50 years of progress in women's health
2021-05-29
(Press-News.org) Debates over women's health have long been contentious, but have also resulted in significant improvements in areas like equitable access to health care and survivorship. But the overall picture remains far from perfect. For example, the United States still has the highest rate of maternal death among high-income countries, particularly among African American women.
As the United States Supreme Court prepares to hear a Mississippi abortion case challenging the landmark 1973 Roe v. Wade decision, some experts are questioning whether women's health may be reversing course.
Cynthia A. Stuenkel, MD, clinical professor of medicine at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, and JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, professor of epidemiology at Harvard T.H. Chan School Of Public Health, review 50 years of progress in women's health in a perspective article published in the May 29, 2021 online issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
"Reproductive justice is broader than the pro-choice movement and encompasses equity and accessibility of reproductive health care, as well as enhanced pathways to parenthood," wrote the authors.
In addition to Roe v. Wade, advances in reproductive health include:
1972 US Supreme Court ruling on Eisenstadt vs Baird ensuring unmarried persons equal access to contraception
2010 Affordable Care Act made contraceptives an insured preventive health benefit
Advances in reproductive technologies, including in vitro fertilization, genetic testing and fertility preservation by cancer specialists
Advances in women's health go beyond reproduction, said the authors. As interest and focus has expanded to all stages of a woman's life, science has begun to catch up to the specialized needs of women and sex-specific risk factors for chronic diseases that disproportionately affect women's health, such as autoimmune diseases, mental health, osteoporosis and coronary heart disease.
Progress in breast cancer care and prevention yielded a five-year overall survival rate of 90 percent
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine reduced cervical cancer mortality decreased by 50 percent
"Moving forward, it will be essential to recognize and study intersectional health disparities, including disparities based on sex, race, ethnicity, gender identity, sexual orientation, income and disability status. Overcoming these challenges and addressing these inequities will contribute to improved health for everyone," wrote the authors.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-29
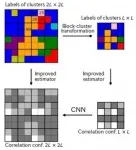
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have enhanced "super-resolution" machine learning techniques to study phase transitions. They identified key features of how large arrays of interacting "particles" behave at different temperatures by simulating tiny arrays before using a convolutional neural network to generate a good estimate of what a larger array would look like using "correlation" configurations. The massive saving in computational cost may realize unique ways of understanding how materials behave.
We are surrounded by different states or "phases" of matter i.e. gases, liquids, and solids. The study of phase transitions, how one phase transforms into another, lies at the heart of our understanding of matter in the universe, and remains a hot topic ...
2021-05-29
Highlight
Among individuals with healthy kidneys, those with more frequent depressive symptoms were more likely to show signs of rapid kidney function decline over a median follow-up of 4 years.
Washington, DC (May 28, 2021) -- In a study of adults with normal kidney function, those who had frequent depressive symptoms were more likely to later experience a rapid decline in kidney function. The study will appear in an upcoming issue of CJASN.
Depression is a common condition in middle-aged and older adults, and it can contribute to a variety of mental and physical problems. Previous research has found a link between depressive symptoms and rapid kidney function decline in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). To look ...
2021-05-28
In 2015, nearly half of Hawai?i's coral reefs were affected by the most severe bleaching event to date. Coral bleaching occurs when warmer-than-normal ocean temperatures prompt corals to expel the algae that normally live inside them and on which the corals rely for food.
Bleaching events are dismaying, but corals can sometimes recover, while others resist bleaching altogether. In a new study in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers led by Katie Barott of the University of Pennsylvania found that these battle-tested, resilient corals could thrive, even when transplanted to a different environment and subjected to additional heat stress. The findings offer hope that hardy corals could ...
2021-05-28
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America regularly publishes
articles online ahead of print. For April, GSA Bulletin topics
include multiple articles about the dynamics of China and Tibet; new
insights into the Chicxulub impact structure; and the dynamic topography of
the Cordilleran foreland basin. You can find these articles at
https://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent
.
Tectonic and eustatic control of Mesaverde Group
(Campanian-Maastrichtian) architecture, Wyoming-Utah-Colorado region,
USA
Keith P. Minor; Ronald J. Steel; Cornel Olariu
Abstract:
We describe and analyze the depositional history and stratigraphic
architecture of the Campanian and Maastrichtian ...
2021-05-28
WACO, Texas (May 28, 2021) - About 36 million people have blindness including 1 million children. Additionally, 216 million people experience moderate to severe visual impairment. However, STEM (science, technology, engineering and math) education maintains a reliance on three-dimensional imagery for education. Most of this imagery is inaccessible to students with blindness. A breakthrough study by Bryan Shaw, Ph.D., professor of chemistry and biochemistry at Baylor University, aims to make science more accessible to people who are blind or visually impaired through small, candy-like models.
The ...
2021-05-28
Five researchers shed new light on a key argument to reduce greenhouse gases (GHG): they provided the first economic analysis of conversion factors of other GHG like methane into their CO2 equivalent in overshoot scenarios. Although the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) considers settling for one value of reference (known as "Common Metric") to make this conversion among the Paris Agreement, the models presented here show the economic advantage of flexibility between various factors of conversion. "A key notion in the UNFCCC is to reduce GHG emissions in the least costly way so as to ensure global benefits" highlights Katsumasa Tanaka, primary author of the Science Advances study.
The research provides series of dynamic variations of ...
2021-05-28
A study coordinated by Luís Graça, principal investigator at the Instituto de Medicina Molecular João Lobo Antunes (iMM; Portugal) and Professor at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Lisbon (FMUL) used lymph nodes, tonsils and blood, to show how the cells that control production of antibodies are formed and act. The results published now in the scientific journal Science Immunology* unveiled key aspects about the regulation of antibody production, with significant importance for diseases where antibody production is dysregulated such as autoimmune diseases or allergies.
In the last few ...
2021-05-28
A new study of dozens of wild fish species commonly consumed in the Peruvian Amazon says that people there could suffer major nutritional shortages if ongoing losses in fish biodiversity continue. Furthermore, the increasing use of aquaculture and other substitutes may not compensate. The research has implications far beyond the Amazon, since the diversity and abundance of wild-harvested foods is declining in rivers and lakes globally, as well as on land. Some 2 billion people globally depend on non-cultivated foods; inland fisheries alone employ some 60 million people, and provide the primary source of protein for some 200 million. The study appears this week in the journal Science Advances.
The ...
2021-05-28
Centuries-old smoke particles preserved in the ice reveal a fiery past in the Southern Hemisphere and shed new light on the future impacts of global climate change, according to new research published in Science Advances.
"Up till now, the magnitude of past fire activity, and thus the amount of smoke in the preindustrial atmosphere, has not been well characterized," said Pengfei Liu, a former graduate student and postdoctoral fellow at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and first author of the paper. "These results have importance for understanding the evolution of climate change from the 1750s until ...
2021-05-28
Since the onset of the CRISPR genetic editing revolution, scientists have been working to leverage the technology in the development of gene drives that target pathogen-spreading mosquitoes such as Anopheles and Aedes species, which spread malaria, dengue and other life-threatening diseases.
Much less genetic engineering has been devoted to Culex genus mosquitoes, which spread devastating afflictions stemming from West Nile virus--the leading cause of mosquito-borne disease in the continental United States--as well as other viruses such as the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and the pathogen causing avian malaria, a threat to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 50 years of progress in women's health