(Press-News.org) Swiftness is essential when treating lung cancer, the second most common type of cancer in the U.S. and the country's leading cause of cancer deaths. For patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer, surgical removal of a tumor-infested lung or of a smaller lung section may be the only treatment needed.
However, some patients postpone surgery while seeking second opinions, because of economic or social factors, or for personal reasons such as waiting until after a child's wedding or a planned vacation. Worries about contracting COVID-19 in a clinical setting also have led to delays.
But a new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis found that delaying lung cancer surgery for more than 12 weeks from the date of diagnosis with a CT scan is associated with a higher risk of recurrence and death.
The findings are published May 27 in JAMA Network Open.
"Patients with early-stage cancer have the best chance for survival," said the study's senior author, Varun Puri, MD, a thoracic surgeon and professor of surgery. "That's why it's critical for patients to promptly seek treatment within 12 weeks after they've been diagnosed."
Non-small cell lung cancer comprises 84% of all lung cancer cases, according to the American Cancer Society, and the overall five-year survival rate is 25%.
"Our data provide particularly timely information regarding delayed medical care, a common issue during the ongoing global pandemic," said Puri, also a research member of Siteman Cancer Center at Washington University School of Medicine and Barnes-Jewish Hospital. "Physicians and patients want to know more about the safety of delaying surgery. The risks have been poorly understood because previous studies have used imprecise definitions for the date of cancer diagnosis. The goal of our study was to provide more uniform data, which we did by tracking patients from most recent CT scan diagnosis to day of surgery."
Shortly after the World Health Organization declared a pandemic in March 2020, medical groups such as the American College of Surgeons, the Society of Thoracic Surgery, and the American Association for Thoracic Surgery advocated postponing elective procedures and, in some cases, necessary but nonemergency surgeries.
Generally, the organizations recommended patients proceed with lung cancer surgeries. Barnes-Jewish Hospital, where Puri treats patients, followed those guidelines. "However, pandemic fears and conflicting research about delaying surgery made it difficult to counsel patients about treatment options," Puri said. "Even in nonpandemic periods, the wide range of estimates about when to delay treatment can be confusing.
"Patients need to know that COVID-19 transmission rates have been low in hospitals, particularly with screenings and mandatory protocols," he added. "As long as those are followed, hospitals are perfectly safe."
For the study, the researchers analyzed de-identified medical records in a database maintained by the U.S. Veterans Health Administration, the nation's largest integrated health-care delivery system. The researchers examined information involving 9,904 patients with stage 1 non-small cell lung cancer who underwent surgery from October 2006 through September 2016. The average age of the predominantly male patients was 67.
"While the patient demographics may not be uniformly comparable to the overall U.S. population, the general patterns of lung cancer care and health outcomes are similar between veterans and nonveterans," said the study's first author, Brendan Heiden, MD, a surgical resident and research fellow at Washington University. "This means our findings are very likely to be relevant for the broad population of early-stage lung cancer patients."
Researchers aimed to establish a standard method to quantify surgical delay and to examine its association with oncologic outcomes. They defined the time to surgery as the period between the patient's most recent CT scan -- considered the most reliable diagnostic tool for lung cancers -- and surgery.
Among the patients, the majority (70%) underwent surgical treatment within the 12-week time frame, with about 30% of patients experiencing delays. On average, patients who received surgery within the 12-week span lived 7.5 months longer than those who did not -- 76.1 months compared with 68.6 months.
Researchers detected recurrence in 4,158 (42%) patients during the study's follow-up period six years after surgery. Recurrence was more likely to occur in patients who had postponed surgery. In addition, for each week of delay, the risk of recurrence increased, although modestly, the researchers said.
The researchers also noted that the data indicated surgical delays were more likely in Black patients than in white patients. They plan to continue research into racial disparities and other aspects of surgical delays.
INFORMATION:
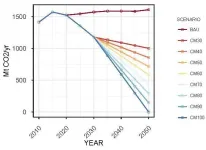
With the COP Climate conference in Glasgow only a few months away, the ambitions of the Paris Agreement and the importance of taking action at the national level to reach global climate goals is returning to the spotlight. IIASA researchers and colleagues have proposed a novel systematic and independent scenario framework that could help policymakers assess and compare climate policies and long-term strategies across countries to support coordinated global climate action.
The Paris Agreement defines a long-term temperature goal for international climate policy: "holding the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C". Its achievement critically ...
