2D natural clay offers a platform for machine learning algorithm
2021-06-01
(Press-News.org) Algorism plays a significant role in predicting future states of a system. Particularly, non-Markov chain algorithm has been widely applied in epidemic spreading processes, social and man-made memory networks, the environment-related quantum entangled states, and artificial algorisms such as face pose tracking. Traditionally, a large number of memories and computing cells are integrated to achieve these goals by software algorisms, showing high complexity. In the paper published in Science Bulletin, a group led by Bilu Liu and Hui-Ming Cheng from Tsinghua-Berkeley Shenzhen Institute (TBSI) of Tsinghua University has realized a non-Markov chain algorithm in a single resistive random access memory (RRAM) based on 2D mineral material for the first time and revealed the related mechanism.
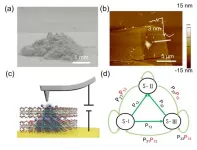
The researchers found that 2D mica is an excellent ionic conductor, the internal potassium ions (K+) in which controllably migrates under the stimulation of a cyclic electric field to induce resistance switching (RS) phenomena. It is interesting that the related RRAM device exhibits both single-window and bipolar RS behaviors, which is modulated by the strength of the electric field. The migration of the intrinsic K+ contributes to the high on/off ratio of 103, long retention time of more than 108 s, high stability and reliability of the 2D mica-based RAAM, superior to the ones relied on the conduction of external ions.
Accordingly, the authors have successfully achieved the non-Markov chain algorithm in a 2D mica-based RRAM with three states (Figure 1). Different polarities of the input voltages were applied to stimulate the device and produce certain passing paths. By this way, the output signal of the device is not only related to the current input voltage but also the previous state, and a multi-path non-Markov chain is realized. This research reveals the controllable ion transport in 2D layer mineral materials and provides a guideline to design and engineer the related functional devices for realization of algorithms in future.
INFORMATION:
See the article:
Rongjie Zhang, Wenjun Chen, Changjiu Teng, Wugang Liao, Bilu Liu, Hui-Ming Cheng. Realization of a non-markov chain in a single 2D mineral RRAM. Science Bulletin,66,doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2021.04.025
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2021.04.025
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-01
Swedish researchers from institutions including Uppsala University have spent four years gathering data from the areas affected by the major forest fire of 2014. In their study of how the ecosystem as a whole has been altered, they could see that water quality in watercourses quickly returned to normal, while forested areas continued to lose carbon for many years after the fire.
The consequences of major forest fires remain poorly studied in Northern Europe. To improve this situation, researchers from Uppsala University, the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU) and the Swedish Meteorological ...
2021-06-01
Siberian jays are group living birds within the corvid family that employ a wide repertoire of calls to warn each other of predators. Sporadically, however, birds use one of these calls to trick their neighbouring conspecifics and gain access to their food. Researchers from the universities of Konstanz (Germany), Wageningen (Netherlands), and Zurich (Switzerland) have now examined how Siberian jays avoid being deceived by their neighbours. The study, published in the journal Science Advances, shows that these birds have great trust in the warning calls from members of their own group, but mainly ignore such ...
2021-06-01
News media reports about scientific failures that do not recognize the self-correcting nature of science can damage public perceptions of trust and confidence in scientific work, according to findings by researchers at the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania and the University at Buffalo, the State University of New York.
News stories about science follow several specific narratives, the researchers write in a new study in the journal Public Understanding of Science. One is that science is "in crisis" or "broken," a narrative driven in recent years by reports of unsuccessful efforts to replicate findings in ...
2021-06-01
A new miniature 3D model of human bone marrow has been described today in the open-access eLife journal.
The model may help clinicians predict which patients will benefit from a new therapy for blood platelet disorders, such as Inherited Thrombocytopenias - a group of familial disorders that inhibit the production of platelets. It could also enable further study of these disorders and give scientists a new tool to test experimental treatments.
Platelets are cells that are necessary for the blood to clot and stop bleeding. Having too few platelets can lead to internal or serious bleeding after surgery or injuries, which is usually treated with therapies that cause clotting. Recent studies have shown that a drug called Eltrombopag increases ...
2021-06-01
A college education is estimated to add $1 million to a person's lifetime earning potential, but for some students the path to earning one is riddled with obstacles. That journey is even more difficult for students who have been in the foster care system or experienced homelessness, according to a new study from the University of Georgia.
But the more college administrators and faculty know about these students' problems, the more they can do to ease the burden.
Getting into universities in the first place can frequently be a challenge for students who've had unstable home lives, said David Meyers, co-author of the study.
"Research tells us that every time a student moves from one foster care placement to another, they lose six months of educational ...
2021-06-01
In recent months, more than three hundred cases of salmonellosis have occurred in various European countries and Canada, which are linked to each other. In the UK the cases could be partly traced back to frozen breaded poultry meat. The cause was contamination with the bacterium Salmonella Enteritidis, which causes gastrointestinal inflammation. Salmonella is not killed by deep freezing and can remain infectious at temperatures below zero degrees Celsius. The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) and the BfR are monitoring the situation together with the Federal Office of Consumer Protection and Food Safety (BVL). In Germany, the number of reported cases has currently ...
2021-06-01
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Scientists have long known that frogs are oddballs when it comes to teeth. Some have tiny teeth on their upper jaws and the roof of their mouths while others sport fanglike structures. Some species are completely toothless. And only one frog, out of the more-than 7,000 species, has true teeth on both upper and lower jaws.
Now, the first comprehensive study of tooth evolution in frogs is bringing the group's dental history into focus. Florida Museum of Natural History researchers analyzed CT scans of nearly every living amphibian genus to reveal that frogs have lost teeth over 20 times during their evolution, more than any ...
2021-06-01
DANVILLE, Pa. - Among people who have strokes and COVID-19, there is a higher incidence of severe stroke as well as stroke in younger people, according to new data from a multinational study group on COVID-19 and stroke, led by a team of Geisinger researchers.
The COVID-19 Stroke Study Group's latest report, published in the journal END ...
2021-06-01
LAWRENCE -- In the early days of COVID-19 vaccine development, a new social media platform provided a place for like-minded people to discuss vaccines, share misinformation and speculate about the motivations for its development. A new study from the University of Kansas shows people flocked to Parler to discuss the vaccines in an echo chamber-type environment, and those conversations can shed light about how to communicate about vaccine efficacy during health crises.
COVID-19 vaccine vial and syringe photo from the U.S. Census Bureau.In the runup to the 2020 election, then-president Donald Trump claimed a COVID-19 vaccine could be ready before ...
2021-06-01
Mass of human chromosomes measured for the first time
The mass of human chromosomes, which contain the instructions for life in nearly every cell of our bodies, has been measured with X-rays for the first time in a new study led by UCL researchers.
For the study, published in Chromosome Research, researchers used a powerful X-ray beam at the UK's national synchrotron facility, Diamond Light Source, to determine the number of electrons in a spread of 46 chromosomes which they used to calculate mass.
They found that the chromosomes were about 20 times ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 2D natural clay offers a platform for machine learning algorithm