INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the U.S. National Science Foundation, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Oak Spring Garden Foundation.
Dinosaur-age fossils provide new insights into origin of flowering plants
2021-05-26
(Press-News.org) Flowering plants (angiosperms) dominate most terrestrial ecosystems, providing the bulk of human food. However, their origin has been a mystery since the earliest days of evolutionary thought.
Angiosperm flowers are hugely diverse. The key to clarifying the origin of flowers and how angiosperms might be related to other kinds of plants is understanding the evolution of the parts of the flower, especially angiosperm seeds and the fruits in which the seeds develop.
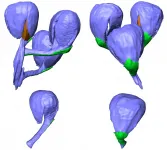
Fossil seed-bearing structures preserved in a newly discovered Early Cretaceous silicified peat in Inner Mongolia, China, provide a partial answer to the origin of flowering plants, according to a study led by Prof. SHI Gongle from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS).
The study was published in Nature on May 26.
The fossils, which date from about 126 million years ago, support an earlier idea that the distinctive outer covering of developing seeds of flowering plants--the so-called second integument--is fundamentally comparable to structures that occur in certain extinct non-angiosperm seed plants from the "Age of Dinosaurs."
The seeds of cycads, ginkgo and conifers are enclosed and protected by a single integument, which is believed to correspond to the inner integument in flowering plants. However, the outer (second) integument is a unique structure. Its development is linked to its curious recurved form and is controlled by different genes than those responsible for the development of the inner integument.
These fossils, exceptionally well preserved and abundant in the silicified peat from China, have two seeds enclosed inside a specialized recurved structure--the cupule.
Similar cupules occur in several groups of extinct plants from the Mesozoic that are known only from fossils, and while it has been suggested some of these cupules may be precursors of the second integument of flowering plants, discussions have been hampered by inadequate information.
The new fossils from China, along with the reexamination of previously described fossils, suggest that the recurved cupules found in several groups of extinct seed plants from the Mesozoic are all fundamentally similar and are likely the precursors of the second integument of flowering plants.
The recurved structure seen in the young seeds of flowering plants is therefore a holdover from an earlier pre-angiosperm phase of evolution. Variation among extinct Mesozoic seed plants in the number of seeds per cupule and other features likely reflect differences relating to pollination, as well as seed output, protection and dispersal.
Recognition of extinct seed plants with a structure comparable to a key feature of living angiosperms provides a partial answer to the question of flowering plant origins. It also helps focus future work on understanding how living and fossil groups of seed plants are interrelated, and has important implications for ideas on the origin of another diagnostic feature of flowering plants that evidently came later--the carpel--the structure that forms the fruit wall in which the seeds develop.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Kentucky researchers discover fundamental roles of glucosamine in brain
2021-05-26
LEXINGTON, Ky. (May 26, 2021) - Using novel imaging methods for studying brain metabolism, University of Kentucky researchers have identified the reservoir for a necessary sugar in the brain. Glycogen serves as a storage depot for the sugar glucose. The laboratories of Ramon Sun, Ph.D., assistant professor of neuroscience, Markey Cancer Center at the University of Kentucky College of Medicine, and Matthew Gentry, Ph.D., professor of molecular and cellular biochemistry and director of the Lafora Epilepsy Cure Initiative at the University of Kentucky College ...
How antibiotic-filled poop helps 'bessbug' beetles stay healthy
2021-05-26
Berkeley -- The lifestyle of the horned passalus beetle, commonly known as the bessbug or betsy beetle, might seem downright disgusting to the average human: Not only does this shiny black beetle eat its own poop, known as frass, but it uses its feces to line the walls of its living space and to help build protective chambers around its developing young.
Gross as it may seem, a new study suggests that this beetle's frass habits are actually part of a clever strategy for protecting the insect's health -- and could help inform human medicine, too.
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have discovered that the frass of the horned passalus beetle is teeming with antibiotic and antifungal chemicals similar to the ones that humans use to ward off bacterial and ...
Study finds physicians support pharmacy dispensing to expand access to medication abortion
2021-05-26
In a new study published online in spring 2021 and in the July issue of the journal Contraception, University of Chicago Medicine investigators and colleagues interviewed primary care providers in Illinois about their interest in providing medication abortion care and found that lifting FDA restrictions on mifepristone to allow pharmacy dispensing could normalize medication abortion, facilitate its use in primary care facilities, and address disparities in reproductive health access.
