Base level and lithology affect fluvial geomorphic evolution at a tectonically active area
2021-05-26
(Press-News.org) The evolutionary history of fluvial geomorphology is the consequences of combined effects of tectonic, climate, lithology and base level. Previous researches had emphasized tectonic impacts on the fluvial system at the tectonically active region, while lithology and base level get little attention. In addition, the resistance of lithology may cause knickpoint and control the evolutionary history of landscape in relatively stable areas, and difference in local base-level is sufficient to induce drainage reorganization. Nevertheless, it is still unclear how far the lithology and base level affect the evolution of fluvial landforms in tectonically active areas.
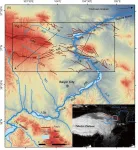
In this study, researchers chose the area in the NE Tibet Plateau (Laohu and Hasi mountains) (Figure 1) where the development of fluvial landform is affected by both the activity of the Haiyuan Fault and the aggradation/incision of the Yellow River. Here, they aim to untangle the role of lithology and base level on fluvial processes in tectonically activity region. And, the geomorphic indices, i.e., drainage pattern and χ anomalies, were calculated and investigated.
Because of basin-mountain structures controlled by the tectonic activities of the left-lateral Haiyuan Fault, the study area formed the Laohu and Hasi mountains (Figure 1), and two radial drainage systems developed surrounding these mountains (Figure 2). however, since some broad valleys exist upstream and canyons develop at the river mouth (Figure 3), local fluvial landforms cannot always be explained distinctly by the tectonic movements. While, other factors, such as lithology and local base level, may play crucial roles in regional landform at various spatial scales.
Our results show that different base levels and/or bedrock lithology have significant impacts on the drainage reorganization (figure 3) and development of the specific fluvial landform at different spatial scales in this tectonically active environment. Firstly, instead of flowing into the southward river with the short path, channels from the southeastern side of the Laohu Mountain have changed their courses from around south to north direction before flowing into the Yellow River (Figure 2). This flow direction change is triggered by river piracy and drainage network reorganization due to a significant altitude difference of local base-levels (the confluences of different tributaries to the Yellow River) (Figure 1). Secondly, lithology differences lead to the formation of the alternative distributions of canyons and wide valleys. In addition, long rivers with higher steepness index invade shorter ones, thereby enhancing their drainage area and further increasing the erosive capacity. This process of positive feedback may gradually transform an unstable parallel river pattern to a stable dendritic one.
INFORMATION:
See the article: Li Z, Wang X, Yu Y, Zhang H, Su Q, Miao X, Lu H. 2021. The impacts of base level and lithology on fluvial geomorphic evolution at the tectonically active Laohu and Hasi Mountains, northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Science China Earth Sciences, 64, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9743-1
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-26
New research could enable better healthcare for patients with benign tumours of the adrenal glands. Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have identified the levels of cortisol produced by the tumours which are associated with higher mortality rates.
Up to half of benign adrenal tumours produce excessive amounts of the hormone cortisol. Until now, researchers did not know at which levels the cortisol could be harmful or even fatal for the patient.
In a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, researchers at Lund University and Skåne University Hospital followed up all patients diagnosed with benign adrenal tumours who came into contact with Skåne University Hospital or Helsingborg Hospital between ...
2021-05-26
Metasurface holograms (meta-holograms) are ultra-thin artificial surfaces designed to shape incident light and project it to extremely wide angles. Meta-holograms have opened up numerous possibilities such as light multiplexing, information processing, 3D display, high-density data storage, and optical encoding. Despite of these remarkable advances, the road to practical applications of meta-holograms is hindered by artifacts that originate from strong interactions between the building blocks of the meta-holographic surface and inevitable fabrication defects, ultimately causing distortion and degradation to the holographic image. The small dimensions of the meta-hologram, together with the random nature of fabrication defects, make the artifacts problem ...
2021-05-26
GEOLOGY There has long been controversy about whether the world's highest region, Tibet, has grown taller during the recent geological past. New results from the University of Copenhagen indicate that the 'Roof of the World' appears to have risen by up to 600 meters and the answer was found in underwater lava. The knowledge sheds new light on Earth's evolution.