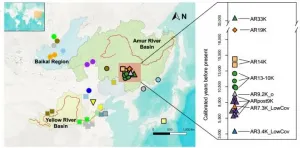
A study led by research groups of Prof. FU Qiaomei from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. ZHANG Hucai from Yunnan University covers the largest temporal transect of population dynamics in East Asia so far and offers a clearer picture of the deep population history of northern East Asia.
The study was published in Cell on May 27.
Northern East Asia falls within a similar latitude range as central and southern Europe, where human population movements and size were influenced by Ice Age climatic fluctuations. Did these climatic fluctuations have an impact on the population history of northern East Asia?
Stories uncovered by ancient DNA in East Asia remain relatively underexplored. The population ...
BOSTON - Although everyone can benefit from exercise, the mechanistic links between physical fitness and overall health are not fully understood, nor are the reasons why the same exercise can have different effects in different people. Now a study published in Nature Metabolism led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) provides insights related to these unanswered questions. The results could be helpful for determining the specific types of exercise most likely to benefit a particular individual and for identifying new therapeutic targets for diseases related to metabolism.
"While groups as a whole benefit from exercise, the variability in responses between any two individuals undergoing the very ...
Geneva, 27 May 2021 - A total investment in nature of USD 8.1 trillion is required between now and 2050 - while annual investment should reach USD 536 billion annually by 2050 - in order to successfully tackle the interlinked climate, biodiversity, and land degradation crises, according to the State of Finance for Nature report released today.
The report finds that annual investments in nature-based solutions will have to triple by 2030 and increase four-fold by 2050 from the current investments into nature-based solutions of USD 133 billion (using 2020 as base year).
The authors of the report - produced by ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A Penn State scientist studying crystal structures has developed a new mathematical formula that may solve a decades-old problem in understanding spacetime, the fabric of the universe proposed in Einstein's theories of relativity.
"Relativity tells us space and time can mix to form a single entity called spacetime, which is four-dimensional: three space-axes and one time-axis," said Venkatraman Gopalan, professor of materials science and engineering and physics at Penn State. "However, something about the time-axis sticks out like sore thumb."
For ...
The way the human brain works remains, to a great extent, a topic of controversy. One reason is our limited ability to study neuronal processes at the level of single cells and capillaries across the entire living brain without employing highly invasive surgical methods. This limitation is now on the brink of change.
Researchers led by Daniel Razansky, Professor of Biomedical Imaging at ETH Zurich and the University of Zurich, have developed a fluorescence microscopy technique that facilitates high-resolution images of microcirculation without the ...
Bethesda, MD (May 27, 2021) -- Crohn's disease, a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes inflammation (pain and swelling) in the gastrointestinal tract, can cause daily health problems, frequent hospitalizations and surgery when not adequately controlled. While there is no cure for Crohn's disease, there are treatments that can help patients live a symptom-free life.
After a detailed review of available literature, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released new clinical guidelines outlining the benefits and risks of each drug currently available to Crohn's patients. Based on this research, AGA recommends the early introduction of biologics for patients experiencing luminal and fistulizing Crohn's disease rather than waiting ...
Signals can be amplified by an optimum amount of noise, but this so-called stochastic resonance is a rather fragile phenomenon. Researchers at AMOLF were the first to investigate the role of memory for this phenomenon in an oil-filled optical microcavity. The effects of slow non-linearity (i.e. memory) on stochastic resonance were never considered before, but these experiments suggest that stochastic resonance becomes robust to variations in the signal frequency when systems have memory. This has implications in many fields of physics and energy technology. In particular, the scientists numerically show that introducing slow non-linearity in a mechanical oscillator harvesting energy from noise can increase its efficiency by tenfold. They publish their findings in ...
Ant workers that are infected with a tapeworm live much longer than their uninfected nest-mates. Parasitic infections are usually harmful to their hosts, but there are some exceptions. According to the results of a multi-year scientific study, ants of the species Temnothorax nylanderi show exceptionally high survival rates when infected with a tapeworm. "The lifespan of the infected ants is significantly prolonged. According to our observations, such workers have a survival rate similar to that of queens," said Professor Susanne Foitzik of Johannes Gutenberg University ...
A new discovery by University of Guelph researchers may ultimately help in devising new therapies and improving quality of life for people with Parkinson's disease.
By showing how entangled proteins in brain cells enable the neurodegenerative disease to spread, the researchers hope their findings will lead to drugs that halt its progression, said PhD candidate Morgan Stykel, first author of a paper published this month in Cell Reports.
Parkinson's disease is the world's fastest-growing neurodegenerative disease and Canada has some of the world's highest rates, according to Parkinson Canada. Its exact cause is unknown.
Current therapies only treat symptoms rather than halting the disease, said Dr. Scott Ryan, a professor ...