(Press-News.org) EUGENE, Ore. -- June 1, 2021 -- Businesses typically rely on banks and financial markets for financing, but credit provided by suppliers also can play an important role, especially in manufacturing. Yet why firms lend and borrow extensively from each other is still an open question.
In a paper online ahead of print in the Journal of Financial Economics, "Trade Credit and Profitability in Production Networks," Youchang Wu, an associate professor at the University of Oregon, and coauthor Michael Gofman, an assistant professor at the University of Rochester, examined trade credit from a new angle.
They noted that for an average nonfinancial firm in North America, the outstanding amount of trade credit it receives from suppliers is about 21 percent of annual production costs. Moreover, most firms simultaneously borrow from their suppliers and lend to their customers, with the average outstanding amount of trade credit provided to customers at around 15 percent of annual sales.
Previous studies on trade credit, they noted, have focused on a firm's role either as a lender or a borrower of trade credit, ignoring the fact that trade credit flows along supplier-customer links in complex production networks.
Using a comprehensive database of supplier-customer relationships from 2003 to 2018, Wu and Gofman analyzed more than 200,000 supply chains formed by more than 5,600 nonfinancial firms. By locating a firm in the supply chain, their study accounts for a firm's dual role as a supplier and a customer. This novel approach allowed the researchers to uncover new details about trade credit within and across supply chains.
In particular, they found that within the supply chain, more upstream firms borrow more from suppliers, lend more to customers and hold more net trade credit, despite appearing to have weaker financing capacity than more downstream firms.
The length of the supply chains they examined varies significantly.
An example of a longer supply chain is one in which Intermolecular Inc. supplies advanced materials to Micron Technology Inc., which creates computer memory and computer data storage that it provides to Nvidia Corp., which uses them to manufacture graphics cards it supplies to Tesla. In contrast, a short supply chain example is one in which Sensata Technology provides sensors directly to Tesla. In longer supply chains, firms tend to be more profitable, and the increase in trade credit provision from the lower to the upper level of the chain is more gradual.
Both within and across supply chains, the authors noted that there is an almost one-to-one correspondence between the variation in the trade credit a firm provides and the variation in the trade credit it receives. These findings are less consistent with the idea of financially strong firms lending to financially weak firms, an implication of the financing advantage theory.
"Our findings are more consistent with the recursive moral hazard theory of trade credit," said Wu, who teaches in the Department of Finance at the Lundquist College of Business and is the John B. Rogers Research Scholar and coordinator of the UO's finance doctoral program.
"This theory argues that more upstream firms have more severe incentive problems, especially when they are not that profitable, because the quality of their products is revealed only after a long delay," he said. "Thus, more net trade credit provided by upstream firms helps to align incentives."
The authors did, however, find evidence that a firm's provision of trade credit is related to its financial status during an economic downturn. For instance, during the 2008-2009 financial crisis, upstream firms experienced a larger decline in profit margins than did downstream firms, and net provision of trade credit dropped significantly, suggesting that financial strength plays a more important role in determining the provision and use of trade credit during a crisis period.
Overall, Wu and Gofman's systematic study highlights variations in trade credit practices across firms, which can help both researchers and practitioners better understand the role of trade credit in production networks as well as examine other economic and financial questions related to supply chains.
INFORMATION:
Links:
Paper in Financial Economics: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2365995
About Youchang Wu: https://business.uoregon.edu/faculty/youchang-wu
Lundquist College of Business: https://business.uoregon.edu/
About Michael Gofman: https://simon.rochester.edu/programs/ptmba/academics/world-class-faculty/faculty-profile/index.aspx?Username=31138802
In ride-sharing, trips of two or more customers with similar origins and destinations are combined into a single cab ride. The concept can make a significant contribution to sustainable urban mobility. However, its acceptance depends on human needs and behavior. For example, while shared rides typically offer a financial advantage, passengers might suffer drawbacks in terms of comfort and trip duration. These factors give rise to different adoption behaviors that explain usage patterns observed in 360 million real-world ride requests from New York City and Chicago in 2019. The study has ...
Besides common symptoms such as fever, cough and respiratory distress, some children have an atypical form of COVID-19 known as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), characterized by persistent fever and inflammation of several organs, such as the heart and intestines, as well as the lungs to a lesser extent. Reports of MIS-C have been increasingly associated with severe cases and deaths in several countries including Brazil since the onset of the pandemic.
Researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo's Medical School (FM-USP) and Adolfo Lutz Institute in Brazil performed the largest ...
In a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), a research team of the Institute of Complex Systems of the University of Barcelona (UBICS) analysed the time evolution of real complex networks and developed a model in which the emergence of new nodes can be related to pre-existing nodes, similarly to the evolution of species in biology.
This new study analyses the time evolution of the citation network in scientific journals and the international trade network over a 100-year period. According to M. Ángeles Serrano, ICREA researcher at UBICS, "what we observe in these real networks is that both grow in a self-similar way, that is, their connectivity properties ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- For many people, the need to go grocery shopping is met with a sigh, or an "ugh." It's generally not considered to be an enjoyable experience.
For moms who shop using WIC benefits, it can be a downright awful experience, one that's often made worse by difficulty finding eligible products and dealing with a lengthy checkout process. Add kids in tow and it's enough for many moms to forego re-enrolling in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children, commonly known as WIC.
But researchers at the University at Buffalo are working on ways to improve ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - Fibroid symptoms, such as heavy menstrual bleeding and abdominal pain, are increasingly driving women to the emergency room.
In fact, tens of thousands of women were seen annually in the emergency department for the condition, which involves benign growths in the uterus, over a 12-year period.
But only 1 in 10 of these visits led to a hospital admission, suggesting that many cases may have been managed in an alternative, non-urgent health setting, according to recent Michigan Medicine research.
"Fibroids are often a chronic disease, so we have opportunities to treat this through established care with a trusted health provider. Yet, we've seen a big increase in women using the emergency room ...
While the term "supergene" may bring to mind the genetic hocus-pocus of Peter Parker's transformation into Spiderman, supergenes are actually fairly common phenomena in the realm of biology. A supergene refers to a genomic region containing multiple genes or genetic elements that are tightly linked, allowing genetic variants across the region to be co-inherited. Supergenes may arise when there is a clear benefit to inheriting specific combinations of biological traits together. Perhaps the most well-known examples of supergenes are sex chromosomes, which allow traits that are beneficial to the reproductive success of one sex to be co-inherited. In humans, this ...
(Boston)--Only a small subset of people who get a lung infection go on to become very sick yet who will become severely ill or why is unclear. This is now widely recognized in the context of COVID-19, where most people have mild or no illness while others with the same infection become extremely sick or even die.
Researchers now have discovered that after recovering from a respiratory infection, new cells get deposited in lung tissue, persist there and then become antibody secreting cells very quickly if the lungs later get re-infected by something similar.
"It is increasingly clear that our lungs contain their own specialized immune system, different from the immune system throughout the rest of the body," explained corresponding ...
In some environments there is no way for a seed to know for sure when the best time to germinate is.
In spring, cues like light, temperature and water may suggest to seeds that conditions are optimal for germination, but a week later an unpredictable drought or frost could kill the emerging seedlings.
So how does a plant make sure that all of its offspring are not killed at once by an ill-timed environmental stress following germination?
There is evidence that some plant species produce seeds that germinate at different times to hedge their bets against this risk. Many species produce seeds that can enter a dormant state and exist in the soil for several years and some also produce seeds that germinate at different ...
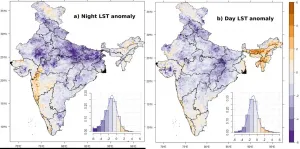
Research by scientists from University of Southampton (UK) and the Central University of Jharkhand (India) and has shown the first COVID-19 lockdown in India led to an improvement in air quality and a reduction in land surface temperature in major urban areas across the country.
The study found that travel and work restrictions imposed early in the pandemic resulted in a significant environmental improvement, due to an abrupt reduction in industrial activities and a major decrease in the use of land and air transport.
The international team used data from a range of Earth Observation sensors, including those from the European Space Agency's Sentinel-5p and NASA's MODIS sensors, to measure changes in surface temperature and atmospheric ...
Efforts to contain the novel coronavirus have caused lockdowns and school closures around the world. These efforts and policies have unfortunately cut off many children from valuable resources such as the opportunity for exercise, access to clean water and food, learning, and socialization. Therefore, the effects on mental health and behavior may be found not just in adults but children. However, studies published thus far have been limited to elucidating the mood of middle school and high school students and the conditions for which mood problems occur ...