Tibet is referred to as the Roof of the World for good reason. With an average altitude of 4,500 meters above sea level and the world's two highest peaks, Mount Everest and K2, the vast Himalayan mountain range towers higher than anywhere else on Earth.
But the Tibetan plateau's height has been ...
2021-05-26
The goal of Kaare Hartvig Jensen, Associate Professor at DTU Physics, was to reduce the need for harvesting, transporting, and processing crops for the production of biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and other products. The new method of extracting the necessary substances, which are called plant metabolites, also eliminates the need for chemical and mechanical processes.
Plant metabolites consist of a wide range of extremely important chemicals. Many, such as the malaria drug artemisinin, have remarkable therapeutic properties, while others, like natural rubber or biofuel from tree sap, have mechanical properties.
Harvesting cell by cell
Because most plant metabolites are isolated in individual cells, the method ...
2021-05-26
When do bees sting and how do they organise their collective defence behaviour against predators? An interdisciplinary team of researchers from the Universities of Constance and Innsbruck has provided new insights into these questions. Their study, published in BMC Biology, combined behavioural experiments with an innovative theoretical modelling approach based on "Projective Simulation". It shows that individual bees decide whether to sting - or not - based on the presence and concentration of an alarm pheromone. The scientists suggest that each bee has a likelihood of stinging that is not constant, but shows at least two internal thresholds for the concentration of the pheromone: one to start stinging and one to stop stinging. The computational modelling also revealed how several environmental ...
2021-05-26
A long-standing theory assumes that terrestrial plants could only have developed by entering into a symbiosis with fungi, whereby the two organisms exchange resources in a mutually beneficial way. A new study by an international group of scientists has now confirmed this theory. By studying a liverwort species (a bryophyte related to mosses), the scientists succeeded in demonstrating that a lipid transfer takes place between the plant and the fungus similar to that already known to exist in plants with stems and roots - so called vascular plants. The study was led by French researchers from the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) and the Université de Toulouse III - Paul Sabatier, in collaboration with the ...
2021-05-26
Researchers at Aalto University in Finland have found strong evidence that warm ice - that is, ice very close in temperature to zero degrees Celsius - may fracture differently than the kinds of ice typically studied in laboratories or nature. A new study published in The Cryosphere takes a closer look at the phenomenon, studied at the world's largest indoor ice tank on Aalto's campus.
Understanding how ice breaks is crucial for ensuring safe harbours and bridges in cool climates, as well as transportation through historically ice-heavy regions. As global warming brings changes to once-predictable seasonal conditions, the rules underpinning infrastructure ...
2021-05-26
A paper published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine presents the results from a study which examined the use of an infrared thermal imaging camera as a novel non-invasive point-of-care tool for lymphatic filariasis lower-limb lymphoedema.
Thermal imaging has been used for several decades in a wide range of medical disciplines, but this is the first time it has been used for filariasis or any skin neglected tropical disease (NTD).
LSTM's Dr Louise Kelly-Hope led the research. She said: "Infrared thermal imaging presents an innovative and objective method for quantifying clinical change in filarial lymphoedema status by using naturally emitting infrared radiation to capture skin surface temperatures. This ...
2021-05-26
A recent study finds that the vast majority of Black adolescents have experienced racism, that they experience anticipatory stress about experiencing racism again, and that their racial identity can influence that stress in a variety of ways.
"We know that racism is stressful," says Elan Hope, corresponding author of the study and an associate professor of psychology at North Carolina State University. "Part of that stress is anticipatory - waiting for the next racist thing to happen. But not everyone experiences this stress the same way. We wanted to know how racial identity may influence ...
2021-05-26
Non-parents expand the range of their facial expressions in caring for infants among primates, a team of anthropologists has found. The study shows the ability, among non-relatives, to both decipher facial expressions and to be attuned to others' emotional states, revealing the evolutionary nature of communication.
The research, which appears in the journal Evolution, focused on the relationship between alloparenting, or infant care by non-parents, and the adoption of detailed facial expressions across more than 30 species of primates.
"Our results confirm previous work indicating ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Base level and lithology affect fluvial geomorphic evolution at a tectonically active area