"Mifepristone is used in combination with misoprostol to end early pregnancies, during the first trimester," ...
A new 'gold standard' compound for generating electricity from heat
2021-05-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Thermoelectric power generators that make electrical power from waste heat would be a useful tool to reduce greenhouse gas emissions if it weren't for a most vexing problem: the need to make electrical contacts to their hot side, which is often just too hot for materials that can generate a current.
The heat causes devices to fail over time.
Devices known as transverse thermoelectrics avoid this problem by producing a current that runs perpendicular to the conducting device, requiring contacts only on the cold end of the generator. Though considered a promising ...
UNH research: Journey of PFAS in wastewater facilities highlights regulation challenges
2021-05-26
DURHAM, N.H.--Researchers at the University of New Hampshire have conducted two of the first studies in New England to collectively show that toxic man-made chemicals called PFAS (per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances), found in everything from rugs to product packaging, end up in the environment differently after being processed through wastewater treatment facilities--making it more challenging to set acceptable screening levels.
"PFAS are persistent substances that are not easily broken down and have been linked to adverse health effects," said Paula Mouser, associate professor of civil and environmental engineering. "They are found in a wide variety of industrial, commercial and medicinal products and can end up in the body, human waste and the environment. If not managed correctly, they ...
HKUST's meta-analysis shows SARS-CoV-2 variants unlikely to affect T cell responses
2021-05-26
In a new study, scientists at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have revealed that most T cell epitopes known to be targeted upon natural infection are seemingly unaffected by current SARS-CoV-2 variants.
In their latest research, the team compiled and analysed data from 18 immunological studies of T cell responses involving over 850 recovered COVID-19 patients from across four continents who are well-distributed in age, gender, disease severity and blood collection time. They demonstrated that T cells in these patients targeted fragments (epitopes) of almost all of ...
Study: Don't count on caffeine to fight sleep deprivation
2021-05-26
Rough night of sleep? Relying on caffeine to get you through the day isn't always the answer, says a new study from Michigan State University.
Researchers from MSU's Sleep and Learning Lab, led by psychology associate professor Kimberly Fenn, assessed how effective caffeine was in counteracting the negative effects of sleep deprivation on cognition. As it turns out, caffeine can only get you so far.
The study -- published in the most recent edition of Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition -- assessed the impact of caffeine after a night of sleep deprivation. More than 275 participants were asked to complete a ...
Ultrafast, on-chip PCR could speed diagnosis during current and future pandemics
2021-05-26
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has been the gold standard for diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the PCR portion of the test requires bulky, expensive machines and takes about an hour to complete, making it difficult to quickly diagnose someone at a testing site. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have developed a plasmofluidic chip that can perform PCR in only about 8 minutes, which could speed diagnosis during current and future pandemics.
Rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 and other highly contagious viral diseases is important for timely medical care, quarantining ...
Young adults with schizophrenia have highest suicide risk
2021-05-26
Adults with schizophrenia have an elevated risk of dying from suicide. Yet there's only limited understanding of when and why people with schizophrenia die of suicide --in part because research studies have looked at relatively small groups of patients.
Now a new study from Columbia that looked at a large population of adults diagnosed with schizophrenia has found the youngest group (18-34) had the highest suicide risk and those aged 65 and older had the lowest. By comparison, in the general U.S. population, younger adults have less risk and older age groups have greater risk.
The Columbia study, published online May 26 in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, (LINK TK) also showed that people with schizophrenia, overall, have a 4.5-fold increased risk of dying from suicide, ...
How the mold influences a chocolate bar's crystalline structure
2021-05-26
When enjoying a chocolate bar, most people don't think about how the molecules within it are organized. But different arrangements of the fats in chocolate can influence its taste and texture. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Crystal Growth & Design have found that the side of a chocolate bar facing the mold has a more orderly crystalline structure than the side facing air, knowledge that might help chocolatiers produce tastier confections, the researchers say.
Chocolate is a mixture of cocoa solids, cocoa butter, sugar and other ingredients that interact with each other in complex ways. In particular, the fat molecules, or triacylglycerols, can remain liquid or crystallize into several phases with different melting points. ...