of the Department of Physics, says it is important to understand how these waves affect the belts - which are filled with expensive and important satellites - and Earth's climate.
"Much like the Earth's atmosphere, the Earth's magnetosphere - the region around the Earth where our magnetic field is stronger ...
2021-05-26
A new study from the University of Kent, Toulouse Business School, ESSCA School of Management (Paris) and ESADE Business School (Spain) has revealed the three primary risks and benefits perceived by consumers towards autonomous vehicles (self-driving cars).
The increased development of autonomous vehicles worldwide inspired the researchers to uncover how consumers feel towards the growing market, particularly in areas that dissuade them from purchasing, to understand the challenges of marketing the product. The following perceptions, gained through qualitative interviews and ...
2021-05-26
There is growing evidence that house design can decrease the force of malaria infection.
The world's most deadly assassin is Africa's malaria mosquito: Anopheles gambiae. In 2019, the World Health Organisation estimated that malaria killed 386,000 people in sub-Saharan Africa, mainly children.
Whilst we think of the home as a sanctuary, in Africa, around 80% of the malaria bites occur indoors at night. Preventing mosquitoes from getting indoors is a simple way of protecting people from this often lethal disease.
As most mosquitoes fly low to the ground, a team of researchers led by Durham University wondered whether ...
2021-05-26
Fishery and aquaculture have given rise to an enormous uniformity in the diversity of bivalves along the more than 18,000 kilometer long Chinese coast, biologist He-Bo Peng and colleagues report in this month's issue of Diversity and Distributions.
Climate zones
Peng and colleagues sampled bivalves at 21 sites along the Chinese coast from the city of Dongliaodao in the tropical south, to the mudflats of Yalu Jiang, more than 2000 km further north and ice-covered for several months in winter. "At 19 out of these 21 sites, commercially exploited species dominated", Peng saw. "In the naturally occurring species, we still recognized the natural gradient with highest diversity in the tropics and lowest diversity in ...
2021-05-26
The Manchester Arena terrorist bomb attack in 2017 exposed flaws in the response of emergency services that could be addressed with a new three-phase approach, research by the University of Bath School of Management shows.
Current government guidelines outline a two-phase structure of 'response and recovery', which researchers discovered hampered effective communication between agencies, created over-reliance on centralised Police decision-making, and inhibited other services' ability to take initiative earlier in an emergency.
"To better prepare responders for emergencies we recommend a three?phase structure of 'response/resolve/recovery' is introduced in place of the current guidelines ...
2021-05-26
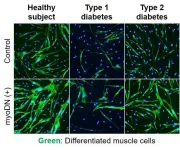
Skeletal muscle is the largest organ in the body that accounts for 30 to 40% of body weight and is responsible for multiple functions such as energy metabolism and heat production. However, skeletal muscle mass is reduced in some diabetics, and that muscle loss correlates with mortality. It has been reported that the differentiation of myoblasts, which are the muscle precursor cells, is reduced in diabetic patients, and this is thought to be one of the underlying causes of muscle loss.
Assistant Professor Tomohide Takaya of Shinshu University recently reported that oligo DNA derived from the genome ...
2021-05-26
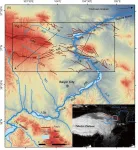
The evolutionary history of fluvial geomorphology is the consequences of combined effects of tectonic, climate, lithology and base level. Previous researches had emphasized tectonic impacts on the fluvial system at the tectonically active region, while lithology and base level get little attention. In addition, the resistance of lithology may cause knickpoint and control the evolutionary history of landscape in relatively stable areas, and difference in local base-level is sufficient to induce drainage reorganization. Nevertheless, it is still unclear how far the lithology and base level affect the evolution of fluvial landforms in tectonically active areas.
In this study, researchers chose the area in the NE Tibet Plateau (Laohu and Hasi mountains) (Figure ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Protein tenascin-C important in retinal blood flow disorders